Vision Sensors

A sensor to solve any detection application. With built-in camera and optimized lighting, a wide area can be captured with an image and stable detection of multiple targets is possible even if they are misaligned. The lineup includes a model with AI that makes a wide range of pass/fail differentiations as easy and stable as possible.
Product Lineup

Installed with the latest in Artificial Intelligence technology, the IV4 Series can now do more than ever. The IV4 Series can detect parts without using position adjustment, can check if the correct amount of parts are in their proper location, and can read and count targets under tough conditions. The IV Series is known for its simplicity and stability and the IV4 is stronger in these than ever before. Increased brightness, wide-and-narrow field-of-view options, and highly optimized built-in hardware mean that the IV4 is highly stable against environmental concerns like ambient lighting or slight finish changes. Even applications that are difficult for conventional vision sensors can be solved easily with the IV4 and its improved AI tools.
Features
Advanced Next-Generational AI Enables Powerful Yet Simple and Stable Detection
AI Identify

Confirming the presence of a fork in a container
No need to fix workpieces in place or use a positioning tool since the AI locates targets.
AI Count

Counting and front/back identification / Kitting management
Stable detection is possible for counting applications frequently used on production floors, including quantity/number checking, kit assembly, and production counting.
AI OCR

Narrow pitch / Metal engravings / Arced / SEMI font
All types of characters and prints supported, including embossed, engraved, laser-marked and ink-jet printed parts. Detection is not affected by individual target differences or environmental conditions.
AI Differentiate

Plastic bottle label differentiation / SMD resistor top/bottom differentiation
Sort and differentiate good and bad parts with just two images to set up. Equally effective with high-speed moving targets of even 250 parts/sec (4 ms).
Easy Setup
No matter how high-performance or stable a sensor may be, if operating the sensor is time-consuming or if configuration requires specialized skills, the sensor’s usability will be reduced. With the IV4 Series, setup can be completed in just 3 easy steps. Operation can be performed easily by anyone even without a manual.
Step 1: Adjust Focus and Brightness

Using Smart Image Optimization, focus and brightness are adjusted automatically. The process can be completed simply by selecting from a number of image candidates.
Step 2: Set Up Tools for Monitoring

Frequently used tools are displayed in obvious locations. Additional explanations are shown on the right-hand side of the screen to avoid confusion.
Step 3: Complete Setup

Check for problems with a trial run within the tool setup. If the tool is running as expected, move to the final step for output settings.

Differing from conventional models, the IV3 Series Vision Sensor with Built-in AI automatically determines imaging conditions and detection conditions with its AI specifically designed for presence and difference checking. Installation and operation are simple: just determine the part to focus on and register a minimum of one OK and one NG image. No specialized knowledge or extensive time and effort for setup are required. The all-in-one design includes a lens and illumination, eliminating the need to select these devices and allowing for immediate finalization of detection results with no adverse effects from ambient light. Setting operations are performed using a small amplifier with a built-in high-performance CPU, eliminating the need for a separate high-performance PC. The ultra-compact head supports an extensive range of installation distances from 50 to 3000 mm, and the maximum field of view of 2730 × 2044 mm allows for detections from extremely wide angles, enabling a wide variety of applications.
Features
All-in-One Presence Detection Solution
AI-Based Imaging
The AI generates the optimum detection image with crisp edges, no glare, and no crushed blacks.
All settings—including illumination intensity, flash method, and exposure time—are automatically configured by the AI. The ideal imaging conditions can be derived for any environment or target conditions to ensure stable detection.
AI-Based Detection
Simply register OK and NG products to automatically configure the optimal settings for AI-based presence detection.
The built-in AI detects even slight differences to automatically configure the optimal detection settings. Because detection is based on target characteristics, stability can be ensured with no adverse effects from ambient light, individual product variations, or surface conditions.
Long-range & Various FOV
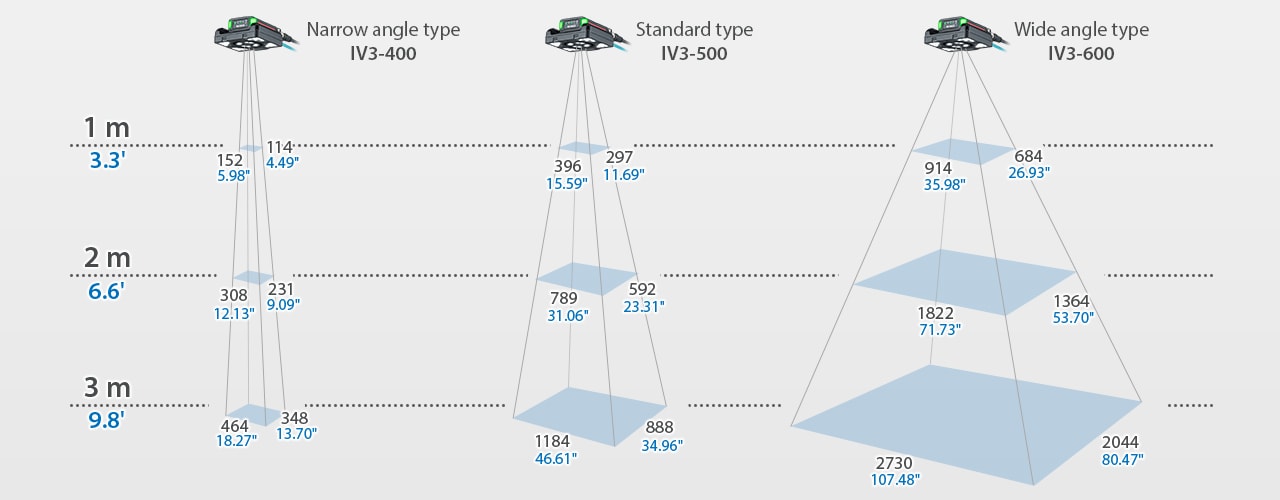

The AI in the IV2 Series vision sensor is specifically designed for presence and difference checking. Users need only register at least one OK and NG product image to complete setup. Brightness, focus, and detection are automatically configured by the AI, allowing for easy adoption and operation with no specialized image-based differentiation skills or extensive time and effort required. Setting operations are performed using a small amplifier with a built-in high-performance CPU, eliminating the need for a separate high-performance PC. The IV2 Series also offers the same ease of use as the IV Series, including intuitive operation with a compact amplifier and touchscreen monitor, and instant OK/NG notifications via the high-visibility LED mounted on the ultra-compact head with built-in lighting. Using AI for detecting features and setting conditions also greatly improves on-site usability.
Features
Stable Detection Thanks to an AI-Based Detection Algorithm
The IV2 Series Vision Sensor with Built-in AI is able to solve various problems conventional vision sensors and smart cameras have trouble with, including ambient light, individual differences of products, and changes in the positions of parts. The built-in AI, specially designed for presence/absence differentiation, is capable of detecting differences between registered images of acceptable and unacceptable products for automatically determining the best settings.

Ambient light

Oil stains

Misalignment

Varied surfaces
The AI Is Able to Optimize the Settings Automatically
This Makes It Possible For Anyone to Perform Measurements
The built-in AI analyzes registered OK and NG product images using various characteristics such as color, brightness, shape, area, and edges to automatically configure optimal detection settings. Users need only register the OK and NG products to complete setup.


Thanks to the integrated lighting, the IV Series is KEYENCE’s best-selling “simple and easy” vision sensor with a proven track record. In addition to color, shape, and edge-based differentiation, the sensors are also capable of character recognition (OCR). Automatic brightness adjustment and high-precision autofocusing mean users need only touch the detection target on the compact monitor to perform detection. Startup is also quick with a wide variety of analysis operations available in just 1 minute. The compact head is also equipped with high-intensity Hi-R illumination. Devices can be installed almost anywhere, and the built-in lighting provides bright, uniform illumination throughout the entire field of view for stable detection. The sensor head lineup includes ten different models to meet various detection, distance, field of view, and target size requirements.

The AI Series detects targets over an area when position is not fixed, reflection is unstable, or to differentiate products. By covering an area, targets that are misaligned or rotated can be easily detected. This series has a range of up to 160mm (6.30") and offers hard wired and M8 connector cable options.
Features

Stable Detection Where Conventional Sensors Struggle
The AI uses images to determine good parts from bad. After an image is registered, the target's brightness and shape are used to automatically determine which target features should be inspected during operation. This image-based method provides stable detection of targets that are difficult to handle when using conventional sensors with light intensity-based detection.

Support for Various Applications
The AI Series can be used for a wide variety of applications. Examples include spring presence, label misalignment, screw tap presence, capacitor direction determination, and felt presence. In addition, the AI Series is capable of performing these detections over an area, which prevents errors due to variations in position or vibrations of targets.
Vision sensors analyze images captured by a camera to determine whether targets are present or to determine the differences between target shape and color.
The compact, integrated sensor heads include a camera, lighting, and controller, making configuration and operation simpler than vision systems.
Vision sensors are different from general-purpose sensors such as photoelectric sensors and fiberoptic sensors in their ability to perform multi-point batch detection and to simultaneously perform color and shape differentiation. Vision sensors also offer a high degree of freedom in terms of detection settings, making it possible to perform various detections with a single vision sensor. In addition, thanks to the principle of capturing a wide area with an image, detection is possible even if the target position is not constant.
Principles of vision sensors
The image captured by the camera in a vision sensor passes through the lens and is converted to an electrical signal by the light-receiving element. The brightness and shape of the target are then determined according to the light/darkness and intensity information separated into the number of pixels of the light-receiving element.
The light-receiving element most commonly used in vision sensors is a CMOS, a semiconductor that acts as an “electronic eye” to enable high-speed transmission by amplifying and directly detecting the signals from each pixel. Because each pixel has its own amplifier, electrical noise generated when reading the electrical signals can be suppressed. Compared to CCDs—image sensors with high-voltage analog circuits—CMOS consume less power thanks to their digital circuitry, and smearing and blooming are not generally a problem.
These advantages make vision sensors a popular choice in various manufacturing sites thanks to their compact size and stable, high-speed detection performance.
Types of vision sensors
Vision sensors are available in two types: monochrome or color. Both types convert brightness captured by the lens into electrical signals and use the light/darkness and intensity information to determine the contour, brightness, and shape of a target. However, the structure of the light-receiving element and the image processing principles between the two types are different, and the characteristics of each differentiation method also differ.
Monochrome vision sensors:
Monochrome vision sensors do not include a Bayer filter used to extract red, green, and blue (RGB) colors. This means the images captured by a monochrome vision sensor are clear black-and-white images with no grating caused by the Bayer filter.
Such monochrome sensors offer high-speed reading and stable detection for applications where color information is not required, such as when reading barcodes, measuring external dimensions, matching patterns, or counting targets. If, however, color images are sometimes needed for differentiation, a color vision sensor is recommended, as a Bayer filter cannot be attached to a monochrome sensor.
Color vision sensors:
Color vision sensors are equipped with a Bayer filter that separates the light captured through the lens into RGB color. The Bayer filter is attached in front of the light-receiving element and is connected to each pixel. As light reflected by the target passes through the Bayer filter, the individual pixels on the light-receiving element acquire either R, G, or B color information. After the acquired color information is converted into electrical signals, the signals are used to create a single image through a process called Bayer conversion.
This enables color vision sensors to accurately determine not only external dimensions, shapes, and quantity but also minor differences between colors and intensity.
Benefits of Vision Sensors
Vision sensors detect the shape of a target by capturing the surface of the target as an image. This eliminates the need to align the position and angle of the target, which eliminates the need for a positioning device and enables detection of targets in motion. With no need to stop the conveyor carrying the targets, stable detection is possible even with high-speed lines.
Contact-type displacement sensors and laser displacement sensors capture information from a specific point on the target, so as many sensors as detection points are required. This results in significant effort installing a large number of sensors and positioning them to the desired locations. In addition, detection is only possible while the target is stopped.
Vision sensors, on the other hand, determine the target shape based on the image captured by the camera. The detection location is then specified using the image, eliminating the need for positioning equipment or for stopping the target. Moreover, the ability to perform detection of multiple points within the camera’s field of view at the same time means there is no need for a large number of sensors as with contact-type displacement sensors and laser displacement sensors. Being able to keep the number of necessary sensors to a minimum significantly reduces the work required for product changeovers.
Vision sensors are capable of accurate color difference checking. Their design also makes them less susceptible to glare caused by reflected light. This enables stable detection even if the target color is uneven or if there are glossy spots in the detection area.
The most common use for color sensors is color differentiation. However, small color differences and color irregularities in the detection area frequently cause false detections with some color sensors. Glare caused by light reflected off metal parts can also cause false detections. Lighting equipment can help reduce the effects of glare, but configuring the lighting conditions requires skill, and changeovers take a lot of time.
Vision sensors, however, can automatically configure settings for color differentiation, glare, and other factors. This means stable detection is possible at all times even without separate lighting equipment, and even subtle color differences are detected. The sensors are also able to automatically detect when the target changes to reconfigure detection conditions and lighting settings as necessary.
With a vision sensor, detection conditions such as contour, color, and area can be configured for multiple locations, and detection is possible for all locations at the same time. This eliminates the need to install numerous sensors. These various detection conditions can also be saved.
In a conventional system, performing various detections such as presence, contour, color, and area means installing color sensors, photoelectric sensors, or laser displacement sensors according to the desired detection.
Vision sensors, however, can be used to use different detection conditions at different locations all at once. The ability to perform detection using the various configured settings all at once means differentiation that conventionally required several sensors can be done with just one device. Also, the ability to save the detection conditions means they can be easily retrieved as needed. This helps significantly reduce not only the number of sensors needed but also the time required for changeovers.
Vision Sensor Case Studies
Automotive industry
When using a contact-type displacement sensor, laser displacement sensor, or color sensor to detect multiple weld nuts on automobiles or clips securing interior components, a large number of sensors must be used, and a lot of time is needed for installation and setup. Accurate positioning is also required.
A single IV4 Series vision sensor with built-in AI, however, can perform detection over an area as large as 2730 × 2055 mm (107.48″ × 80.91″). This area is large enough to include up to 16 installed nuts or interior clips all at once, reducing the overall number of sensors that need to be installed. Moreover, because detection is not affected by glare from reflected light, stable detection is possible even for glossy targets.
Electrical and electronic parts industry
Using a vision system to check the connection of cables for electrical components and circuit boards, the wide field of view eliminates the need for positioning, and the system’s high resolution ensures stable detection even for thin cables with small components. However, installation and configuring such a system takes a lot of time, and the system itself is expensive.
Meanwhile, the IV4 Series vision sensor with built-in AI comes equipped with automatic focus and brightness adjustment functions. This means detection of missing or incorrect wiring can be performed with the optimal focus and brightness. Also, because a single device can cover a wide detection area, even large PCBs can be inspected easily. The built-in AI can also perform the necessary settings for battery wire detection such as color differentiation and edge detection.
This makes the IV4 Series the ideal choice in terms of functionality, ease of use, and price.
Resin, rubber, and other industries
Various types of sensors can be used to detect molding remaining on molded products, including photoelectric sensors. However, the number of sensors required depends on the number of detection points. With large molds, the detection area also becomes wider, making it necessary to align numerous sensors.
KEYENCE’s AI Series of pattern matching sensors is able to capture surfaces as an image, and AI is used to position targets automatically. This makes positioning easier than photoelectric sensors and other sensors that detect only points on a target, while also enabling stable detection. The AI Series can also be used in presence check mode or difference check mode. Enjoy convenient functionality with the same ease of use as a general-purpose sensor.
Unlike point-based detection sensors such as photoelectric sensors, the AI Series enables stable detection and offers all the necessary functions with easy setup and operation.

This collection of vision sensor application examples offers an in-depth look at the IV4 Series, enabling easy, stable detection for any user. Examples are categorized by industry for simpler browsing.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vision Sensors
Misaligned products can cause false detections with sensors that detect points on a target, such as photoelectric sensors. This means positioning devices are required to ensure accurate positioning.
Vision sensors detect the shape of a target by capturing the surface of the target as an image. The target’s features are then analyzed to determine the position and orientation of the detection target. This ensures accurate differentiation even if the position of the passing target is misaligned.
In addition, with the IV4 Series, the detection area is wide (2730 × 2055 mm 107.48″ × 80.91″), and accurate detection and differentiation are possible anywhere within the area even for misaligned targets.
Photoelectric sensors and contact-type displacement sensors capture information from a specific point on a target, requiring the same number of sensors as detection points. All of these sensors must be installed and configured before performing detection. Moreover, if the product type changes, a significant amount of time is required for changeovers.
The IV4 Series, however, captures the surface of the target, enabling detection of up to 16 different points within the field of view. This includes not only presence checking and shape analysis, but also color, pitch, and various other differences. Up to 32 different detection setting configurations can also be saved (for 32 different products), and changing the settings is as easy as loading the configuration for the specific target.
This means the number of sensors required for difference checking as well as the time spent on installation, setup, and changeovers can be significantly reduced.
Glare caused by the strong reflected light from polished metal surfaces can cause false detection with conventional systems. With photoelectric sensors and color sensors, color is detected at a single point, making stable detection difficult.
The IV4 Series vision sensor with built-in AI, however, features automatic focus and brightness adjustment functions that enable stable detection by determining the optimal focus and brightness without separate lighting equipment even if glare is present. Detection settings for color differentiation, contours, and other factors are also configured automatically by the AI.
The IV4 Series uses AI to ensure differentiation even with glossy surfaces by determining the ideal detection conditions, allowing users to construct inspection systems with superior detection stability.

Discover a variety of useful functions, including switching between multiple vision sensors on the same network, and how to capture and save images displayed on the monitor to a USB memory device.

Learn all about stable detection methods for difficult-to-detect targets, effective use of color filters, and the benefits of infrared light devices. This guide includes a variety of tips and techniques for advanced detection.

Browse methods for further shortening detection times with vision sensors, stably detecting even minute targets, and detecting LED illumination. This guide includes a variety of tips and techniques for reducing takt time and ensuring stable detection.

See how to ensure stable detection even with small objects, how to remove backgrounds that may affect detection, and how to eliminate glare caused by reflected light.

This collection of vision sensor application examples offers tips for solving on-site problems such as false detection due to target position deviation, and how to reduce the number of sensors required.

