Dimensional Measurement of Floodgates

In recent years, large-scale disasters have happened frequently. In light of damage from these disasters, awareness of disaster prevention is growing nationwide. As damage from flooding, high tides, and tsunamis is particularly severe, the national resilience plan released by the government urges the improvement of the performance of existing floodgates, dams, sluices, etc. and additional construction of these types of buildings.
Floodgates, dams, and sluices are equipped with doors. The shapes and dimensional accuracy of these important parts greatly affect performance. Additionally, more efficient production is urgent in response to an increasing number of installation cases.
This section focuses on the measurement of the shapes and dimensions of the doors of floodgates and introduces basic knowledge of structures and types, problems of conventional measurement methods, and their solutions.
- What Is a Floodgate?
- Floodgate Structures
- Floodgate Types
- Necessity of Dimensional Measurement of Floodgates
- Problems of Dimensional Measurement of Floodgates and Their Solutions
- Optimization of Dimensional Measurement of Floodgates
What Is a Floodgate?

A floodgate is a structure designed to control the flow of water. They are installed in rivers, canals, irrigation channels, lakes, reservoirs, harbors, and similar locations. They are installed to cut through river dikes and adjust the amount of running water. In addition, they function as levees when closed.
Floodgates may be confused with dams and sluices, but dams do not function as levees. Also, the term sluice refers to a floodgate buried within a levee.
Floodgate Structures
An understanding of floodgate structures and the roles of floodgate parts is important for the dimensional measurement of these parts.
Floodgate structures are diverse and are used for various applications. The sliding gate is a typical floodgate, and its structure and the roles of its parts are as follows.
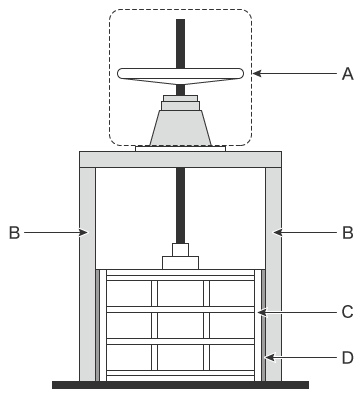
- A: hoist
- This device raises and lowers the door. It is connected to the door with a threaded rod known as a spindle, which allows the door to be opened/closed when the handle of the hoist is turned. Flat hoisting, bevel, worm gear, and other such opening/closing devices are available. Some use hydraulics and others use electric motors.
- B: doorstops
- These parts act as the rails for the door. They are constructed from H-beams and bent materials. For large-scale floodgates installed in dams and similar structures, the doorstops are buried in concrete.
- C: door
-
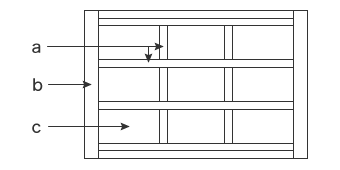
The door stops the flow of water. It comprises the main girders that are the frame (a), the edge girders (b), and the skin plates that hold back the water (c).
- D: watertight rubber
- This part is installed between the door and the doorstop and plays the role of a gasket that increases the watertightness of the structure. P-shaped, flat, and various other types of watertight rubber are available.
Floodgate Types
There are various ways to open/close the door of a floodgate, some are opened with a hoist and others with hinges used as a fulcrum. Methods are selectively used according to the size and required functions of the floodgate. This section explains typical floodgates that belong to the two types described above.
Types that use a hoist
The door is raised and lowered with a device known as a hoist to control the flow of water.
Sliding gate (sluice gate)
This gate controls the flow of water by raising and lowering its door with a hoist installed at the top of the gate.
This is the most common floodgate shape. The door is made of materials such as steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy.
Roller gate
This is a sliding gate with rollers installed between the door and the doorstops.
For large-scale doors and when the door is subjected to high water, a large amount of force is necessary to lift the door due to its weight and the friction between it and the doorstops. With a roller gate, the installation of rollers between the door and the doorstops results in low friction, allowing the door to be lifted with a small amount of force.
Types that use hinges as a fulcrum
One side of the door is secured with hinges, which are used as a fulcrum to open/close the door, controlling the flow of water.
Flap gate
This gate is designed to prevent outside water from flowing backward. It operates via differences in water level before and after the gate, so no opening/closing device is required. Hence, this gate can work without human supervision and without motive power. The door is made of materials such as steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy.
Swing gate
These gates are used as tide protection (watertight) gates installed at the entrances/exits of, for example, structures for housing heavy machinery at factories and levees adjoining rivers and beaches. Rotating the door around the hinges on the side opens/closes the water channel. The door is made of materials such as steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy.
Necessity of Dimensional Measurement of Floodgates
In addition to their water stopping and economical properties, floodgates are also required to operate quickly in disasters and other emergencies. Furthermore, they are used for long periods of time after installation, so their durability and watertightness are also important. Floodgate doors are important parts that directly impede the flow of water, so the shape and dimensional accuracy of these parts greatly affect the operability, durability, and water tightness.
Doors comprise main girders, edge girders, skin plates and watertight rubbers. During the manufacturing process, the main girders, edge girders, and skin plates are temporarily assembled and the dimensions are measured to check the assembly accuracy.
Then, the parts are welded together, and the dimensional accuracy of the completed product is checked. Strain may occur during welding, so the dimensions of each part are measured after welding, and strain is removed from any parts that are outside the tolerances. Then, the dimensions are checked to make sure they are within the tolerances.
In this manner, it is necessary to repeatedly measure dimensions multiple times during various floodgate manufacturing processes. Hence, in addition to requiring accuracy, the dimension measurement systems used must also have efficient operability.
Problems of Dimensional Measurement of Floodgates and Their Solutions

It is important to confirm the accuracy not only when measuring the dimensions of a completed floodgate but also during its maintenance. It is also important to confirm the assembly accuracy during temporary floodgate assembly. Conventionally, these measurements are performed using transit theodolites, tape measures, calipers, and similar tools. However, there are problems with variations in measured values from measurer to measurer, difficulty to understand strain tendencies, and long measurement time.
To solve these problems, the latest CMMs are used in an increasing number of cases. KEYENCE’s Wide Area Coordinate Measuring Machine WM Series enables a single person to perform high-accuracy dimensional measurement of large-scale floodgate doors with the wireless probe. Even recessed areas of workpieces can be reached with no movement restrictions within the measurement range, which allows for measurements with the simple operation of touching targets with the probe. Unlike measurements using measuring instruments such as transit theodolites, tape measures, and calipers, results do not vary, enabling quantitative measurement.


Measurement of floodgate welding strain and skin plate flatness
Even small-scale floodgates have door areas of up to 10 m2. Large-scale floodgates have door areas of up to 50 m2. Hence, measurement using tape measures or calipers requires at least two workers.
However, measured values vary according to the angle and strength used to apply a tape measure or caliper to the target, which causes variations in measured values among operators. Also, when checking for welding strain, it is necessary to repeat the measurements each time that strain is removed, which makes the measurement work take a long time.
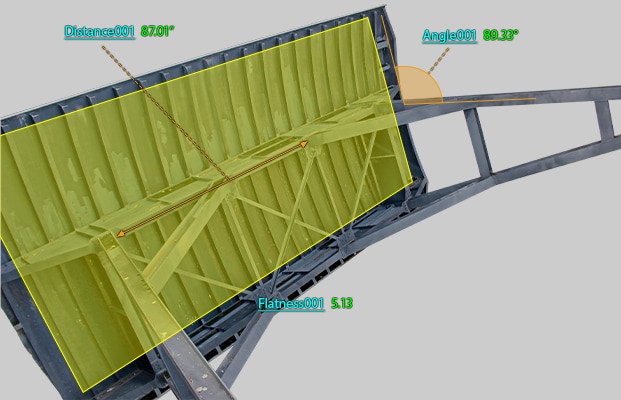
The WM Series enables measurement by simply touching measurement points with the probe. The total length, total width, and diagonal length of a large-scale floodgate as well as the flatness of its skin plates can be measured by simply touching with the probe. Strain can be displayed with color maps, allowing dimensions to be corrected accurately and easily.
Quick single-person measurement without variations in measured values among operators is possible even for long dimensions.


Dimensional measurement after temporary assembly
In temporary assembly—where the assembly accuracy of the main girders, edge girders, and skin plates is checked—the spacing between girders and the clearance between parts are measured to check that actual assembly is possible. If the main girders and edge girders are subjected to welding, they are checked for strain due to welding. The skin plates are checked for warpage and curvature.
Multiple workers are required for the measurements of the main girders and edge girders, which are a few meters in length, and measurements with tape measures are difficult to quantify. Also, it is not possible to measure the skin plate flatness, 3D coordinate positions, and similar items with hand tools such as tape measures and calipers, so it is necessary to use a laser tracker or other CMM. CMMs can accurately measure complex measurement items but may have to be operated by skilled technicians. Hence, workers must flexibly select measuring instruments and measurement systems according to applications and costs.
With the WM Series, it is possible for a single person to perform quantitative measurement by simply touching measurement points with the probe. Simply by touching the target with the probe, the operator can measure not just the distortion and strain caused by welding the girders of a large-scale floodgate but the flatness of its skin plates as well. Even 3D position coordinates can be measured. Additionally, deviations from designed tolerances can be judged instantaneously.
Optimization of Dimensional Measurement of Floodgates
The WM Series enables accurate single-person measurement of the dimensions and shapes of floodgates with the simple operation of touching targets with the wireless probe. In addition to the features introduced above, the WM Series has the many advantages listed below.
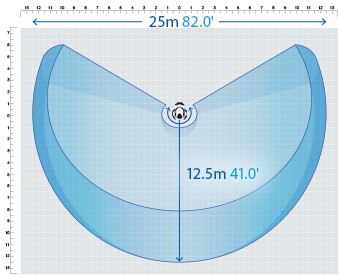
- High-accuracy measurement over a large area
- A wide measurement range up to 25 m (82.0'′) can be measured with high accuracy. The WM Series is equipped with the navigation measurement mode, which enables measurement at the same point according to a memorized measurement procedure, allowing anyone to obtain the same measurement data.

- The portable body can be placed on-site
- The main unit can be carried around on the cart. The WM Series can be brought into worksites and immediately measure the status of the work.
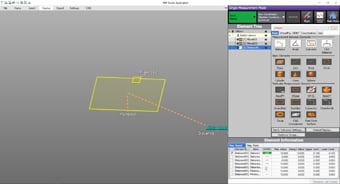
- Easy-to-understand interface
- CMM interfaces are often a mess of complex and unfamiliar commands. The WM Series provides intuitive operation using images and icons, so anyone can easily understand how to operate the system.
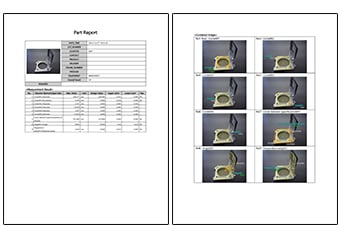
- Inspection reports can be created with photos
- Inspection reports can be automatically created with photos that allow you to understand measurement points at a glance. These inspection reports can not only gain you the trust of your business partners but also allow you to digitally save measurement results, leading to higher efficiency of in-house data management.
The WM Series provides powerful support for not just shape and dimension measurements of floodgates at factories and manufacturing sites but also for data analysis and inspection report creation. It dramatically improves the efficiency of manufacturing of floodgates and of work indispensable for their installation and maintenance.