Filtering
The standards for filtering are still under review by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
This section introduces the filtering methods being evaluated by ISO for the S-filter and the L-filter.
Gaussian filter
The Gaussian filter (named for Carl Gauss) is one kind of smoothing filter that suppresses noise using the Gaussian function. Gaussian filters that are specified in JIS B 0632:2001 (ISO 11562:1996) and ISO 16610-21:2011 are applied to areal surface roughness measurements.
Spline filter
The spline filter is one kind of filter used to obtain a smooth profile by interpolating the sections between effective adjacent points using the spline function. Spline filters that are specified in ISO/TS 16610-22:2006 are applied to areal surface roughness measurements.
S-filter and L-filter settings
Cutoff wavelength for S-filter
A value equal to or more than 3 times the measurement resolution for the XY plane (horizontal plane) is used. If the set value is not sufficiently effective, increase the set value until the scale-limited surface noise is removed. If a different kind of filtering was applied beforehand, this may not be used.
Cutoff wavelength for L-filter
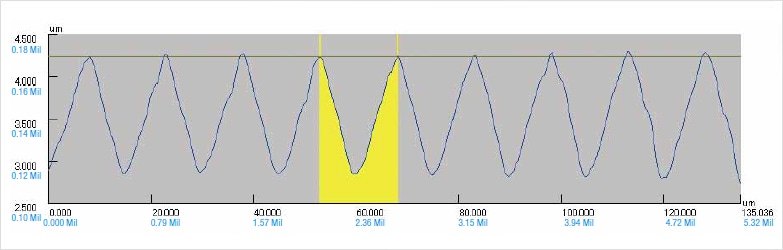
The cutoff wavelength for the L-filter is difficult to uniformly specify based on lens magnification or stylus tip diameter; therefore, it must be adjusted with reference to the real surface. Set a value 5 times the XY-directional length of the profile that you want to remove as waviness.
Example:
| Profile 1 |
Horizontal distance |
| Section 1 |
14.678 μm 0.58 Mil |
In the example above, the cutoff value is 0.1 mm 0.004".
14.678 x 5 = 73.39 ≈ 0.1 mm 0.004"



