Stroke and Positioning
Realtime feedback for position or stroke is important for both process control and process improvement. The target's speed, distance, and accessibility will all impact which type of sensor best suits your needs. Take a look at the typical approaches for position measurement below, or feel free to request a consultation with a local measurement expert.
Confocal sensors do not have the dead zones characteristic of triangulation sensors, and can therefore measure into smaller and deeper holes more reliably.
Confocal Displacement Sensor
CL-3000 series


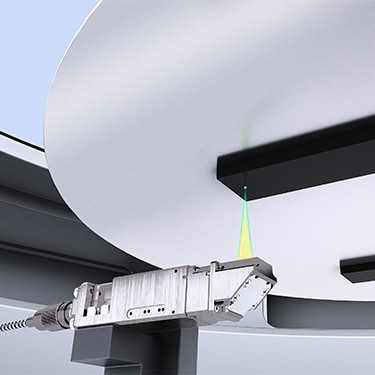
Compatible with ultra-high-vacuum environments, the CL Series heads can be used to measure the stage position in such environments. The four-direction side view attachment allows for highly flexible installations.
Confocal Displacement Sensor
CL-3000 series


Check for press fit failure with contact displacement sensors.
High-Accuracy Digital Contact Sensor
GT2 series


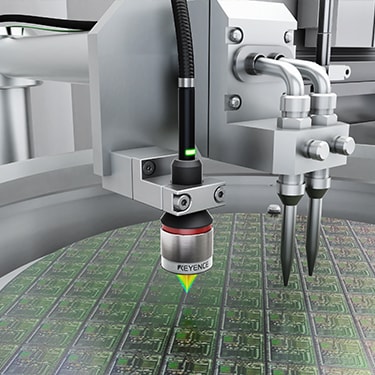
Accurately adjusting the distance between the dispensing head and the wafer is essential for maintaining stable dispensing accuracy. Thanks to the small head size, CL Series sensors can be easily installed on equipment for accurate distance measurement even for silicon wafers and other targets with mirror surfaces.
Confocal Displacement Sensor
CL-3000 series

Target positioning is used to ensure the next process is performed accurately. Laser profilers provide stable position feedback anywhere in the measurement range, regardless of target material, color, or size.
2D/3D Laser Profiler
LJ-X8000 series

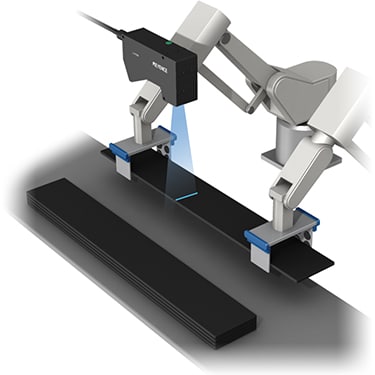
Robot teaching is used to ensure tools are set in the specified position. The 2D Telecentric Measurement System enables precise position feedback for end-of-arm tools and other axial targets.
Telecentric Measurement System
TM-X5000 series

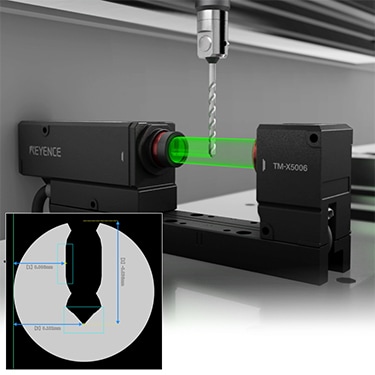
Angled mirrors can be used for measurement where installation space is limited. This setup enables position detection of tangent circle coordinates or intersection point coordinates as well as simultaneous shape and dimension verification for wafer notches.
Telecentric Measurement System
TM-X5000 series

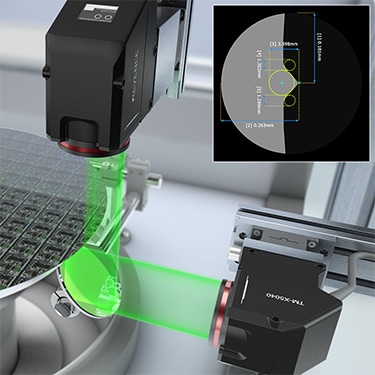
The stage height in a vacuum environment is measured through the viewport. The CL Series lineup includes sensor heads that are capable of long-distance measurement. The newly designed optical system ensures high accuracy while measuring at a long range.
Confocal Displacement Sensor
CL-3000 series

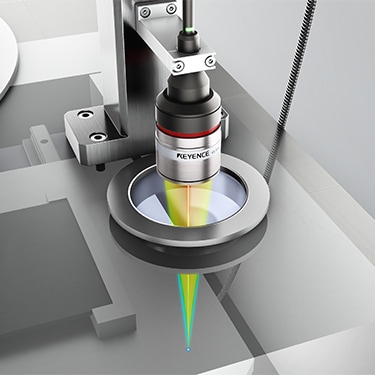
The arm position is measured in a vacuum environment. The CL Series heads are compatible with ultra-high-vacuum environments, allowing it to capture equipment movements that cannot be detected in atmosphere. Furthermore, the ultra-compact sensor heads can also be installed in the limited space inside equipment.
Confocal Displacement Sensor
CL-3000 series