CC-Link
This section explains CC-Link.
Overview
CC-Link is an open network developed by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation in the 1990s. CC-Link stands for control and communication link. To develop CC-Link-compatible products, manufacturers need to apply to Mitsubishi Electric Corporation for a partnership to be provided with the technical information and then purchase communication LSIs.
CC-Link achieves high-speed transmission of up to 10 Mbps and a total extension distance of up to 1200 m (3937.0′) (at a transmission speed of 156 kbps). With the release in 2003 of CC-Link Ver. 2.0, which allows for large-volume data communication, CC-Link increased the number of partner manufacturers to 2097 by March 2013.
Wiring Method and Communication Protocol
Wiring method
With the network structure based on RS-485, the total distance can be extended up to 1200 m (3937.0′) (at a transmission speed of 156 kbps). Terminating resistors are required at both ends. Up to 64 slave stations can be communicated.
Expanded cyclic communication, which is supported from version 2.0, divides data into multiple link cycles, increasing the volume of data that can be communicated.
Communication protocol
Communication data frames use high-level data link control (HDLC) and communication uses the master/slave method. Data communicated with each slave station is defined as a profile according to the type. Communication between products from different manufacturers can be easily performed by registering a corresponding CC-Link family system profile (CSP) file on the master. CSP files are provided by manufacturers of CC-Link compatible devices.
CSP files called CSP+, which integrate CC-Link IE profile specifications, have also been developed.
Characteristics
CC-Link is a network that uses the master/slave method. Link devices and communication control are centrally managed by the master, so no settings are required for slaves. Two communication functions are available: cyclic communication which updates data in a fixed cycle, and transient transmission which updates data as needed.
CC-Link also supports duplicate communication to continue communication using the standby master station when power supply to the active master station stops.
Cyclic communication function
This function automatically exchanges link device data between the master and slaves.
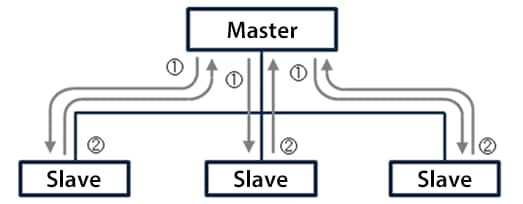
Transient transmission function
In this transmission method, the master sends data to and receives data from specified slaves as needed. The transient transmission function is supported by master stations, local stations, and intelligent device stations.
Standby master station
When the master station cannot operate due to abnormalities, such as power outages, this function continues communication by operating the standby master station (a backup station for the master station) in place of the disabled master station. This function can be used to duplicate the master station.
Related Networks
CC-Link IE
This is an Ethernet-based open network. There are two variations: CC-Link IE Field which can be used at the device level, and CC-Link IE Control which can be used at the controller level.
CC-Link LT
CC-Link is designed for communication using small numbers of I/O points. It supports communication with slave stations with small numbers of I/O points, such as four or eight points. CC-Link LT cannot be used with CC-Link.
- Company, product, and network names mentioned on this page are either trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
- Note that some information, such as applicable standards and specifications, may have changed since this page was published.
November 2015





