Technological Innovations and Development of a Traceability System
Proliferation of OCR, 2D Codes, and Direct Marking and Development of Traceability
Ensuring traceability has now become an imperative duty. In addition to the identification using labels and markings, management based on the link between information and objects is conducted in every company.
The driving force behind this expansion of traceability is certainly the breakthrough in IT technologies that provided accurate marking and reading techniques, and allowed comprehensive handling of such information. This section focuses on the technological innovations that supported the development of traceability systems.
Improved Identification Accuracy
For traceability, identification symbols are used to identify parts and products. At the scene of production control, identification symbols such as characters and 2D codes are used to record delivery status, production plans, procurement plans, shipment plan achievement rates, inventory quantities and other information in forms for management. For this purpose, the technology to accurately recognize identification symbols has become important.
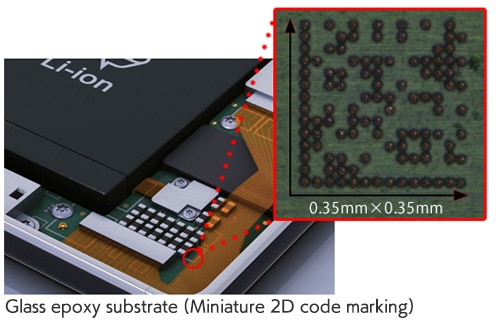
Small marking of characters and 2D codes on a PCB
Labels attached to an object with a curved surface such as a pipe

2D code marked on materials with hairline metal surface or casting surface

The characters and 2D codes shown above were susceptible to reading errors. In recent years, however, accurate identification has become possible due to the improved reading accuracy of handheld mobile computers and barcode readers.
Evolution of OCR Technology for Enhanced Character Identification Accuracy

The evolution of OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology has made it possible to accurately read and record characters such as expiration dates and part numbers. One example of the rise in safety awareness is that expiration dates for food now includes not only a date but also the production time frame. The greater the quantity of information, the more labor is required on the production site. OCR-based automation of the reading process can be a solution for problems of both labor and safety.
What is OCR?
OCR is a technology for recognizing characters contained in an image. A traceability system captures an image of a target with a camera, recognizes the characters in the captured image, and compares their shape with the data in the registered dictionary (character font group) to read them as characters. This has become an essential technology for the identification and recording of expiration dates or part numbers. It is also an effective solution for preventing errors due to visual reading and manual input.

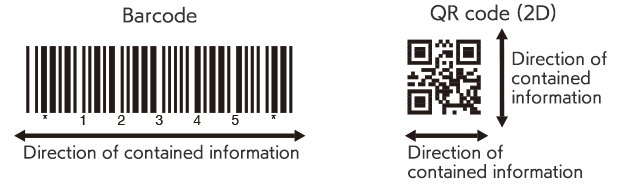
2D Codes for Space Saving
To ensure traceability, you need to add various kinds of information to the product, such as part numbers, quantity, serial number, and shipment volume. Unfortunately, standard barcodes cannot contain all of this information. 2D codes can store more information in a limited space and have been used for part and product management including traceability. You can use 2D codes to achieve reliable individual management by marking them even on components with limited space, such as PCBs of electronic devices that require miniaturization and higher density.
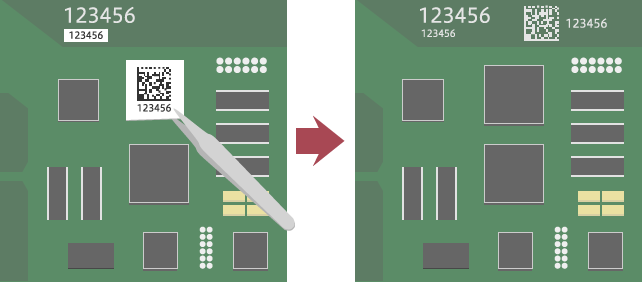
Direct Part Marking for Further Flexibility
Direct part marking (DPM) marks serial numbers, lot numbers and 2D codes directly onto the parts and products, and has also greatly contributed to the advancement of traceability systems. At the site of PCB manufacturing mentioned above, fake chips have become a social problem. Direct part marking has been used as a countermeasure against this problem by marking information directly on parts. The combination of direct part marking and 2D codes allows identification symbols to be shown even on components that have no space for attaching labels.

Direct part marking is also suitable for products subject to high temperatures and used for long periods in outdoor environments, such as car engines and transmissions. Labels attached to such products are subject to peeling off or discoloration. Direct part marking eliminates worries about reading failure.
Stream of New Technologies for Expanding the Range of Traceability
OCR, 2D codes and direct part marking have been introduced by many companies to ensure traceability. Other new technologies are coming onto the scene such as printing with ink-jet printers and RFID for reading/writing information using electronic tags and radio waves.
The evolution of IT technologies is spurring coordination between traceability systems and MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), which is starting to bring benefits not only to production but also to every aspect of business activity. Furthermore, the information can be shared with domestic and overseas companies and plants via networks. Traceability will certainly attract more attention in how it can promote globalization.
The range of traceability is expected to expand further due to the diversification of identification methods and improved accuracy of information recording and transfer.