Food and Pharmaceutical Industry
Overseas Traceability Laws and Regulations for Food and Pharmaceuticals
In addition to international rules such as ISO 9000/9001 for general quality management, HACCP for food, and GMP for pharmaceuticals, there are other laws and regulations regarding traceability which are specific to different countries and regions.
As globalization continues to progress, it is important to understand and take measures for overseas laws and regulations in order to achieve traceability. This page introduces laws and regulations regarding food and pharmaceuticals in various countries, including the General Principles of Food Law in EU countries and the Bioterrorism Act in the U.S.
HACCP
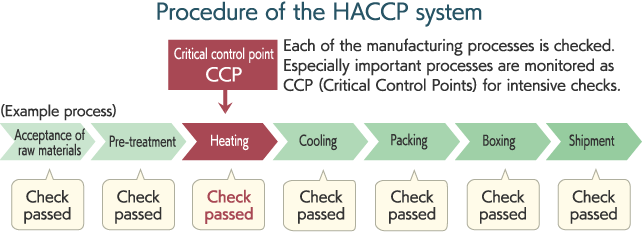
HACCP is an acronym that stands for Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points. This is a method of food hygiene control based on the report issued in 1993 by the Codex Alimentarius Commission, a joint organization of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO), and has been promoted in countries all over the world.
HACCP is a method of controlling safety by conducting scientific analysis of potential hazards that may cause food to be unsafe, such as food poisoning, in every phase from acceptance of raw materials to manufacturing, processing and shipment and then identifying critical control points necessary to reduce or remove such hazards. In Japan, HACCP was introduced into the Comprehensive Sanitation Management and Production Process started in 1995.
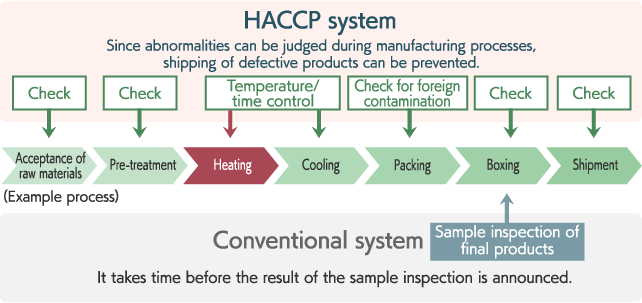
Differences Between HACCP and Conventional Hygiene Control
Conventional hygiene control had confirmed safety by specifying the standards for relevant facilities/equipment and food handling methods, and inspecting final products. On the other hand, HACCP analyzes hazards in every manufacturing process, conducts intensive checks for important processes, and performs control/inspection based on a standard specifically stated for each process. Since countermeasures are taken throughout the process, you food poisoning and entry of foreign contaminants can be prevented before problems occurs to enhance safety.
Food Traceability Principles Unified in EU: General Principles of Food Law
Before the BSE (mad cow disease) problem occurred in Europe in 1996, the EU had no unified principles regarding food. At that time, there was just a collection of laws established individually for each item. This fact was brought to the fore by the BSE problem, which lead to the establishment of a unified regulation called General Principles of Food Law (laying down the general principles and requirements of food law, establishing the European Food Safety Authority and laying down procedures in matters of food safety (EC) No. 178/2002) which was promulgated in 2002.
Even Items for Traceability Records Are Specified
As for traceability, the principles are described as follows in Article 18 of General Principles of Food Law: the traceability of food, feed, food-producing animals, and any other substance intended to be, or expected to be, incorporated into a food or feed shall be established at all stages of production, processing and distribution.
It is specified that food supply chains must retain the following information in a status available to the controlling authority. The principles also mention the retention of more detailed product information, such as amount or quantity, in the form of a recommendation.
| Supplier | Customer |
|---|---|
| Name | Name |
| Location | Location |
| Type of product supplied to the customer | Type of product supplied by the supplier |
| Date of transaction and delivery | Date of transaction and delivery |
Food Traceability-related Law in the U.S.: Bioterrorism Act
Food traceability in the U.S. is specified in the Bioterrorism Act (The Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002).
The Bioterrorism Act requires measures such as registration of product-related facilities, prior notice of imports, storage of records, and administrative detention as mandatory. The measures in the act related to traceability are part of storage of records.
For the storage of records, it is mandatory to record the operators immediately before and after the process of manufacture, processing, packing, distribution, receipt, holding, and importation of food in the U.S. and to store the records. Association between the processes one step upstream and one step downstream, as described in Building an Identification System, is required by the act. Furthermore, if a product may affect human or animal health, the relevant operator must submit the record and related information to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Record Storage Period
The Bioterrorism Act has defined storage period in accordance with the perishability of food as follows:
| Category | Non-transporter | Transporter |
|---|---|---|
| Foods subject to quality deterioration within 60 days | 6 months | 6 months |
| Foods subject to quality deterioration between 60 days and 6 months | 1 year | 1 year |
| Foods not subject to quality deterioration for more than 6 months | 2 years | 1 year |
| Animal feed or pet food | 1 year | 1 year |
Regulation Regarding Traceability for Pharmaceuticals in China: Drug Administration Code
The drug administration code is a system administered by the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA), an authority ensuring safety of food and pharmaceuticals, that started full-scale operation from 2016. Operators who want to sell pharmaceuticals in China must obtain approval and drug administration codes from the CFDA and indicate this information as barcodes.
The drug administration code was introduced in 2012 for the purposes of preventing incorrect use of pharmaceuticals, ensuring traceability, and improving distribution efficiency. Although the implementation has been limited so far, all companies, including overseas operators, are required to implement the system from 2016. It is mandatory to indicate the barcode by attaching a label or marking on the exterior of the package of individual products and of the unit of use.

Drug Administration Code Configuration

Drug administration codes consist of 20-digit numbers and are expressed as Code128C barcodes.
| 8 | 123456 | 123456789 | 1234 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
- 1 Fixed number, 1 digit, "8"
- 2 Product code, 6 digits, item code assigned to each item or package, provided from the administrative authority (China Drug Electronic Supervision and Administration Network)
- 3 Serial number, 9 digits, number assigned to each product of a production company for production
- 4 Verification code, 4 digits, data for verification