Detection based on “Light”
Features of Color sensor
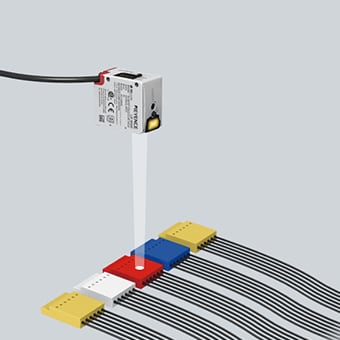
A color sensor is a type of "photoelectric sensor" which emits light from a transmitter, and then detects the light reflected back from the detection object with a receiver.
A color sensor can detect the received light intensity for red, blue and green respectively, making it possible to determine the color of the target object.
This section explains the features of color sensors.
Features
Can stably detect differences in color and appearance
Since the light source is not just red, but includes the red, green, and blue wavelengths, and the ratio between each of these lights can be calculated, it is possible to differentiate the appearance and color of target pieces.

By using a red wavelength photoelectric sensor, there are some color combinations, such as red and white, that are difficult to differentiate. A color sensor allows for stable detection, even for these kinds of difficult combinations.
Note: Ratio of reflection for each color in red light
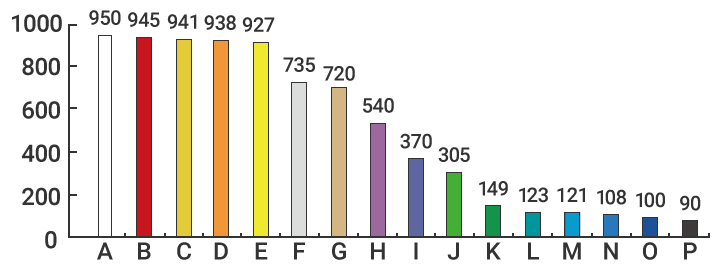
* The graph shows differences in the intensity of light received from different colored targets when a KEYENCE fiber optic sensor (red light) is used. It shows that combinations such as white and red, or orange and yellow are difficult to differentiate by simply looking at received light intensity only.
Stable detection, even when distance changes
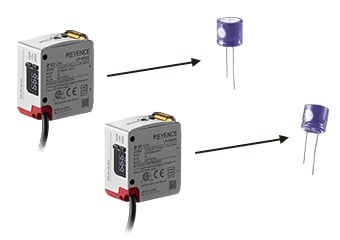
With a conventional photoelectric sensor, when the distance to the target object changes, the received light intensity also changes. On the other hand, with a color sensor, there is no change in color identification even when the distance to the target changes. As a result, the target's color can be stably differentiated even if the distance changes or the target is tilted.
When the distance to a target changes, the following occurs for conventional photoelectric sensors (received light intensity) and color sensors (ratio of light received).
Received light intensity
When the distance to the target changes, the received light intensity also changes.
Example: Vibration of a conveyor. Variations in target's passing position.
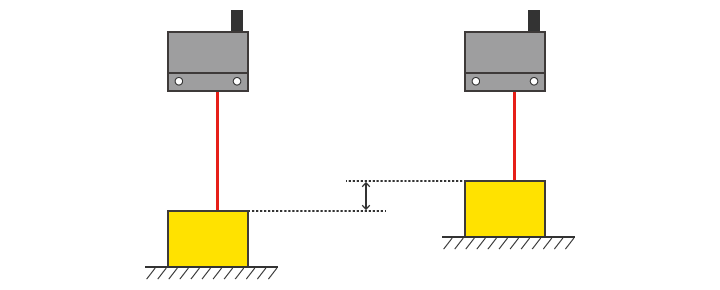

Changes in received light intensity
Left: Received light intensity 30
Right: Received light intensity 100
Ratio of received light
Even when the distance to the target changes, the color ratio does not change.
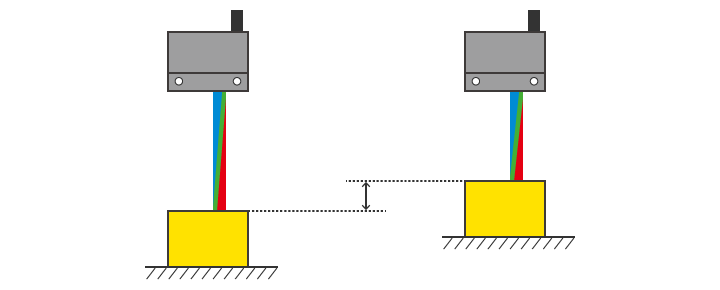

No change in ratio of light received
Left: Received light ratio 4:4:1
Right: Received light ratio 4:4:1
-
Detection based on “Light”
What is a Color sensor?
Color sensors -
Detection based on “Changes in Eddy Current”
What is an Inductive Proximity Sensor?
Inductive Proximity Sensors