DeviceNet®
This section explains DeviceNet®.
Overview
DeviceNet® is an open network developed by an American company, Rockwell Automation, Inc., in the 1990s.
Now, it is managed, certified, and promoted by ODVA (formerly Open DeviceNet Vendors Association, Inc.). To obtain the specifications to manufacture DeviceNet®-compatible equipment, venders need to participate in ODVA. As of July 2015, DeviceNet®-compatible products have been released by more than 500 vendors.
Wiring Method and Communication Protocol
Wiring method
DeviceNet® supports topologies such as daisy chain, bus connections using branching, and star type connections using branching taps which makes wiring highly flexible. The total wiring distance can be extended up to 500 m (1640.4′), depending on the transmission speed. Communication is performed according to RS-485, requiring terminating resistors at both ends of cables. One multi-core cable supplies power and transmits signals, which enhances noise immunity. This network uses special 5-pin connectors that specify the colors for wires including the signal line, preventing damage caused by incorrect wiring. Up to 64 nodes can be connected.
Communication protocol
Data is transmitted using the CAN communication protocol. Communication is performed using the master/slave method. Data transmitted with each node is defined as a data profile prepared according to the type. Products from different manufacturers can easily communicate with each other by registering the Electronic Data Sheet (EDS) corresponding to the data profile to the master. EDS files are provided by manufacturers of DeviceNet®-compatible devices. The device range contained in an EDS file may not be one pattern. The range can be changed according to the application by selecting an appropriate pattern from multiple options.
Characteristics
DeviceNet® networks use the master/slave method. Link devices and communication control are centrally managed by the master, so no settings are required for slaves. This network supports I/O communication which automatically updates data, and message communication which communicates at arbitrary timings.
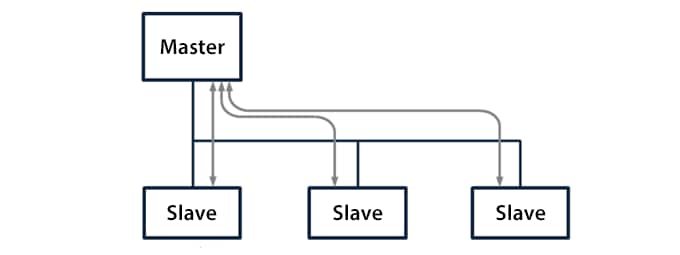
I/O communication function
This function automatically exchanges link device data between the master and slaves. DeviceNet® has four selectable methods to determine data sending and receiving timing: polling, bit-strobe, change of state (COS), and cyclic.
Polling
Data is sent to and received from each slave in sequence.
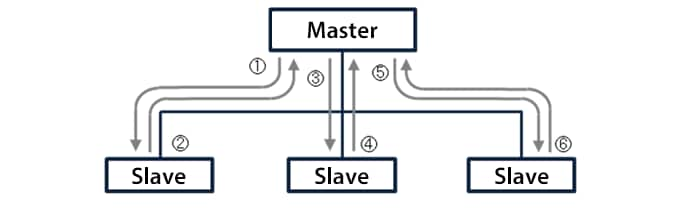
Bit-strobe
The master sends one-bit output information to all slaves simultaneously and each slave sends back response data to the master.
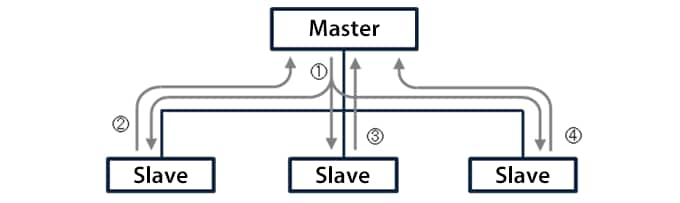
COS
When I/O data changes, data is transmitted between the master and corresponding slaves.
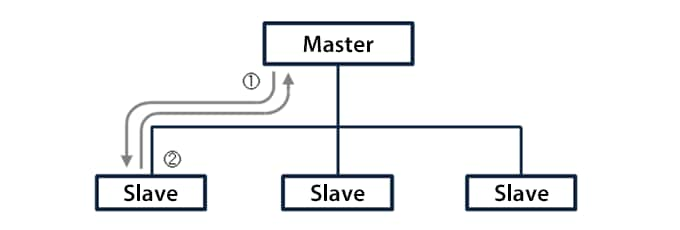
Cyclic
Data is sent to and received from each slave in a fixed cycle.
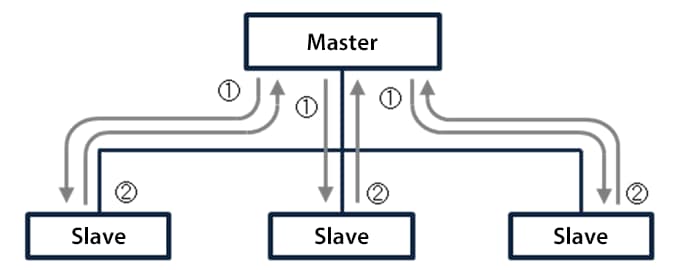
Message communication function
With this function, the master sends a command to a slave at an arbitrary timing and the slave sends back a response. This function is used for changing slave setting contents, reading error details, and other communication. Details of data and instructions transmitted via command–response communication are determined with a slave.
- Company, product, and network names mentioned on this page are either trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
- Note that some information, such as applicable standards and specifications, may have changed since this page was published.
November 2015






