FL-net
This section explains FL-net.
Overview
FL-net (OPCN-2) is an open network developed by the Japan Electrical Manufacturers' Association (JEMA). This network was developed for controlling and monitoring devices by interconnecting FA controllers, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and computer numerical control (CNC) systems, and PCs from multiple manufacturers.
Wiring Method and Communication Protocol
Wiring method
This network is wired based on general-purpose Ethernet. When Ethernet switches are used, the maximum cable length between nodes (or Ethernet switches) is 100 m (328.1′). There is no limit on the total extension distance. Up to 254 nodes can be connected. However, FL-net (OPCN-2) cannot be used with general-purpose Ethernet communication because it sends data simultaneously to all connected devices (broadcasting).
Communication protocol
FL-net (OPCN-2) uses UDP/IP to send data simultaneously to all connected devices. It also uses the token passing method in which communication is performed by passing the right of transmission (token) among all nodes. This method prevents communication in a network from completely stopping even when some nodes malfunction and also prevents communication performance from decreasing because transmission timing collision cannot occur.
Characteristics
FL-net supports cyclic communication to communicate in a fixed cycle, and message communication to communicate at arbitrary timings. In cyclic communication, data is transmitted and received using shared areas called common memories. Nodes share data by individually reading data sent from each node to the common memories. The common memory needs to be set for each node.
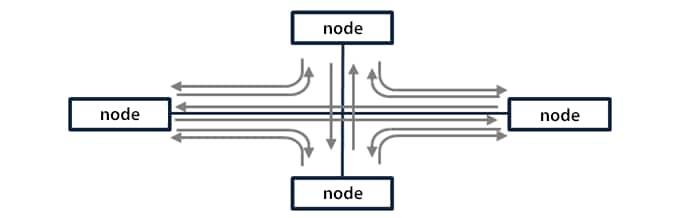
Cyclic communication function
A node that received the right of transmission (token) sends data simultaneously to all other nodes. Other nodes read any necessary information from the data received. When broadcasting is completed, the right of transmission (token) is passed to the next node.
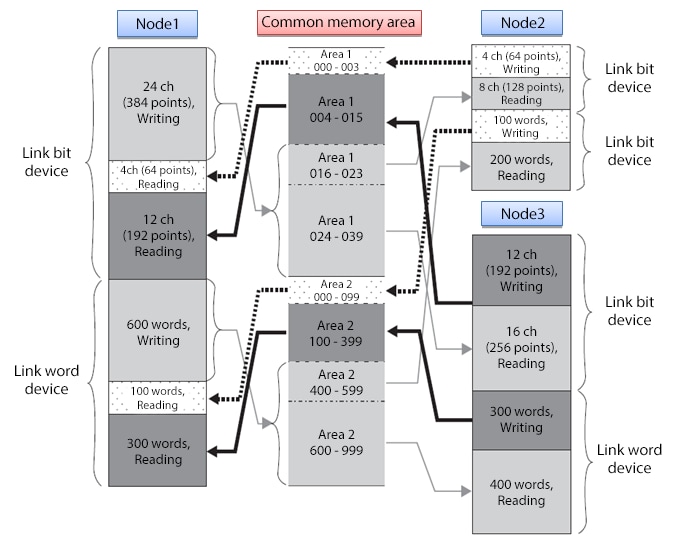
(Reference) Common memory area
In cyclic communication, each node shares data by setting areas to use in a virtual memory space called a common memory.
Message communication function
This communication method performs one-to-one data communication from one node to another node at arbitrary timing.
- Company, product, and network names mentioned on this page are either trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
- Note that some information, such as applicable standards and specifications, may have changed since this page was published.
November 2015






