Hybrid welding
Hybrid welding is also known as hybrid laser-arc welding (HLAW).
This welding method was developed for simultaneously performing arc welding (such as TIG, MAG, or MIG welding) and laser welding, thereby utilizing the advantage of both methods to make up for any shortcomings.
Hybrid welding is considered an effective means of achieving higher gap management tolerance, deeper penetration, lower heat input, reduced deformation and shrinkage, higher weld hardness and strength, higher fatigue resistance, improved welding speed and quality, and reduced costs.
Comparing laser welding and arc welding
Laser welding features a small laser beam spot diameter that requires strict gap control (groove precision) during butt welding. With wider grooves, countermeasures such as slower processing speeds are required. Laser welding is also generally good for welding thin plates but not suitable for welding thicker plates. Arc welding, on the other hand, is suitable for welding thick plates, but the welding spot diameter is large, penetration is shallow, and high-speed welding is not recommended.
Arc welding
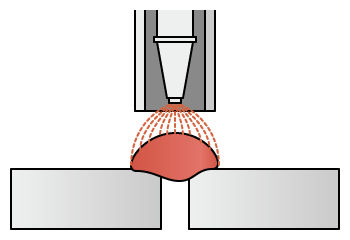
- [Advantages]
- Strong against gaps and possible buildup
- [Disadvantages]
- Slow welding speeds with high welding distortion
Laser welding
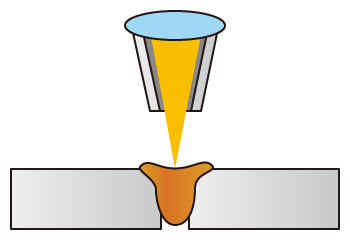
- [Advantages]
- Fast welding speeds with deep penetration and low distortion
- [Disadvantages]
- Weak against gaps and impossible buildup
Features of hybrid welding
High-speed and high-quality hybrid welding involves simultaneously performing laser welding, which is ideal for thin plates and detailed welding, and arc welding, which is ideal for thick plates and offers strong gap management with high groove precision. Hybrid welding is becoming a popular choice in applications requiring high processing speeds even under complicated conditions such as welding base materials with different thicknesses during tailored blank processing in the automotive industry, and welding different materials with different melting points.
Hybrid welding
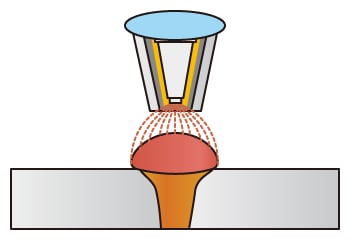
- [Advantages]
- Fast welding speeds with strong gap resistance, deep penetration, and low distortion





