Features of CAN
This section explains the features of CAN, which is now utilized in place of conventional wiring methods, and its advantages in terms of both hardware and software compared to other communication methods.
Advantages of using CAN
One of the advantages of using the CAN serial communication protocol is that various devices can be connected with the minimum amount of signal wires. Another feature is resistance to external noise because CAN was originally developed for automobiles.
Minimized wiring resulting in low cost
As described above, CAN is a serial communication protocol, so devices can be connected to each other using one or two signal lines. Because CAN generally requires only two communication lines, the number of wires can be reduced drastically compared to when using a conventional communication method. This is effective not only in reducing the cost, but also in suppressing weight increases.
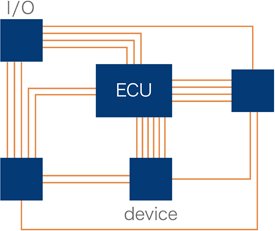
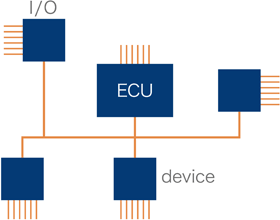
High external noise resistance and high reliability
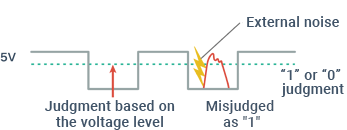
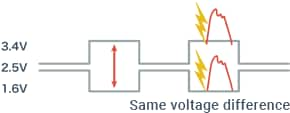
This communication protocol features high resistance to noise because it was originally developed to be used in automobiles. The high-speed CAN (CAN-C or class C) adopts the “2-wire differential voltage method” that transmits data depending on the existence of a voltage difference generated between two communication lines. Because noise added externally is identical to both lines, no voltage difference occurs. Therefore, this method reduces the effect of noise, if any occurs.
Smooth data communication with no waste
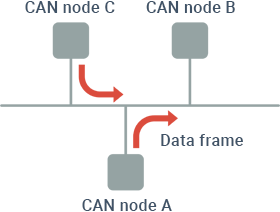
Devices on a network are called “nodes,” and communication lines that connect each node are called “buses.” CAN adopts a “multi-master method” that enables equal access from each connected node. Therefore, communication can be started from any node as long as there is an available bus. Also, transmission is generally disabled if data is concentrated from multiple nodes, but CAN allows for smooth transmission with no waste thanks to its arbitration function, which transmits messages with higher priorities.
- Multi-master method
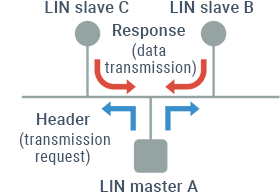
- Single-master method
High-speed and reliable data sharing
The high-speed CAN offers a maximum communication speed of 1 Mbps and is implemented with various error detection mechanisms, thereby enabling different types of errors to be detected in almost 100% of cases. CAN also adopts a method that repeats data transmission if even a single abnormal transmission occurs by deleting all data and retransmitting data to all nodes until the transmission succeeds. Furthermore, arbitration and noise resistance enable data to be transferred safely at high speed.
Flexible system construction
Because CAN assigns identifiers (IDs) to data to be transmitted, which is called “message addressing,” the receiver can judge the content of the received data on the basis of the ID. This makes it easier, for example, for an on-board network to synchronize engine control data with other systems such as meters and air conditioners. Advantages of this function include flexible system construction and self-diagnosis performed in batches thanks to data sharing throughout the network.



