Data Acquisition (DAQ)
How to Measure Voltage
Voltage is the foundation of all electrical systems and acts as the force that moves an electrical charge through a conductor. Without voltage, current cannot flow and an electrical device cannot function.
Understanding Voltage: The Basics
Voltage is the foundation of all electrical systems and acts as the force that moves an electrical charge through a conductor. Without voltage, current cannot flow and an electrical device cannot function. Whether working with household circuits or precision electronic components, accurate voltage measurements help make sure that systems can operate safely. Measurement is used to determine the potential difference between two points in a circuit.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

What is Voltage? (Potential Difference)
Voltage, or potential difference, is the force that drives electric current through a circuit. Too little voltage can cause devices to malfunction, while too much can lead to damage.
To measure voltage accurately, specialized voltage-measuring instruments like digital multimeters (DMMs), oscilloscopes, and data acquisition (DAQ) systems (like KEYENCE data logger NR-X Series) are used, depending on the application.
Units of Voltage (Volts)
Voltage is measured in volts (V). One volt equals the energy needed to move one coulomb of charge through one ohm of resistance.
Common voltage levels, and examples of them, include:
- 1.5V – AA battery
- 5V – USB power supply
- 12V – Car battery
- 120V / 230V – Household AC power (U.S. / Europe)
- 400V+ – Industrial systems
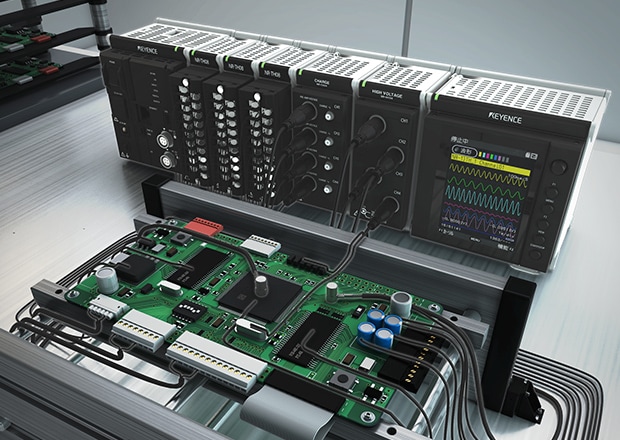

Digital multimeters and other precision instruments can detect even microvolt variations in sensitive circuits.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Types of Voltage (AC vs. DC)
Voltage exists in two primary forms:
- Direct Current (DC) Voltage: Remains constant and flows in one direction; used in batteries, automotive systems, and solar power applications.
- Alternating Current (AC) Voltage: Periodically reverses direction, used in household electrical outlets, industrial power grids, and large-scale energy systems.
Accurate voltage measurement depends on identifying whether the signal is AC or DC, as using the wrong setting can lead to incorrect current measurements.
Methods for Measuring Voltage
Selecting the right voltage measuring instrument depends on the application, accuracy needs, and environmental conditions. Several methods exist for voltage measurement, depending on the level of precision required.
- Multimeters: Widely used for quick and accurate readings of both AC and DC voltage.
- Oscilloscopes: Provide a visual representation of voltage waveforms, useful for analyzing electrical signals.
- Data Acquisition (DAQ) Systems: Monitor and record voltage levels over time, commonly used in industrial automation and research.
- Voltage Sensors and Probes: Used in high-voltage environments where direct contact measurements are impractical.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Using a Multimeter
A digital multimeter (DMM) is the most common tool for voltage measurement versatile and easy to use. Here’s how to measure voltage with a multimeter:
- Set the Correct Mode:
-
- Choose DC voltage (V—) for batteries and electronic circuits.
- Select AC voltage (V—) for household and industrial power systems.
- Insert the Test Leads:
-
- Plug the black lead into the COM (common) port.
- Insert the red lead into the V (voltage) port.
- Connect the Probes:
-
- For DC voltage, place the red probe on the positive terminal and the black probe on the negative terminal. If reversed, the reading will display a negative value.
- For AC voltage, probe polarity does not matter.
- Read the Voltage Value:
-
- Ensure the measurement voltage is within the expected range. If the display shows “1” or “OL”, select a higher voltage range.
For advanced voltage measurement needs, explore KEYENCE’s DAQ voltage measurement solutions for high-precision applications. Contact us today for more information!
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Related Downloads

Learn about how to choose the best DAQ for voltage measurement based on several key points, including the maximum voltage being measured, the number of channels, accuracy, sampling rate, and simultaneous measurement with input signals other than voltage.

![Introductory Guide to Voltage Measurement [Basic Knowledge of Voltage Measurement]](/img/asset/AS_118629_L.jpg)

