Safety Interlock Switches
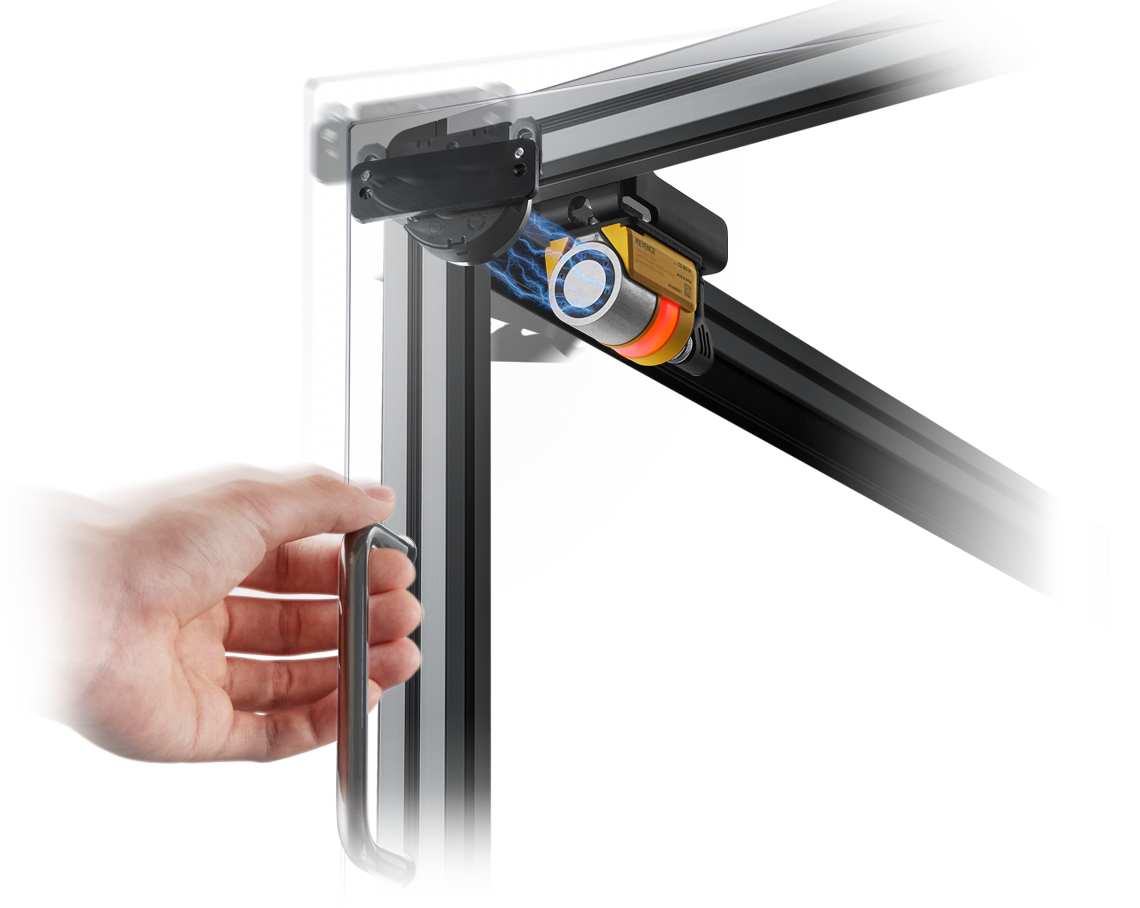

Safety door switches and safety interlock switches are safety components that can be installed on safety gates and doors to detect entry. This lineup includes models that use the power-to-release and power-to-lock methods. Non-contact types are also available that eliminate issues traditionally caused by dust, debris, and long term wear and tear.
Product Lineup

Safety interlock switches are safety devices used for checking whether movable machine guarding such as safety fence doors and covers are open or closed. KEYENCE’s GS-M Series safety interlock switch uses an electromagnetic locking principle and flexible actuator to prevent door rattling and misalignment for easy locking. The ultra-compact design can be used with any kind of door and can be installed anywhere. The GS-M Series offers superior safety in addition to the usability and reliability required for manufacturing sites without hindering productivity.
Features
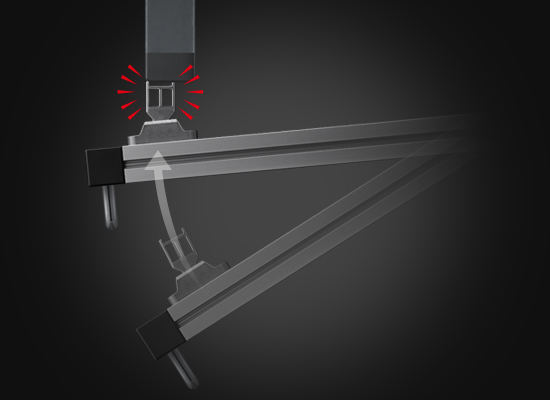
Introducing KEYENCE'S New Hybrid Door Interlock.
With the hybrid technology of the GS-M Series, one unit can act as either a locking type or non-contact type interlock. It also features a built-in magnetic latch that can hold the door closed, even when the lock is not activated.
Hybrid Door Interlock
Locking Type
Non-contact
Easy to Use
Alignment is no longer an issue with the GS-M Series.
It's keyless design does not require any insertion to lock, eliminating misalignment caused by improper positioning. The built-in spring and magnetic latch eliminate gaps between the sensor and actuator, significantly increasing alignment forgiveness.
Conventional
With conventional interlocks, the key cannot be inserted if the door is misaligned, preventing it from being closed.
GS-M Series
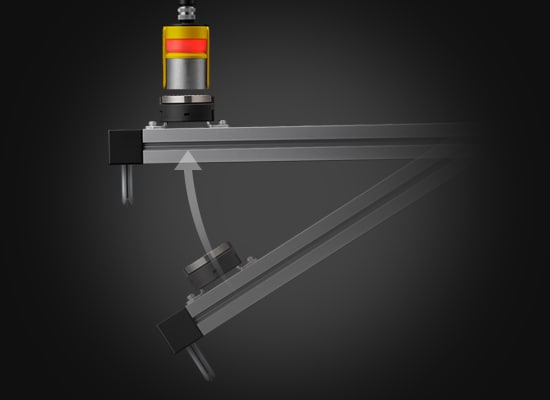

Because the GS-M does not require any insertion to lock, common misalignment issues are eliminated.

Safety interlock switches are safety devices used for checking whether movable machine guarding such as doors, fences, and covers are opened or closed. KEYENCE’s GS Series Safety Interlock Switches are available in locking type—either power-to-release (GS-50) or power-to-lock (GS-70) models—and non-contact type (GS-10). Both types feature a slim-yet-rugged design with an enclosure rating that ensures usability, even when exposed to water or oil (IP65/67/69K). The GS Series not only offers superior safety but also the usability and reliability required for manufacturing facilities without hindering productivity.
Features

Intuitive Design
- Compact size to maximize versatility
- Robust construction prevents damage to ensure longevity
- Highly visible indicators to easily identify status at a glance

Versatile Mounting
- Mount directly to the machine or choose from dedicated brackets
- Locking type and non-contact models available
- Designed to prevent nuisance trips related to door sag, vibration, and more
Safety interlock switches are used as interlock devices that can prevent machine operation or startup in an unsafe situation, such as when a door or guard is open. Interlock devices with a locking function can also prevent doors or guards from being opened while the machine is in operation.
Safety interlock switches (interlock devices) are an important factor in ensuring machine safety, with many relevant safety standards. Two of the most typical standards are ISO 14119 and ISO 13849, and safety performance that meets these standards is essential.
Benefits of Safety Interlock Switches
Safety interlock switches are used on safety doors, fences, and guards that physically separate workers from hazards. These devices are essential to ensuring reliable safety precautions.
Sometimes working in dangerous areas is necessary, such as during equipment maintenance or troubleshooting. In such situations, safety interlock switches for doors and movable guards are needed to ensure both worker safety and productivity.
Locking types can also reduce risks while the machine is in operation and prevent the machine from stopping unnecessarily.
Locking-type safety interlock switches are available in power-to-release or power-to-lock models. These types can be used in a variety of ways depending on the situation and hazard.
Power-to-release models use a spring to lock the device, ensuring the device remains locked even when the power is turned off. This means these models are ideal for protection against large robots, rotating objects, and other hazards that cannot be stopped immediately due to inertia. Power-to-lock models, however, use a powered solenoid to lock the device, meaning, the lock is released immediately when the power is turned off. These models are useful in situations where a lock is necessary to protect workers from a hazard that can be immediately shut down if the power is interrupted, or to protect the operation of the machine.
Non-contact safety interlock switches are most commonly used when dust and debris must be avoided to prevent product contamination. These types eliminate any risk of dust and debris because door conditions can be detected with no contact between the sensor and the actuator.
Because non-contact types do not have a locking mechanism, no wear debris is created. This makes these types are ideal for clean environments and food industry settings where a sanitary manufacturing environment is required. The surface of these types is also relatively smooth, preventing foreign particles from adhering to or accumulating on the sensor or actuator. Non-contact types also boast a high enclosure rating (IP65/67/69K), ideal for withstanding the environment and cleaning.
Safety Interlock Switch Case Studies
Safety precautions for processing machines
For processing machines, safety precautions are required to detect intrusion into the processing area. Machines require door locks and other measures for quickly responding to the actions of workers, such as when entering the processing area during operation. Additional safety precautions such as slowing down the operation of the machine when working in the processing area are also important.
Power-to-release safety interlock switches (GS-50 Series) are recommended for processing-machine doors. After the machine stops completely, an unlock signal is sent to the safety interlock switch to unlock the door. With a power-to-release safety interlock switch, the door will remain locked even when the power is turned off. This will prevent workers from entering the processing area until the machine’s inertial movements completely stop. Once the worker closes the machine door, the operation can be resumed.
Safety precautions for SCARA robots (horizontal multi-joint robots)
Used in a variety of fields including assembly lines, SCARA robots are known for their space-saving design and high-speed operability. However, because of the limited space used for installation, such as inside cases, the robots can be dangerous if operated while a worker is inside the case with the robot. Workers entering the transfer areas between machines is also dangerous.
A KEYENCE safety interlock switch (GS Series) can be used to monitor the status of doors in such situations. If a door is opened, the robot is stopped and an interlock state is enforced. Once the worker exits the case and closes the door, robot operation can be resumed. Safety light curtains in the transfer area between machines can also be used to turn off the OSSD if a worker is present. This makes it possible to prevent the robot from operating while workers are inside the case.
Reducing costs and improving efficiency with cascade connections
For large machines with numerous doors, individual controller cables are required, making the wiring for safety devices very complicated. Such situations can also be troublesome due to the limited number of diagnostic methods for troubleshooting, causing the machine to be stopped for unnecessarily long periods and increasing maintenance and repair costs.
KEYENCE’s GS Series Safety Interlock Switches offer cascade connections between contact emergency stop switches and safety interlock switches. This enables a unified safety output for a reduced number of inputs and less wiring. Cascade connections also comply with safety standards such as Category4 and PLe (ISO 13849‑1). (Up to 30 non-contact types or 25 locking types can be connected.)

This site includes information on machine safety standards and risk management. Also learn about ISO international standards, safety precautions for industrial robots, safety equipment functions, and how to choose an appropriate device.
Frequently Asked Questions About Safety Interlock Switches
Safety interlock switches are used to increase machine safety and reduce risks. Machines are generally enclosed by a fence or similar equipment as a basic safety precaution (separation-based safety). However, if it is necessary to get close to a machine for troubleshooting or maintenance, workers must stop the machine to enter the fenced area (stoppage-based safety). Safety interlock switches can be used to check the door status in such situations.
For example, a safety interlock switch can be used to lock the door and keep it from being opened while the device is in operation, preventing accidental operation if a worker opens the door and enters the fenced area without turning off the machine first.
Power-to-lock models unlock when the power is turned off, while power-to-release models remain locked even without power. Because of this, power-to-lock models are used with machines that are not affected by inertia and are able to stop immediately when a door is opened or where a safe distance can be maintained. Power-to-release models use a spring to remain locked even when the power is turned off, so these devices are often used to ensure worker safety with machines affected by inertia, such as rolling machines. Power-to-lock models also unlock immediately in the event of a malfunction because the power to the solenoid is no longer supplied. Power-to-release models, however, will remain locked even after power is no longer supplied. This makes power-to-release models useful to ensure safety in the event of a power failure.
The standard used for designing and selecting interlocking devices such as door switches is ISO 14119, “Safety of machinery — Interlocking devices associated with guards — Principles for design and selection.” This standard defines the following categories (levels) for encoding actuators.
• Low: 1 to 9 coding patterns
• Medium: 10 to 1000 coding patterns
• High: 1001 or more coding patterns
With specific actuator teaching, the GS Series can support the High encoding level for more than 1000 different coding patterns, allowing use with minimal design constraints.

This guidebook introduces a wide range of safety information, including machine safety standards (for manufacturing equipment and other machines), the Performance Level (PL) classification used for defining risk assessment and safety factors, and specific safety devices.

Browse a collection of actual SZ Series application examples with a focus on six different types of problems regarding safety measures. This guide is a must-read for anyone experiencing problems with safety mats or light curtains, or having problems selecting or installing safety devices.

![[NON CONTACT TYPE DOOR INTERLOCKS]Verify the door is shut / [LOCKING TYPE (Power-to-Lock) DOOR INTERLOCKS]Keep the door locked](/Images/series_gs-m_features_05-01_2032123.jpg)
![[Based on Wiring]Door Closed / Door Closed & Locked [STRONG ELECTROMAGNET]](/Images/series_gs-m_features_05-02_2032124.jpg)
![[Conventional Setup]Magnet latch / Non-contact Interlock [GS-M Series] Built-in permanent magnet](/Images/series_gs-m_features_05-03_2032125.jpg)
