Barcode Scanners
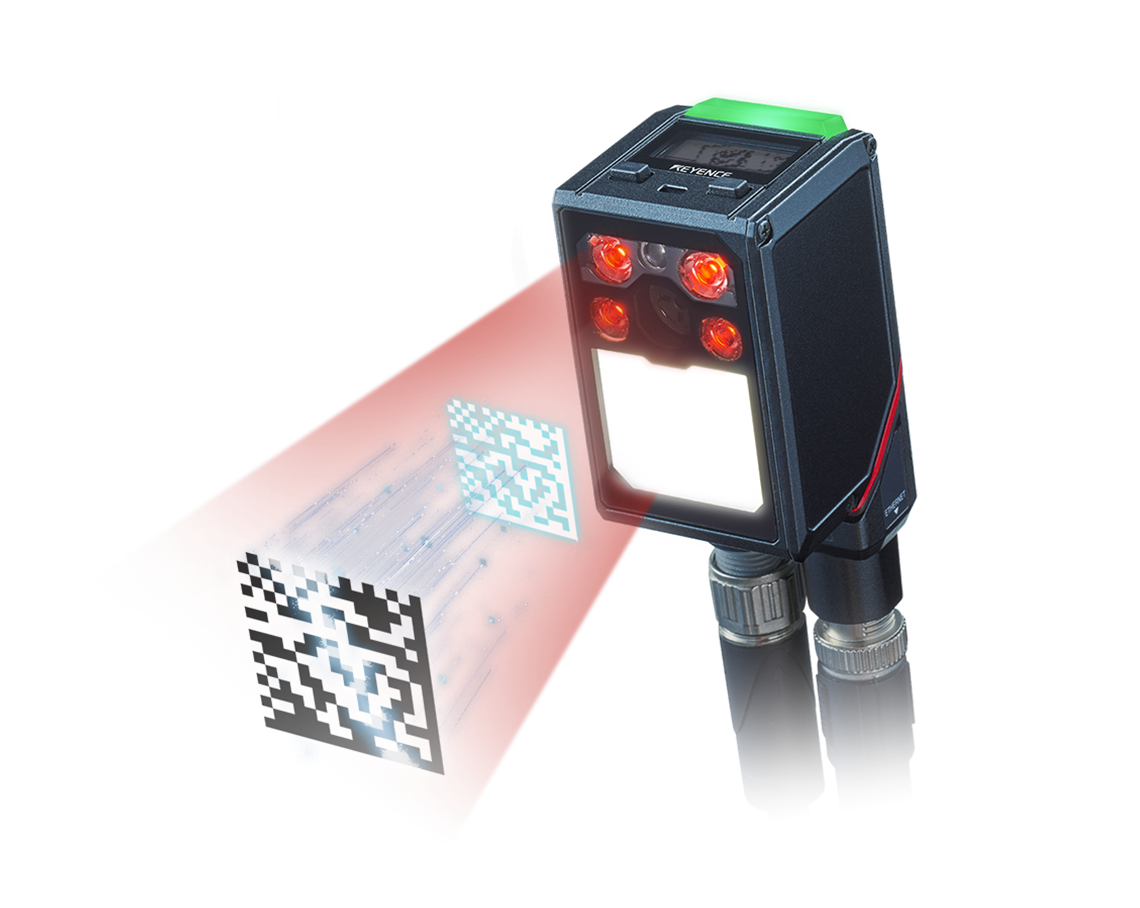

A rich lineup of code readers that support an ultra-wide field of view, and ultra-long reading depth. These products allow for stable inline reading of barcodes and 2D codes at high-speeds in the logistics and manufacturing industries. The lineup includes a fully automatic tuning type that requires no external lighting so that anyone can easily install, operate, and monitor the readers from nearly anywhere.
Product Lineup

The SR-X Series of AI-powered code readers has a compact design - 72% smaller than our conventional models - while still providing high-performance reading for a wide variety of codes. The AI and latest decoding algorithms provide stable reading between processes, tracking changes in codes that occur from one process to the next. It is also possible to link code readers between processes for improved reading performance. With these connections, the operating status and current settings of readers on the same network can be viewed together in a list. Automatic focus adjustment and fully automatic tuning make setup easy with the press of a button.
Features
Impressive Imaging Capabilities in an Integrated Design
With a typical camera lens, the corners of the captured image are distorted and essentially unusable for reading. KEYENCE’s newly developed imaging lens makes effective use of the entire area captured by the CMOS image sensor, ensuring readability even in the corners of the image.
- Ultra-compact imaging lens
- New HDR wide CMOS
- Built-in 3-way lighting (direct, polarized, diffused)
Integrated Lens, Lighting, and High-Resolution CMOS
The integrated design provides completely automatic configuration of the best settings with no need to select equipment or adjust settings. The reader automatically selects the optimal lighting conditions for the target.
Reliably Identify Codes
SR-X Drive: A New Decoding Algorithm from KEYENCE
AI filters help read difficult codes. Optimized specifically for code reading, the built-in inference-specific AI chip was created through learning of a database of over 100,000 images. This results in dramatically improved code reading performance.
Stains

Scratches

Rough Backgrounds

Uneven Cell Color


The ST Series Scan Tunnel System for logistics sites—where high throughput is necessary—utilizes an offset focal plane to ensure stable reading of barcodes even with package gaps as short as 50 mm (2″). Reducing package gaps allows for more packages to be processed every hour, leading to higher throughput. The ST Series also offers a wider field of view and greater depth of field than conventional models, reducing the required installation space to half the size for greater design flexibility. KEYENCE also offers bottom-side readers with a unique side-mounted design, logistics-focused dimensioning systems, and AI-equipped analysis software. The ST Series is the ideal tool capable of meeting a variety of logistics industry needs, from inbound through outbound scanning.
Features
Reliable Reading Even with Gaps as Short as 50 mm (2″)
Increases in logistics volume have resulted in shorter gaps between packages. With conventional code readers, multiple codes entering the field of view would result in reading errors. KEYENCE’s newly developed DynaTrax technology combines software, hardware, and algorithms to achieve high-speed reading even with small gaps between packages.
Best-in-Class Coverage Area for Six-Sided Scanning and Dimensioning
With a 2.3 times larger field of view and 2 times greater depth of field compared to KEYENCE’s conventional high-performance models, the new ST Series is capable of reading over an even larger area. KEYENCE also offers logistics-oriented dimensioner that incorporates our extensive technical expertise as well as a unique bottom-side code reader that reads codes while mounted beside the conveyor. These and other products make it possible for us to meet a variety of logistics industry needs.

KEYENCE’s offset focal plane technology and optimal lighting design provide a large reading field of view and depth of field.

KEYENCE's logistics-focused dimensioner measures package dimensions regardless of color or shape and improves reading reliability when linked with a code reader.
Installing KEYENCE’s bottom-side code reader next to a conveyor prevents dirt and dust from disrupting reading compared with conventional models that read from below.
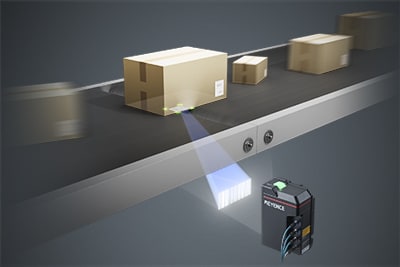
The SR-5000 Series logistics code reader offers an ultra-wide field of view, ultra-long depth of field, and high-speed reading, resulting in easy installation and operation in logistics environments for reliable capture of codes on fast-moving packages. Stable reading is ensured even when packages of different shapes and sizes are on the same line moving at high speeds, regardless of where the barcode labels are found on the packages. These readers eliminate the need to prepare to align the packages to one side of the conveyor, thereby contributing to reduced costs and a lower risk of malfunction thanks to the simplified conveyor system. While multiple readers were conventionally necessary for reading one side, simply installing one SR-5000 Series reader per side makes it possible to read the codes on labels affixed on the top and sides of packages of different sizes and varying locations. This is possible thanks to the ultra-wide field of view and deep depth of field of the SR-5000 Series.
Features
Ultra-Wide Field of View & Ultra-Long Reading Depth
Reliable reading even for packages of different sizes.
Ultra-High Speed
Stable reading even on high-speed lines exceeding 150 m/min.

The SR-2000 Series of 1D/2D code readers achieve high speed reading over long distances with a wide field of view and large depth of field. With a field of view more than twice that of conventional models, these scanners support simultaneous reading of multiple barcodes and varying positions, contributing to shorter cycle times and increased stability. Also, this series achieves a reading distance that is more than double that of conventional models, so there is no need for barcode position control or changeovers. This 1D/2D code reader can instantly read codes on moving objects such as sites using conveyors or robotic transfers. No expert imaging knowledge is required, and there is no need for additional lighting or other external equipment. The fully automatic calibration function easily makes automatic code reading stable under a variety of conditions just by installing the unit.
Features
Ultra-wide Field of View
A field of view 4x wider compared to conventional models makes for easy reading of multiple codes and varying code positions.
- No need to check code positions
- Read multiple codes all at once
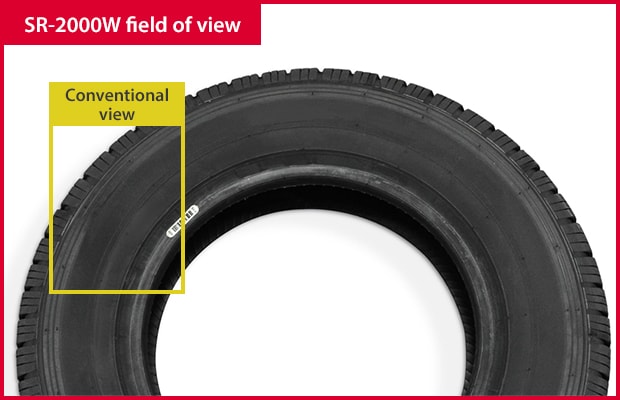

Greater Depth of Field at Longer Ranges
With more than twice the reading distance of conventional models, there's no need for controlling code position or tooling changes.
- No code position controllers or tooling changes required
- Read minute codes at long distances
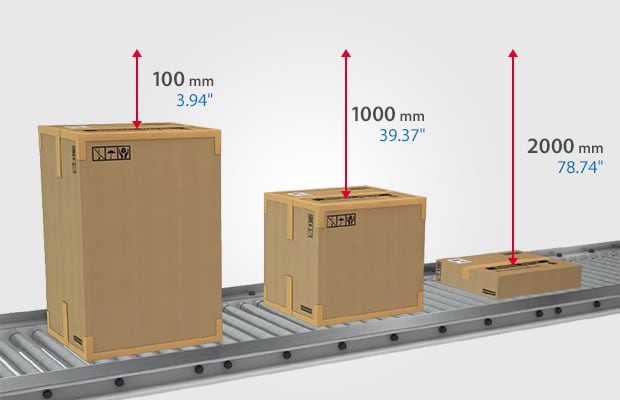


With just a single button, the SR-1000 Series autofocus 1D and 2D code reader solves the issues of conventional fixed-mount code readers. The autofocus function allows this code reader to read codes at any distance up to 1 meter away. The automatic tuning feature sets the exposure time, filters, and other parameters without requiring the operator to have specialized knowledge. On top of that, this series is equipped with the world’s first polarizing filter automatic control that can eliminate glare without the need for external lighting. The optimal settings can be configured with just the press of a button, offering simplified and improved flexibility in installation and setup as well as reducing the time spent on such tasks. The polarizing filter automatic control results in a stable reading of 2D codes directly marked (DPM) on cylinders, hairline metal surfaces, and metal casting, which were conventionally difficult to read due to glare.

The SR-750 Series compact 1D and 2D code reader offers a stable automatic reading of challenging codes despite its compact size. Adopting a new image capturing and processing algorithm and using the latest correction techniques, this series achieves best-in-class reading performance for the most difficult-to-read codes. This code reader can reliably read codes directly marked on products (DPM) of various materials. Operators can also use the easy tuning feature which provides optimal settings in three steps either on the unit itself or from a computer, thereby resulting in quick integration and product changeovers. This series is also the first unit in its class to be equipped with a marking quality judgment function based on industry standards. This function outputs judgment results as signals and can be useful for predictive maintenance of the marking process.

The SR-700 Series ultra-compact 1D and 2D code reader offers easy installation and excellent reading performance in a compact design. The latest reading engine integrated with a small body delivers great reading ability over its entire field of view. This series features robust performance for reading codes at an angle and handling codes that are damaged or blurred. Even with fast-moving products, this series can provide stable reading with its burst read function to capture 10 continuous images and its ultra-bright LED lighting which can shorten the exposure time. Brightness and image filters can also be configured automatically using buttons on the reader itself, which not only makes installation easy but also facilitates faster product changeovers.
Features

Compact Body
The compact body can be mounted in small spaces, expanding the range of applications.

High-Quality, High-Speed Reading
New algorithms provide best-in-class reading capability even when the code is hard to read.

The BL-1300 Series ultra-compact digital barcode reader is the first in its class to be designed with a digital processing engine in its small body. This laser barcode reader features high speed, high resolution, and high performance. The high-speed motor and processing engine achieve 1300 scans or decodes per second—the fastest speed in its class—thus making rapid scanning possible even on fast cycle lines. This series also supports reading a narrow bar width as small as 0.08 mm. Noise generated by dirt or blurred marking is corrected to ensure reading of even the faintest codes. Additionally, by adopting a new decode process, this series can use the edge detection function to reliably extract the bars and spaces of challenging codes. The digital correction feature ensures reliable and fast reading of barcodes in any state.
A barcode scanner is a device that reads barcodes. Typical barcode scanners include laser barcode scanners and CCD barcode readers. Laser barcode scanners emit a laser beam on an oscillating mirror to scan the barcode. The narrow and wide bars, as well as the spaces, are detected and decoded. CCD barcode readers emit light onto the barcode and generate an image from the diffused reflection using the CCD. The image is decoded and output as information.
A 2D code reader extracts a 2D code from the captured image and decodes it. The captured grayscale image is binarized. A code is extracted and decoded to output information. Codes may not be readable depending on the lighting/camera conditions or settings, as well as glossy surfaces or the marking condition on the target. For inline installations, lighting-integrated type barcode scanners that can automatically adjust the image capturing conditions are effective.
Handheld barcode scanners are designed to allow operators to hold them in their hands to scan codes. Wireless models with fast, stable scanning performance are effective for improving work efficiency.
Benefits of Barcode Scanners
Barcode scanners can be installed on production lines or logistics sites to get package or product information automatically. While significantly improving the efficiency of package and product management, barcode scanners can also support traceability. Traceability can prevent shipping mistakes and product mix-ups.
Because barcode scanners can read barcodes and 2D codes on packages and products being transported on a logistics or production line, they can eliminate the time and labor spent on visual checks. Barcode scanners and 2D code readers that have good scanning speed, reading distance, wide field of view, large depth of field, and distortion corrections for variations in code position and angle can stably read codes on objects of different sizes and shapes on the conveyor. Installing such code readers eliminates the need for extra mechanisms for aligning and positioning targets, thereby helping simplify the system and reducing maintenance costs.
Some barcode scanners and 2D code readers can fit into a variety of worksites and operation lines. Selecting a compact code reader that does not require lighting or other external equipment can drastically increase the flexibility of an installation.
There are various barcode scanners that you can choose from, including compact models with integrated high-performance lighting and barcode scanners with excellent laser angle characteristics. There are even code readers that are only half the size of a typical business card and can be installed inside the equipment. Code readers that provide both easy installation and rapid scanning of fast-moving codes can be used to reduce reading errors in conveyor lines and provide code-based management without affecting cycle time.
Some barcode scanners feature simple, smart settings and operations. Barcode scanners and 2D code readers that can instantly find optimal reading conditions can significantly shorten the time taken not only for installation but also for product changeovers on the operating line. A barcode scanner that is easily configured minimizes the time and effort to prepare for the operation.
For this reason, barcode scanners that can adjust to the optimal scanning settings either using buttons on the unit or easy operations from a computer are attracting attention. For barcode scanners that use a camera, focusing on codes during operation, the exposure time setting, polarized lighting control, and image correction are all key components for successful reading. It is recommended to choose barcode scanners that can, once the basic setup is completed, automatically adjust camera conditions and image processing such as optimal position correction and binarization without needing the operator to have specialized imaging knowledge.
Barcode Scanners Case Studies
Scanning packages at random orientations
At logistics worksites, cardboard boxes often do not move down the line neatly. Typically, the orientation of these boxes and the positions of their barcodes are random. Gate-type barcode reader configurations are the solution to this problem and can read the barcodes on randomly flowing boxes without mistakes. This operation is also called tunnel scanning. Barcodes can be scanned over a wide area, and if there is a barcode on any of the five surfaces (excluding the bottom), that barcode can be read without problems. This eliminates the need to have workers stand along the line and adjust the positions of the cardboard boxes, greatly contributing to reduced labor requirements.
Reading on a line with cardboard boxes of mixed sizes
In large logistics centers, warehouses, and delivery centers, a wide variety of cardboard boxes in different sizes are handled every day. Conventional barcode readers have difficulty with stable detection due to problems involving the field of view, depth, vibration, and speed. Currently if there are cardboard boxes with different sizes, multiple barcode readers must be installed to handle this situation. There is some frustration because this involves extra costs and slows down processing for data verification.
Recently, there have also been wide field of view and long depth of field types of barcode readers as well as methods to implement stable reading with fewer barcode readers regardless of the sizes of the boxes and the locations of the barcodes.
Reading using multiple barcode readers
Multiple barcode readers are used when it is difficult to scan boxes with a single barcode reader, such as when there are barcodes affixed to multiple surfaces and when there are different box sizes. To automate barcode reading, the optimal barcode reader installation must be selected according to where labels are affixed, the number of labels, and the shape of the box. For example, two-surface reading involves scanning the top and one side of the box. Three-surface reading involves scanning the top and both sides of the box. Five-surface reading (scan tunnels) involves scanning all surfaces except the bottom. Lastly, six-surface reading involves scanning all sides of the box, including the bottom. However, the more barcode readers that are used, the greater the installation costs and the more significant the required data verification efforts will be, so it is important to select the most suitable method for the packages.

The “Barcode Information & Tips” site explains the basic principles of barcodes and 2D codes, types of codes, how they work, examples of use, and techniques used for scanning the codes.
Frequently Asked Questions About Barcode Scanners
The barcode scanner may be installed perpendicular to the labels. If a barcode scanner is installed perpendicularly, even the bars of the barcode will reflect strong light (specular reflection) which the barcode scanner identifies as spaces, thereby making the barcode scanner unable to read the labels.
It is because the emitted laser does not reflect diffusely from such barcodes. Specular reflections tend to occur when laser light shines on barcodes with glossy surfaces. Because diffuse reflections hardly occur in this situation, it is difficult to read such barcodes.
The quiet zone may be insufficient on the barcode labels. Metal surfaces do not reflect light diffusely, and therefore the barcode reader identifies the metal surface as black. In this case the margin, or quiet zone in barcode terminology, is insufficient which makes it difficult to read the barcode.
Ambient lighting may be affecting the barcode reader. If there is natural light coming in from a window, indoor lighting, or ambient light from an electronic sensor nearby, this is the same issue as when the barcode reader is exposed to specular reflection. The result is that reading becomes unstable.
Possible causes are:
• Insufficient quiet zone: Margin around 2D code is too small
• Background affects reading: Code is surrounded by a black frame
• No quiet zone: Code is printed on the edge of the label
Are the finder patterns (the corner cut-out symbols) damaged? The barcode scanner first finds the finder patterns, and then recognizes the 2D code for reading. QR codes have three finder patterns in three corners while micro QR codes have one in a single corner. The finder patterns are used for position detection. If any of these finder patterns are damaged, the barcode scanner cannot detect the position of the 2D code and as a result fails to read the code.
The combination of colors may be creating a low contrast. A 2D code reader reads the code by referring to the contrast between the marked parts and the background. If the combination of colors has a low contrast between the marking color and the background color, the 2D code reader cannot read the code.
Are the version and the marking size of the 2D code appropriate?
Also, any curvature may cause the cell (marking part) position to shift from its original position, an issue that can cause problems with reading.
![Basic Practice of 2D Codes Vol.2 [2D Code Implementation and Marking Size]](/img/asset/AS_150961_L.jpg)
This introductory book covers the characteristics of typical 2D code types, barcode types, and other basic knowledge. This includes details on marking data organization as well as key points and techniques for 2D code marking that results in stable code reading.
![1D/2D CODE READER: ACTUAL INSTALLATION EXAMPLES [AUTOMOTIVE INDUSTRY EDITION]](/img/asset/AS_127221_L.jpg)
This compilation introduces examples of using fixed-mount barcode readers for the core purposes of improving traceability and providing checks to prevent human errors. It is a must-read for barcode reader operators in the automotive industry, covering everything from the background and purposes of each need to application examples and summaries.
![1D/2D CODE READER: ACTUAL INSTALLATION EXAMPLES [ELECTRONIC DEVICE INDUSTRY EDITION]](/img/asset/AS_127802_L.jpg)
This compilation introduces examples of using fixed-mount barcode readers for the purposes of traceability and operation logging in the electronic device industry. It is a powerful guide to help you improve barcode reader operations in the electronic device industry, covering everything from the background and purposes of barcode readers to application examples.
![1D/2D CODE READER ACTUAL INSTALLATION EXAMPLES [FOOD, PHARMACEUTICAL, AND COSMETICS INDUSTRIES EDITION]](/img/asset/AS_127567_L.jpg)
This booklet summarizes everything from the background of key issues in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries to code reader application examples for product mix check and traceability. This is a recommended guide for people working in the food, pharmaceutical, or cosmetic industries.

