Data Acquisition (DAQ)
Comprehensive Guide to Acceleration Measurement
-
Tags:
- Acceleration
Acceleration measurement in the form of shock or vibration provides enormous benefits in many industries. Industries use this measurement in automotive testing, structural testing of buildings and bridges and condition monitoring of motors, drives, pumps, fans and other machinery. They also use it in other applications that make everyday life easier. Accelerometers or acceleration sensors help provide precise measurements of shock and vibration.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

What is Acceleration?
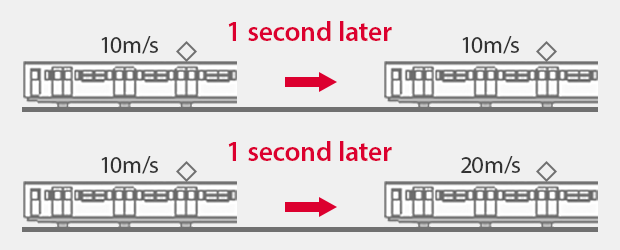
“Acceleration” is the rate of change in speed per unit of time.
It is “0” when the speed is constant. Any change in speed, even slow, generates acceleration. In the SI system, acceleration is expressed in m/s2, indicating how much speed (m/s) changes in one second.
The following three units are commonly used for acceleration:
| Unit name | Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|---|
|
Unit name
Meter per second per second
|
Symbol
m/s2
|
Definition
SI unit system
|
|
Unit name
Gravitational acceleration
|
Symbol
G
|
Definition
The acceleration when an object naturally falls by the gravity of the earth
|
|
Unit name
Gal
|
Symbol
Gal
|
Definition
“1 Gal” means that the speed increases by 1 cm/s per second
|
Relationships Between Acceleration, Speed, and Displacement
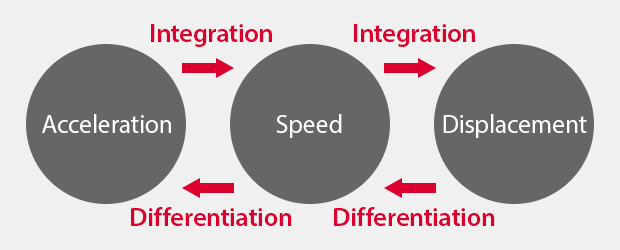
The following relationships exist between acceleration, speed, and displacement:
- Integration of the acceleration gives the speed
- Integration of the speed gives the displacement
- Differentiation of the displacement gives the speed
- Differentiation of the speed gives the acceleration
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Types of Accelerometers
These four categories include different types of acceleration sensors. Each sensor type has its applications, strengths, and working principles.
- Piezoelectric-type acceleration sensors
- Strain gauge-type acceleration sensors
- Semiconductor-type acceleration sensors
- Servo-type acceleration sensors
Principles of Acceleration Sensors
With piezoelectric acceleration sensors, mass is linked to a piezoelectric crystal. When the accelerometer receives mechanical stress, the mass exerts a force on the crystal, leading to an electric charge. In turn, the sensor sends out an electrical signal that helps quantify vibration or shock.
In a strain gauge accelerometer, the gauge changes resistance when it receives an impact. The sensor converts the impact to an electric signal which is measured to quantify vibration or shock.
Semiconductor-type acceleration sensors work on the principle of piezoresistivity. When silicon or any other type of semiconductor used in this type of sensor is subjected to an applied force, its resistance changes, and the sensor converts that to an electrical charge, which is then processed to quantify shock or vibration.
Servo-type acceleration sensors use a closed-loop, mass-spring system. The mass is attached to a servo motor controlled by a feedback loop. The loop keeps the mass in an equilibrium state.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
How Do We Measure Acceleration?
Some ways to measure acceleration are:
- Gyroscopes
- Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs)
- GPS Systems
- Optical sensors
- Accelerometers
Accelerometers are the most common types of acceleration measure used in automotive, transport, laboratory, construction, and other industries due to:
- High-precision measurement
- Impressive shock and impact resistance
- Flexibility
KEYENCE offers data loggers, also known as DAQ systems, that utilize accelelerometers or other sensors to measure acceleration. These data loggers can also capture other parameters, such as voltage from voltage measurement sensors. Our portable data acquisition systems are compact, portable, and fit for many use cases.
For example, the NR-X Series is a multi-input Data Logger that can perform multi-channel measurements using up to 576 channels. It’s portable and can be moved around, with a high-capacity battery for non-stop data collection. The KEYENCE’s NR-500 Series is also a multi-input data logger that can connect directly to a PC for fast and efficient work.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
How DAQ Systems Utilize Acceleration Data
DAQ systems use acceleration data for motion and vibration analysis. With the help of Data Acquisition systems or accelerometers, industries can perform vibration and motion analysis to:
- Reduce vibration of machines for increased lifespan.
- Perform quality control to detect potential issues before products are rolled out.
- Improve safety by exposing potential safety hazards in cars or industrial equipment.
- Prevent equipment failure.
- Reduce costs by reducing downtime and repair costs and extending equipment lifespan.
Applications of Acceleration Measurement
Acceleration measurement is part of manufacturing procedures in different industries, including automotive, aerospace, construction, sport, and transport.
In the automotive industry, for example, acceleration measurement is used to assess vehicle safety and crashworthiness. Accelerometers are also used in transmission testing, brake controls, and engine diagnostics.
In sports equipment, vibration, and motion testing help evaluate theme park rides and other sports equipment for performance and safety.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Data Acquisition for Acceleration Measurement
For acceleration measurement and analysis, there’s a system for collecting and storing data from accelerometers or acceleration sensors. This process includes signal conditioning and data logging and analysis.
Signal conditioning relates to such activities as amplification of signal strength for better accuracy. It also caters to filtering noise and unwanted frequencies. Any analog-to-digital conversion must also be done at this stage of data acquisition.
The data logging and analysis phase involves using DAQ applications or software to collect and store data. The same application or another application is then used to perform analysis to extract meaningful information from the data. Data visualization is the final step. It involves organizing and displaying key performance indicators/metrics (KPI) so that relevant departments can make data-driven decisions.
Common challenges faced in Data Acquisition for acceleration measurement include:
- Noise and interference from electromagnetic, mechanical, and other sources.
- Sensor calibration issues due to human errors or lack of training.
- Data quality problems from corrupt or missing data points.
These challenges can be reduced to a bare minimum with the right acceleration sensors. From the data collection to the data visualization phase, suitable sensor technology can help.
Industrial Use Cases
In the industrial sector, acceleration sensors play a vital role in measuring vibration and shock levels on various types of machinery. This is important because excessive vibration and shock can greatly impact the performance, lifespan, and safety of equipment.
One common use of accelerometers in industry is to monitor machinery such as pumps, motors, and turbines. These machines are subject to constant movement and vibrations during operation, which can lead to wear and tear over time.
Another important use case for acceleration measurement in industry is structural monitoring. Structures such as bridges, buildings, and pipelines are subject to various types of forces, including vibration and shock. Additionally, strain measurement is used for quality control purposes in industrial production processes.
KEYENCE has a line of data logger devices suitable for measuring acceleration, voltage, temperature, and other data types. These devices provide all-in-one solutions, making work fast and easy.
Looking to improve your data acquisition system? Contact us to learn more about our products and how they can benefit your business today!
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us


