Digital Microscopes
Observation of Optical Fibers Using a Digital Microscope
Optical fibers are made from quartz glass and plastic and are mainly used in Internet communication.
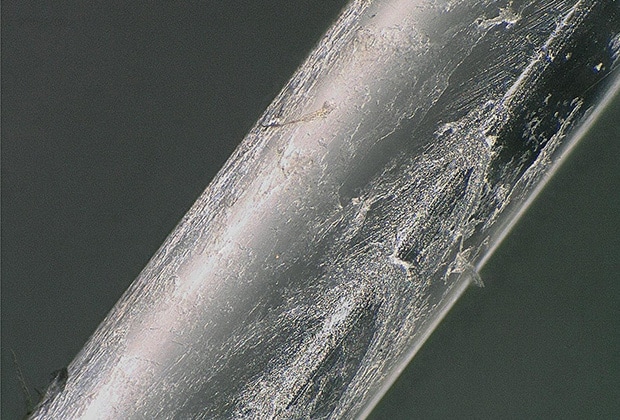

This section provides an overview of optical fibers and introduces examples of their observation using a digital microscope.
Optical Fibers and the Structure of Optical Fiber Cables
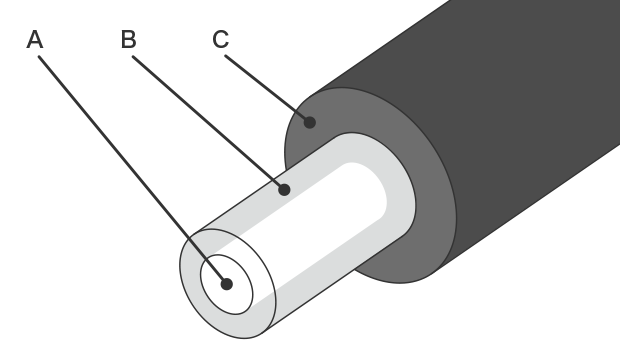
A: Core B: Cladding C: Outer jacket
Optical fiber core wire
The core in the center of the fiber is the transmission path for light. The cladding is a layer of material having a lower refractive index that encloses the core.
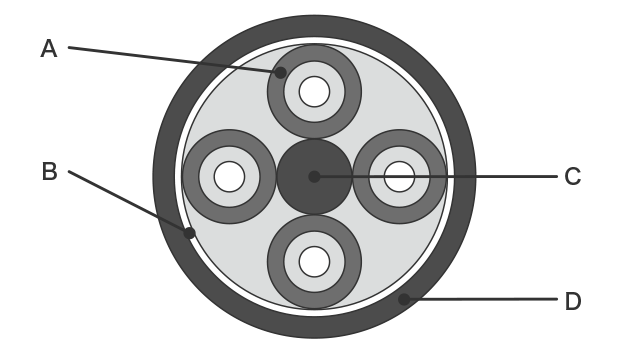
A: Optical fiber core wire B: Press winding C: Tension member D: Outer jacket
Optical fiber cable
The tension member in the center of the cable mitigates tension during installation.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Benefits of Using Optical Fibers
- Faster communication speed and greater communication capacity (1000 Mbps) than the ADSL method (50 Mbps), which uses conventional telephone lines
- Allows for long-distance communication by minimizing transmission loss
- Not electrical communication, so not affected by electromagnetic noise
- Lightweight and compact, with one fiber, including the outer jacket, having an outer diameter of 0.25 mm (0.010")
- Quartz, the fiber raw material, has a longer service life and lower resource consumption than copper
- Explosion-proof, with no chance of short circuit accidents
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Multi-mode Fibers and Single-mode Fibers
There are two types of optical fibers: multi-mode and single-mode.
Single-mode fibers have a core diameter of approximately 10 micrometers and are limited to a single light pulse. Multi-mode fibers are larger with a core diameter of approximately 50 micrometers and can transmit multiple light pulses with different reflection angles.
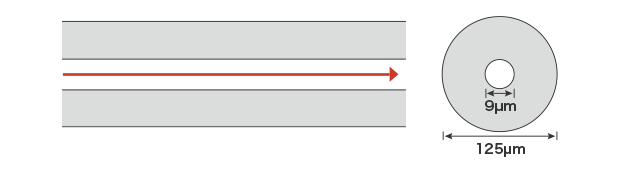
Single-mode fiber
Ideal for mid- to long-range transmission over lengths of a few kilometers or more. This type is used for intra-city, inter-city, and international submarine communication.
Core diameter: 9 μm (0.0003")
Cladding diameter: 125 μm (0.004")
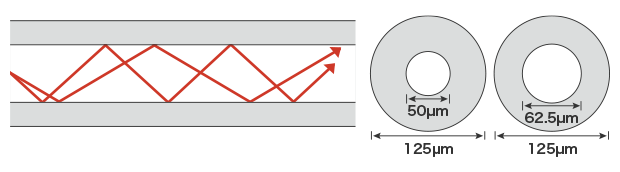
Multi-mode fiber
Ideal for short-range transmission over lengths of a few meters to a few hundred meters. This type is used for wiring within buildings and between devices.
Core diameter: 50 μm (0.001") or 62.5 μm (0.002")
Cladding diameter: 125 μm (0.004")
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Example Observations of Optical Fiber Surface Flaws Using a Digital Microscope
This section introduces the latest examples of observation of optical fiber surface flaws using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K Digital Microscope.

150x, multi-lighting + depth composition

80x, transmitted illumination

1000x, coaxial illumination + depth composition
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog




