Digital Microscopes
Image Capture and Analysis of Offset Printing Using a Digital Microscope
We encounter printing everywhere, on food and medicine packages, books, magazines, and many other items.
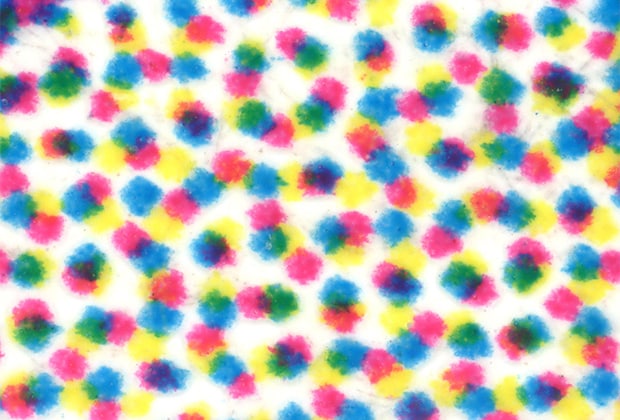
This section introduces examples of image capture and analysis of offset printing using our digital microscope.
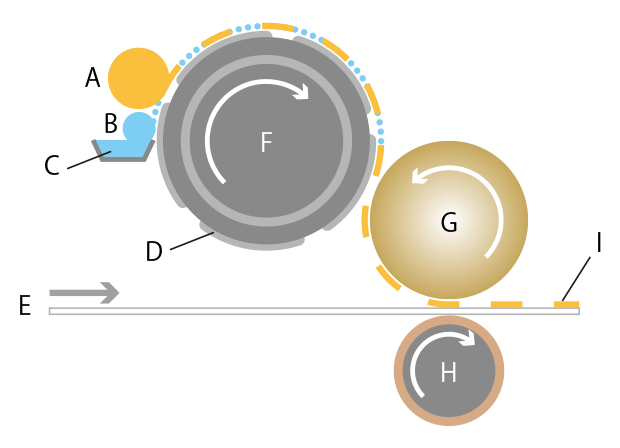
A: Ink roller B: Water roller C: Damping water D: Plate E: Printing paper F: Plate cylinder G: Blanket H: Impression cylinder I: Ink
What Is Offset Printing? (Suitable for High-volume Printing)
Offset printing is a typical planographic printing method.
Planographic printing literally means flat plate printing. In this printing method, areas to hold oil and water are created on a plate using chemicals, and then the water-holding areas are moistened with water. Ink adheres to the oil-holding areas and is repelled from the wet areas.
Ink applied to the flat plate is transferred to a resin or rubber transfer roller called a blanket (off) and the ink is then transferred to printing paper from the blanket (set). This method is called offset printing because there is no direct contact between the plate and printing paper.
In offset printing, the ink is moved off of the plate to a rubber surface and then set to the paper.
Gradation in images, such as for photographs, is expressed with halftone dots, instead of ink gradation. Conversion of data into halftone dots is called screening, and the printing definition is determined by the screening type and the number of lines (the number of halftone dots lines per inch).
Offset printing uses flat plates, which can be created relatively easy. The original plates can also be copied easily and accurately. Printing multiple copies of plates that are arranged side by side saves printing cost and time, which makes this method suitable for high-volume printing. Offset printing is often used for leaflets and similar media.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Examples of Image Capture and Analysis of Offset Printing Using a Digital Microscope
This section introduces the latest examples of image capture and analysis of offset printing using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K digital microscope.
Automatic area measurement of halftone dots
The automatic area measurement function can quantify printing variations.
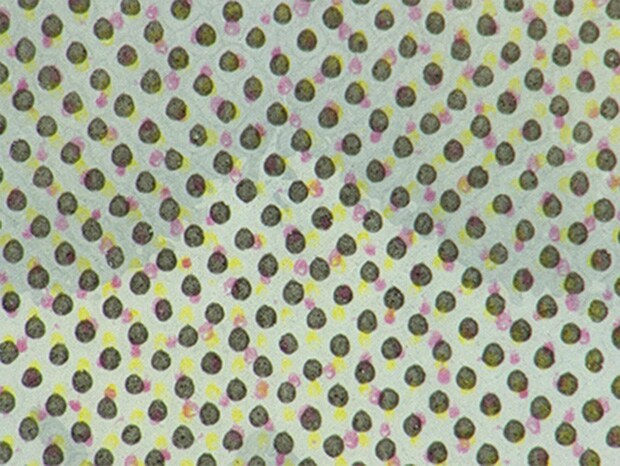
200×, ring illumination, before measurement
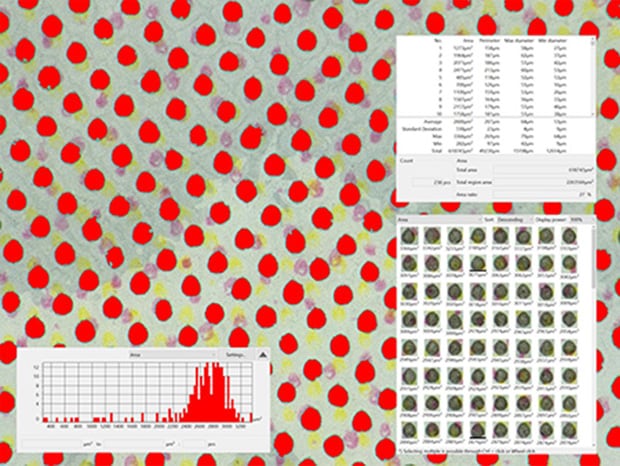
After measurement
Observation of halftone dots
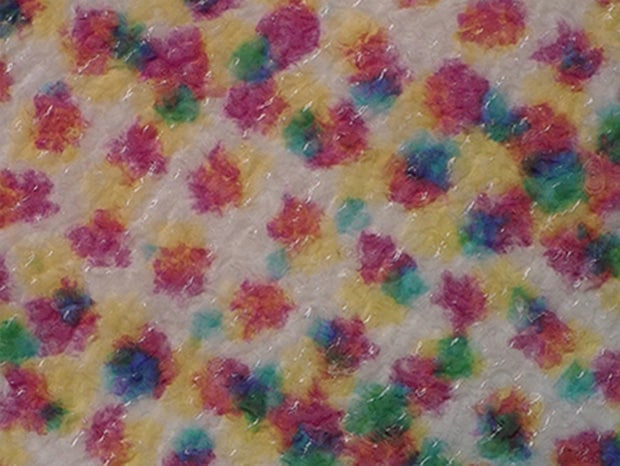

500×, ring illumination, before coating
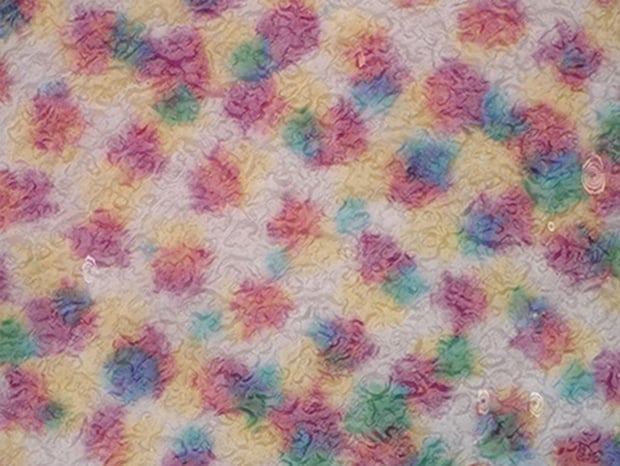

After coating
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog




