Continuous Inkjet Printers / Case Coder
Materials and Products
Production Machines
Printing Applications
A Comprehensive Overview of Continuous Ink Printer Technology
Thanks to their versatility, continuous ink printers have found their ground in the industrial setting, and in this guide, we'll provide you with a comprehensive overview of continuous ink printers. Let's dive right in.
How Do Inkjet Printers Work?
Continuous inkjet printers, abbreviated as CIJs, are industrial inkjet printing machines that work by relying on the continuous flow of ink coming from a pressurized reservoir.
A piezoelectric oscillating element breaks the ink stream up into individual droplets as they are fired through a microscopic nozzle. Droplets are then assigned a charge and then go to an electromagnetic field generated by the deflector plates. The varying charge on the droplets results in different deflections that exit the print head to form the vertical aspect of the printed content. The print head or substrate must then be moving to create the width or X-axis of the print.
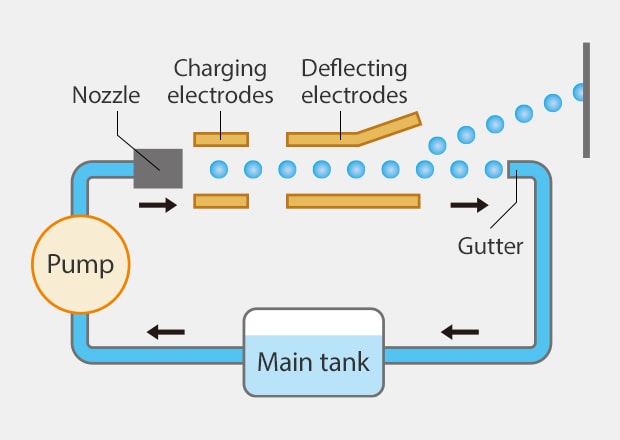
The continuous inkjet technology fires out between 70,000 and 110,000 dots per second, allowing for extremely fast printing speeds. The speeds can be in excess of 470 m/min. But the best part about how continuous ink printers work is that the non-electrically charged ink droplets aren't discarded.
Instead, these droplets are collected and recirculated inside the system, which is then fed through the print head once again—hence the name, continuous inkjet.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Key Features of Continuous Ink Printer
High-speed printing, variable data printing, and wide substrate compatibility are the main key features of continuous ink printers, but they're far from the only notable features.
Here's a more comprehensive list:
High-Speed Printing
Due to the highly pressurized nature of the CIJ system, these printers can print on substrates at a fantastic rate, especially compared to other printers. For example, the maximum printing speed of an industrial thermal inkjet printer is around 100 meters 381′ per minute.
CIJ printers, on the other hand, can exceed 470 m 1542′ , and their average print speed is approximately 300 meters 1143′ per minute. This makes continuous ink printers perfect for high-output manufacturing operations, such as food packaging.

Vertical form-filled packaging machine

Line conveyor

Extrusion molding machine
Variable Data Printing
Continuous ink printers excel at handling variable data printing, and they are able to update serial numbers, date codes, and other info on the fly at high speeds.
Resolution and Print Quality
Continuous ink printers are capable of the continuous printing of small but quality prints composed of between one to six lines of text, 1D and 2D barcodes, and simple logos. CIJ is limited in resolution overall, but as mentioned, it more than makes up for it with speed. This is why it is perfect for food, beverage, and other industries that require a quick expiration date or lot code.

5-12 dots

14-32 dots

Four-line printing
Logotypes
Unique-character languages

Barcode

2D codes
Wide Substrate Compatibility
One of the key features of industrial continuous ink printers is maintaining resolution and print quality across various substrates. CIJ printers are capable of printing on metal, plastics, glass, paper, and a variety of different materials. This is due to the nature of the industrial inks and solvents used. The quick-drying capability of these solvents allows for rapid and durable adhesion to most surfaces.

Cans

Packaging film

Cartons
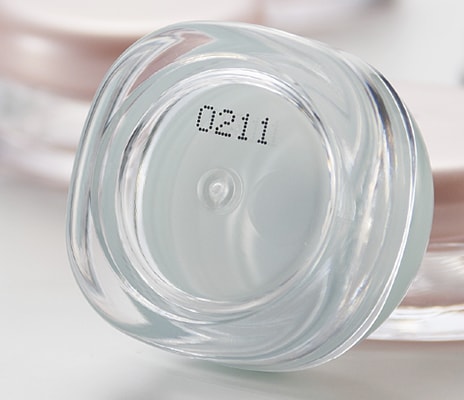

Glass containers
Maintenance
As stated above, the ink/solvents are quick drying, and this can cause clogging and other issues throughout the internal pathways and print head of continuous inkjet printers. Traditionally, this results in frequent cleaning and maintenance needed to be done by a skilled maintenance technician. In many cases, a service contract or visit is required to fix and maintain these systems.
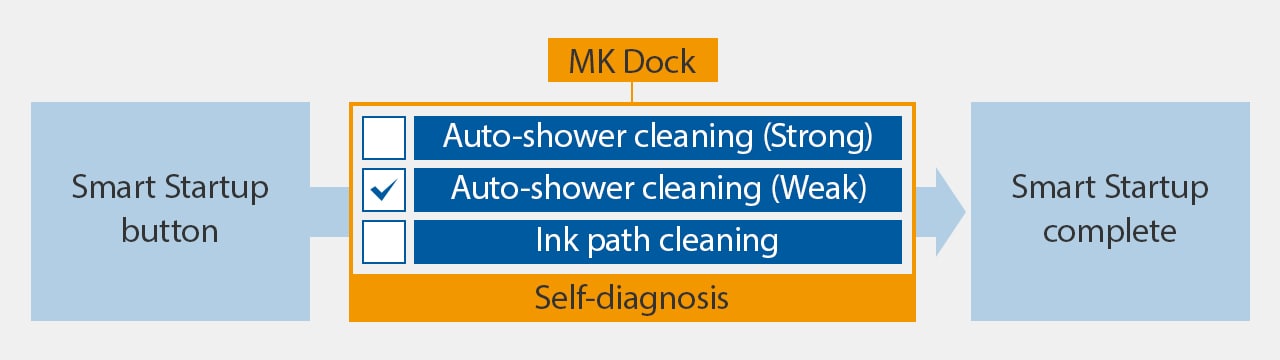
KEYENCE recognized these issues and designed a continuous inkjet system that resists clogging, needs less cleaning, and can be maintained by anyone. This eliminates expensive service costs and downtime and frees up skilled employees to focus on other critical manufacturing requirements.
Conventional
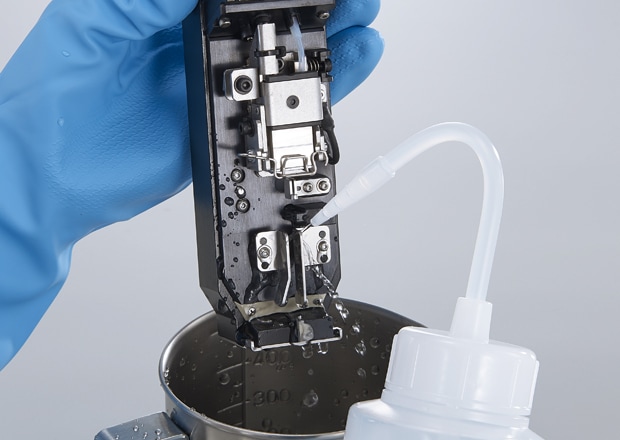

Manual cleaning
MK-G Series
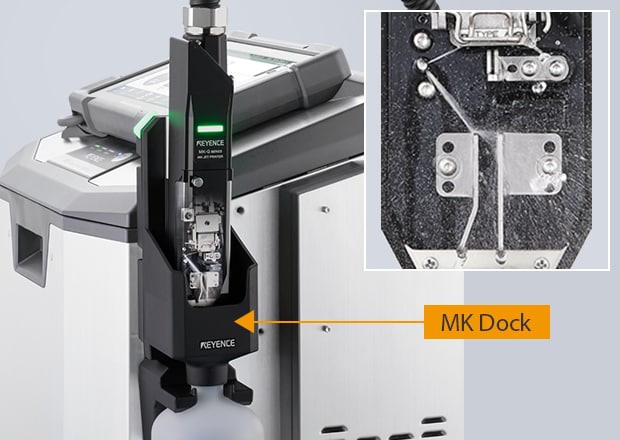

The printer conducts self-diagnosis and optimal cleaning automatically
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Types of Inks Used in Continuous Ink Printer
An appropriate ink selection is very important for each particular application. Without proper ink selection, the printer might not be able to provide the contrast or adhesion needed.
Thus, selecting the proper ink is crucial. However, not all inks are made equal. Industrial continuous ink printers typically use MEK (methyl ethyl ketone)-based ink due to its excellent adhesion to the substrate and fast drying times—typically under one second. Other applications might demand a different ink type:
Black Inks
There are a few options when it comes to black ink, and the most common is the standard MEK-based ink. This ink composition is extremely versatile and can cover a wide variety of applications and substrates. For those customers who want to avoid MEK, an MEK Free ink uses an ethanol base instead. Last, strong adhesive ink is offered for specialty substrates that struggle with adhesion. This is often useful for smooth and non-porous plastics.
Conventional Ink
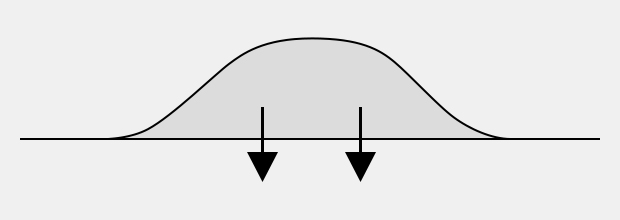
Weak adhesion
Super-adhesive Ink
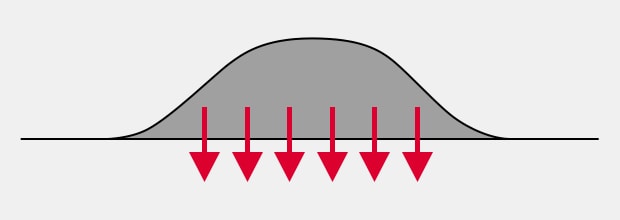
Strong adhesion
Reliable adhesion on bottles or film
The super-adhesive ink eliminates worries even for targets that exhibit low ink adhesion.

Standard ink

Strong adhensive ink
Pigment Inks
Generally still MEK-based, but for customers looking to print on dark substrates with contrast. White or Yellow pigment allows for easy-to-read codes on black plastic, rubber, amber bottles, and many more. The pigment ink uses solids like titanium dioxide and tends to require specialized pumps and filtration. This is because the larger solid pigment is more prone to precipitating than dye. Yellow ink is a great option when customers have a mixture of black and white parts. Yellow pigment provides surprisingly good contrast on white.



Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
FAQs About How Continuous Ink Printers Work
What Is Continuous Ink Printer Technology?
Continuous inkjet printer technology relies on the continuous ink flow throughout the industrial printer's system, which has immense benefits when it comes to print speed and adhesion.
How Does a Continuous Inkjet Printer Work?
The printer uses an electromagnetic field to direct ink droplets for printing, while the unused ink is recycled back into the system for further use.
What Are the Advantages of a Continuous Ink Printer?
As stated above, the advantages of continuous ink printers are print speed, precision, print quality, and sheer versatility, making them suitable for a variety of applications within different industries.
Related Downloads
![Inkjet Printer Tech Guide [BASIC KNOWLEDGE EDITION]](/img/asset/AS_114378_L.jpg)
Continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers work by discharging ink particles to print information such as characters and figures on targets. This document describes the differences between industrial use inkjet printers and office-use printers, as well as their structures, circulation principles, and application examples.

This is a technical guide describing basic knowledge of continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers from mechanisms such as the types, printing fundamentals, and internal structure, to running costs and legal compliance. Subsequent issues will also be available. By reading all of these issues, you can understand the entire overview of continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers.
Related Products
Applications
Materials and Products
- Glass Bottles
- Plastic Bottles/Containers
- Cans
- Wires, Cables, & Pipes
- Pouches
- Metal Parts
- Corrugate Boxes
- Packaging Film
- Kraft Packaging
- Folding Cartons
- Building Materials
- PCBs
- Cartons
- Pallets & Lumber
- Corrugate Trays
Production Machines
- Paper Bag Packaging
- Box Conveyor
- Automatic Palletizer
- Sealer/Taping Machine
- Bottle Filling Machine
- Flow Wrapper




