Digital Microscopes
Observation and Measurement of Hollow Fibers Using Digital Microscopes
A hollow fiber is a processed fiber with a hollow space. Due to the hollow space, hollow fibers are light and flexible and characterized by high heat retaining properties, water absorption properties, and quick-drying properties. Hollow fibers are used not only for apparel products but also a wide range of filtration equipment. This section introduces observation and measurement of hollow fibers using digital microscopes.
What is a Hollow Fiber Membrane Filter?
A hollow fiber membrane filter is made of hollow fiber membranes, which take the shape of a hollow cylinder, produced by jetting melted raw materials from a nozzle. Hollow fiber membrane walls have countless numbers of micropores.
Different components and foreign particles can be separated and extracted by adjusting the diameter of these pores.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Use of Hollow Fiber Membrane Filters for Household Water Purifiers
Water purifiers commonly used activated carbon until the first half of the 1980s. Since then, use of filters that combine activated carbon and hollow fiber membranes has spread. Hollow fiber membranes are thin straw-like fibers made from artificial polymers, such as polysulfone, polyethylene, or polypropylene, that are bundled to form a filter. Membrane walls have micropores that absorb impure substance particles.
Activated carbon absorbs residual chlorine, chlorine odor, mold odor, trihalomethanes, agricultural chemicals, and other unwanted substances, and hollow fiber membranes eliminate iron rust, bacteria, turbidity, and other unwanted substances.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Medical Use of Hollow Fiber Membrane Filters
Hollow fiber membrane filters are also used for various applications in the medical field.
Major application examples
Artificial kidney (dialyzer)
Hollow fibers in artificial kidneys used for artificial dialysis have pores with a diameter of approximately five nanometers. As red blood cells, white blood cells, and many plasma proteins are larger than the pore diameter, only excess water and uremic substances (waste products) exit from hollow fibers.
Plasma separator
Pores with a diameter of approximately 300 nanometers can separate blood cell components, such as red blood cells and platelets, from plasma components containing proteins.
Plasma component separator
Plasma component separators incorporate hollow fibers with pore diameters controlled to specific sizes, such as approximately 10 nanometers, 20 nanometers, or 30 nanometers.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Observation and Measurement Examples of Hollow Fibers Using Digital Microscopes
These are the latest examples of observation and measurement of hollow fibers using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K Digital Microscope.
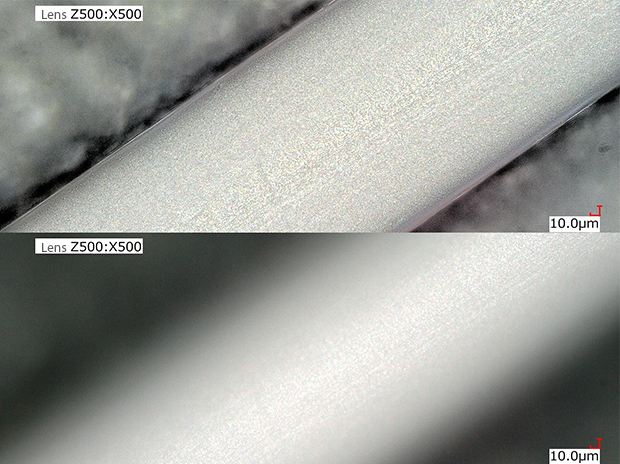
Surface observation of an artificial kidney hollow fiber
Using the HDR with depth composition allows for defect analysis without using a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
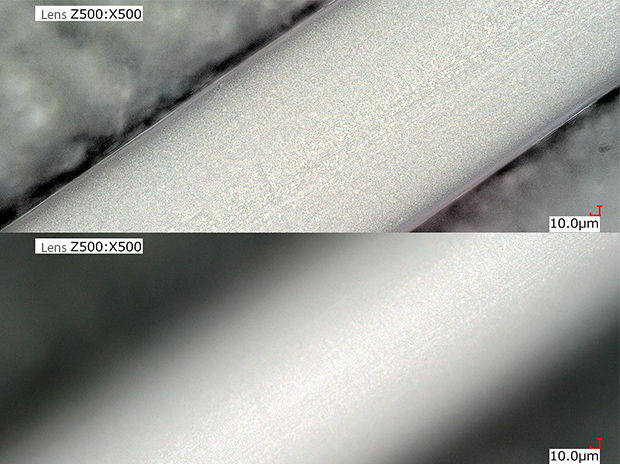
VH-Z500, 500×, coaxial illumination + HDR
Upper : Depth composition Lower : Normal image
Automatic area measurement image of a hollow fiber cross-section
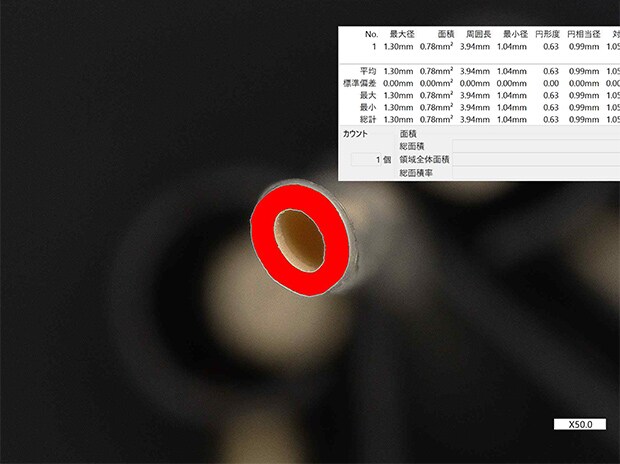
VH-Z20, 50×, ring illumination
Automatic area measurement image of a hollow fiber cross-section
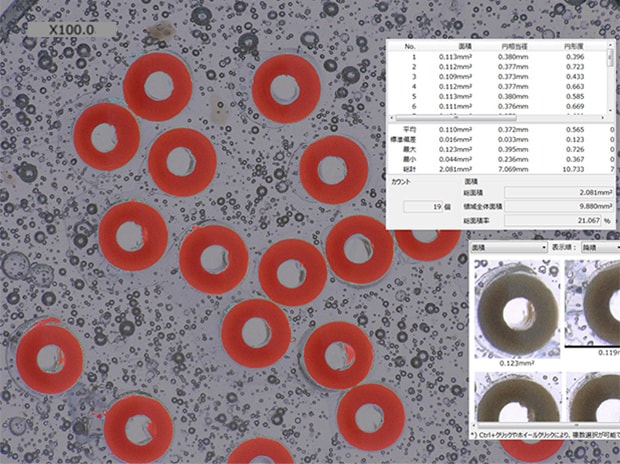
VH-Z20, 100×, ring illumination
Automatic area measurement of an artificial kidney
Cross-section measurements that used to be done manually can now be automated.
The HDR function can accurately count the number of fibers and evaluate the inner and outer diameters.
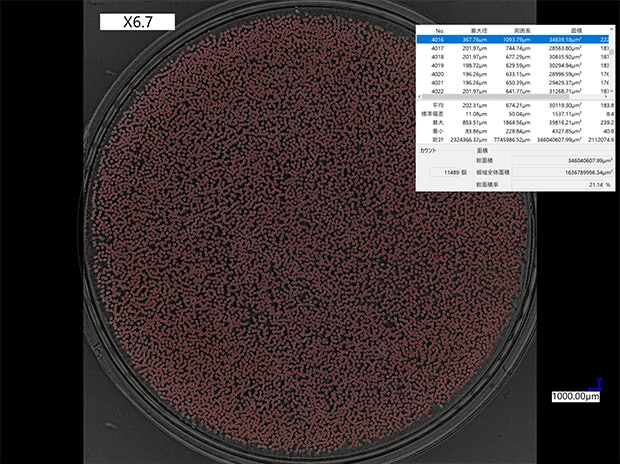
VHX-Z20, 20×, ring illumination + HDR
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog




