RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA helps you turn tedious, complex processes into effortless automated workflows—freeing your team to focus on high-value work instead of repetitive tasks. With a true no-code platform, anyone can design and launch automation without needing IT expertise.
Product Lineup
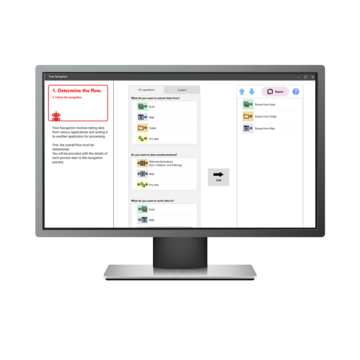
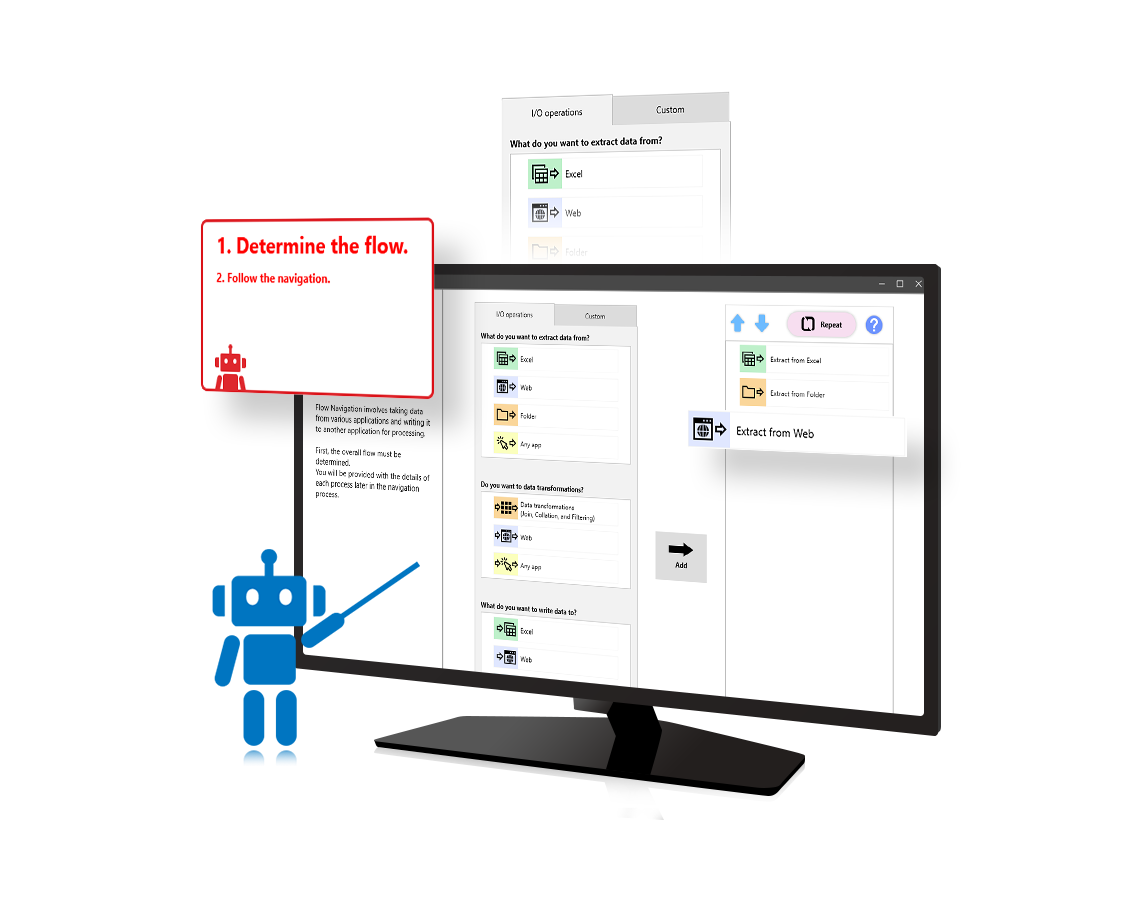
The RK Series RPA software makes automation accessible to anyone—no technical skills or programming experience required. It is equipped with Flow Navigation which allows users to simply follow guided prompts to build and run your automation scenarios with ease. RK handles a wide range of tasks, from data entry, reporting, and invoice processing to email management and digital file organization. By minimizing human error, reducing reliance on specific staff, and driving greater operational efficiency, RK empowers your team to work smarter, faster, and more consistently—every day of the year.
Features
KEYENCE’s RPA Solution
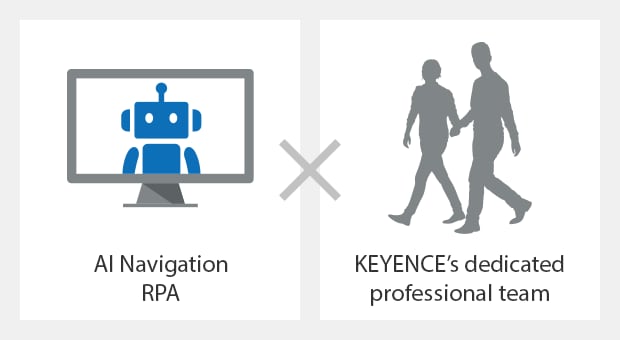
Multi-Faceted Approach to Drive Successful RPA Implementation
Navigation + People + AI
Navigation Support
Intuitive tools make automation setup quick and effortless.
Personal Support

KEYENCE’s dedicated staff provides support specifically tailored to each situation.
AI Support

AI simplifies scenario creation and enhances efficiency.
Unique Advantages of AI Navigation RPA Navigation Guided Scenario Creation for Quick and Easy Task Automation, Backed by Dedicated Support Staff for Peace of Mind
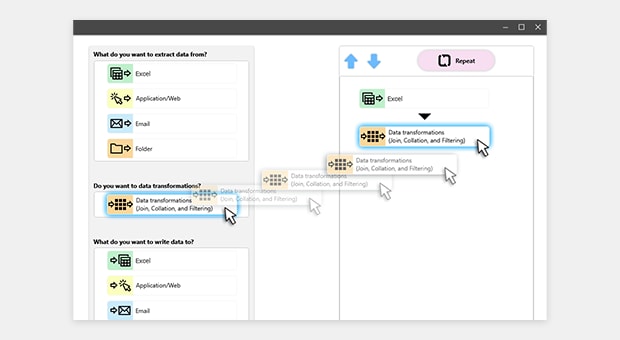
- Flow navigation: Easy-to-follow navigation for first-time users
- Smart process recording: Record on-screen operations for automatic scenario creation
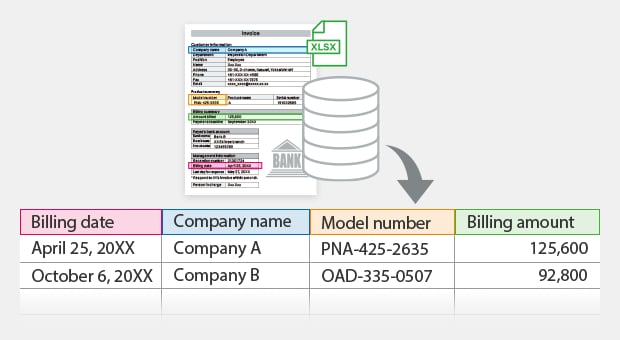
- Key database: Easily extract unstructured data
- Free premium support: Comprehensive support from dedicated KEYENCE staff
Easy-to-follow navigation for first-time users
Record on-screen operations for automatic scenario creation
Easily extract unstructured data
Comprehensive support from dedicated KEYENCE staff
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a software technology that enables businesses to automate routine, repetitive tasks. It uses virtual "robots" to mimic human actions within digital systems, such as interacting with user interfaces, reading emails, entering data, and completing various other workflows. By automating these processes, businesses can achieve significant efficiency gains, eliminate human errors, and reduce operational costs.
Why RPA Matters
RPA is reshaping industries by reducing the burden of manual tasks and allowing employees to focus on higher-value work. In an increasingly digital world, the speed at which tasks are performed and the precision with which they are completed can make the difference between success and failure. From the finance sector to healthcare, RPA is driving transformation across the globe.
Is RPA the Same as AI?
Not exactly. RPA follows predefined rules, set by you, to automate repetitive tasks, while AI learns from data to handle more complex decisions. Both have value, and with KEYENCE you don’t have to choose—we offer automation with and without AI, so you can use what fits your needs best.
RPA is designed to automate simple to complex business processes without altering existing IT systems. The core idea is that robots act as digital workers, interacting with business applications just like humans do.
Key Components of RPA
Scenarios
Workflows and processes that are automated utilizing virtual robots that execute predefined tasks across applications.
RPA Software
Platforms that manage and deploy virtual robots to perform automated workflows.
Orchestration
A central hub that monitors, schedules, and manages scenarios to ensure they are working in sync.
RPA software can operate on multiple systems simultaneously, without the need for any changes in backend systems, making it a non-invasive way to automate operations.
Benefits of RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA allows businesses to automate processes that previously required significant manual input. Bots can work continuously without downtime, handling high volumes of tasks at a much faster pace. This increased efficiency directly impacts productivity and resource utilization.
Human error is inevitable, especially with repetitive tasks. RPA eliminates these errors by following predefined rules and ensuring consistency throughout. The increased accuracy means fewer mistakes, less rework, and higher quality outcomes.
RPA helps businesses stay compliant with industry regulations by ensuring that tasks are performed according to standard operating procedures. Automated workflows can be tracked, and reports can be generated to demonstrate adherence to regulations.
As demand for services grows, RPA can quickly scale to handle additional tasks without requiring additional human resources. This means that businesses can handle increased workloads without significant changes to their existing workforce.
RPA Case Studies
Finance & Accounting
RPA can be used to automate manual tasks such as invoicing, reconciliation, tax calculations, and financial reporting. For instance, data can be extracted from invoices, matched with purchase orders, and posted into accounting systems, saving hours of manual data entry.
Retail
RPA can streamline order processing by automating order validation, inventory management, and shipment tracking. This reduces human error and ensures a seamless customer experience, enabling faster order fulfillment.
Manufacturing
RPA can automate supply chain management, production scheduling, inventory checks, and order processing.
Healthcare
In healthcare, RPA can automate patient data entry, claims processing, and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations. For example, patient data can be extracted from multiple sources and then used to populate electronic health records (EHR) systems to reduce administrative workloads for medical staff.
Human Resources
HR departments can use RPA to automate employee onboarding, payroll processing, and benefits management. Validating employee timesheets, generating pay slips, and ensuring payroll calculations are accurate can all be automated.
Operations
Operations teams can automate workflow management, document routing, and email responses. RPA helps businesses streamline day-to-day operations, improve service delivery, and reduce bottlenecks in production.
Customer Service
RPA can be applied to customer service tasks such as automating ticket routing, handling simple queries through chatbots, and processing customer requests. This not only speeds up response times but also allows human agents to focus on more complex issues.
IT Support
RPA can automate routine IT tasks such as system monitoring, software updates, and troubleshooting. For example, bots can automatically handle routine checks and notify IT teams about system downtimes, reducing response time and minimizing errors.

We asked our customers who have installed RK how they have used the product and what makes it so appealing.
Steps to Implement RPA
1. Identify Repetitive Tasks
Begin by analyzing business processes to identify high-volume, rule-based tasks that are good candidates for automation.
2. Choose RPA Software
Evaluate different RPA tools and select the one that aligns with your company's needs, whether you need low-code platforms or more advanced, customizable solutions.
3. Deploy and Monitor
Once tested, deploy RPA scenarios and continuously monitor their performance. Built-in alerts can be programmed to notify users when a scenario fails to complete.
Considerations Before Implementing RPA
Process Readiness
Well-documented processes with minimal exceptions are ideal for RPA. Preparing processes for automation is crucial for success.
Employee Training
Employees should be trained to work alongside automated workflows and understand how RPA complements their work.
System Integration
Ensure that RPA tools integrate seamlessly with existing systems to avoid disruptions and leverage existing IT infrastructure.
Invoice Processing
Automating invoice data extraction, approval workflows, and payment posting. RPA ensures faster payment cycles and improved vendor relationships.
Data Entry and Migration
Bots can handle large-scale data entry from spreadsheets, emails, and documents, ensuring faster, error-free migration between systems.
Employee Timesheets and Payroll Automation
RPA automates timecard validation, payroll processing, and reporting, reducing the risk of errors and improving employee satisfaction.
Document Management
Automate document filing, classification, and storage to maintain an organized and easily accessible record system.
Order Fulfillment
RPA improves order processing by automating data entry, inventory checks, and shipment tracking, ensuring faster and more accurate fulfillment.
Scenario
A series of automated steps performed by virtual robots to complete a task.
Orchestration
The coordination and management of multiple scenarios working together to complete a complex task.
Automation
The use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention.
Ready to transform your business with RPA?
• Book a Demo and see how RPA can be implemented in your business.
• Explore Solutions by Industry to discover how RPA can streamline processes in your specific industry.
• Explore Solutions by Department to see how RPA can assist in your role.
Frequently Asked Questions About RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA is a software technology that automates routine, repetitive tasks using software robots, improving efficiency and reducing human errors.
RPA can integrate seamlessly with existing IT systems and applications without requiring significant changes to infrastructure. RPA works with existing software and tools to execute tasks across platforms.
Yes! RPA is scalable and can benefit small businesses by automating common administrative tasks, allowing them to operate more efficiently and cost-effectively.
RPA is designed to be easy to implement, especially with no-code platforms. Many businesses can automate tasks quickly and see a return on investment within months.
Virtually every industry, from finance to retail to healthcare, can benefit from RPA by automating routine tasks and improving overall operational efficiency.
No. RPA automates tasks using rules that are set by the user, while AI adds learning and decision-making. KEYENCE provides both options so you can automate your way.