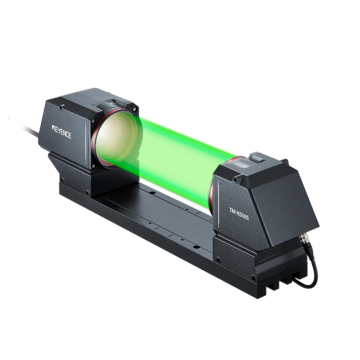
Measurement Sensors
Dimension Measurement
Displacement Measurement
How to Choose a Laser Micrometer

Choosing the right laser micrometer can make or break your daily operations, as it significantly impacts the accuracy and efficiency of your measurement tasks regardless of industrial applications. These highly advanced instruments are used for non-contact dimension measurements — such as diameter, thickness, and position — with precision in the single-digit µm (micrometer) range.
However, with various models and their respective features on the market, selecting an adequate model isn't as easy as it might seem. It can be outright challenging to find a device that suits your needs.
So, in this guide to choosing a laser micrometer, we'll discuss what key features to look for, what the different types there are, what their applications are in different industries, and how to choose the laser micrometer for you.
Key Features to Look for in a Laser Micrometer
Choosing the right laser micrometer starts with clearly defining your application's physical setup.
Physical setup is important because laser micrometers vary in accuracy depending on the measurement distance. Longer measurement distances = less accurate results. You'll also want to look at the measurement window to ensure what you're trying to measure will fit.
Next, you need to determine your accuracy requirements.
Laser micrometers are accurate to single-digit microns. For applications that require sub-micron results, laser microscopes might be a better fit.
The speed of measurement is also very important, especially in fast-paced, high-throughput applications. Fortunately, many modern laser micrometers can perform thousands of measurements per second, which makes them ideal for high-throughput applications.
Integrability is also a key consideration, as it dictates how easily a micrometer integrates with your existing system. So, look for models with user-friendly interfaces, intuitive accompanying software, and compatibility with common industrial communication protocols used for data transmission.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Types of Laser Micrometers: Which One Is Right for You?
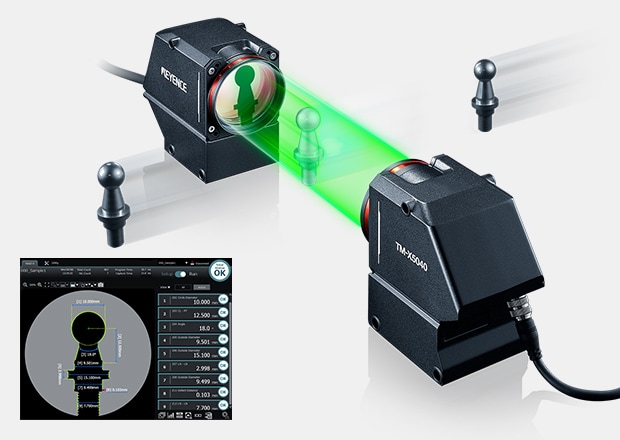

KEYENCE TM-X5000 Series
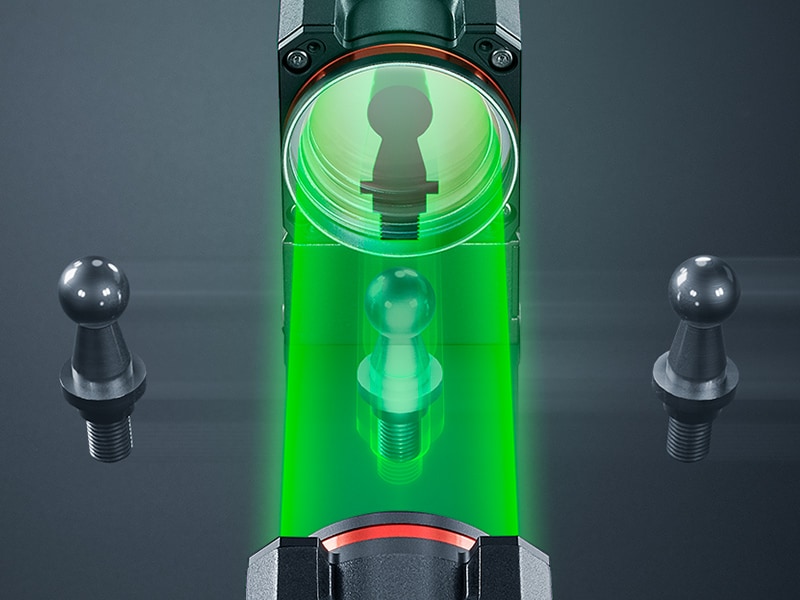
All laser micrometers use the same measurement principle. They emit light from a source (transmitter) and direct it towards a light-receiving element (receiver). When an object is placed between the transmitter and receiver, it casts a shadow onto the receiver.
However, not all laser micrometers are the same. There are significantly different types and models available, with each being better suited for different applications and measurement requirements.
For example, KEYENCE's TM-X5000 Series is a type of measurement system that provides 2D measurements by capturing the silhouette of a target, enabling accurate measurements anywhere in the field of view. This effectively eliminates the need for precise target placement, external lighting sources, and even on-site calibration.
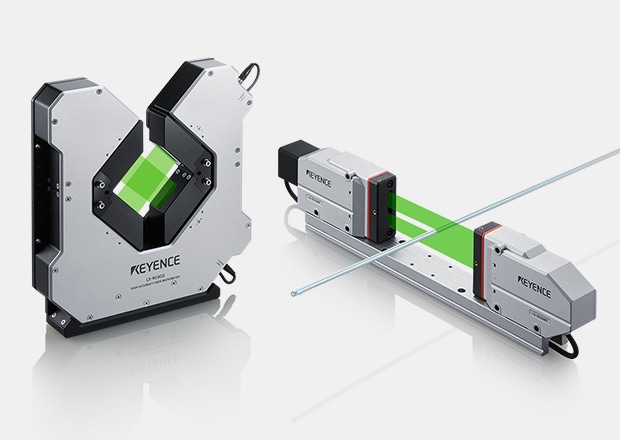

KEYENCE LS-9000 Series
The LS-9000 Series, on the other hand, is a 1D micrometer with highly durable construction and repeatability of ±0.03 µm. It boasts an impressive sampling speed of 16,000 samples per second, which is more than enough to capture fast-moving targets in great detail, regardless of the target material. It's IP67-rated, which means it can be used in a variety of locations and environments.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Cost Considerations When Choosing a Laser Micrometer
The cost of a laser micrometer varies significantly depending on the features and precision a particular model offers. It's important to strike a balance between the initial investment, long-term benefits, and potemtial cost savings of using a more economical model.
Naturally, high-precision laser micrometers with advanced features have a higher price tag, but they make up for it with greater accuracy and reliability. In addition to the initial purchase cost, you should consider the cost of ownership (such as calibrations and maintenance) since these expenses can rack up over time.
Applications and Uses of Laser Micrometers in the Industry
Thanks to their precision, reliability, and versatility, laser micrometers are used in a wide range of industries. They're used in the semiconductor and electronics industries, where dimensions often scale from mere millimeters to nanometers for measuring the thickness of silicon wafers, chip features, and spacing between circuitry.
Automotive
The automotive industry also relies on optical and laser micrometers for quality control and the precise measurements of components such as shafts, valves, and engine pistons. These non-contact measurement devices ensure that the parts and components meet strict specifications and dimensional tolerances—which often measure in the µm range.
Aerospace
Laser micrometers are used in the aerospace industry to measure aircraft parts and components. Precision is paramount, so parts must be manufactured within strict dimensional tolerances and fit together perfectly.
Medical Equipment
The production of medical equipment requires strict adherence to dimensional specifications and a whole range of safety standards, underscoring the importance of non-contact measurement as a means of avoiding equipment contamination. Laser micrometers are used to measure small and precise components that are used in medical implants and instruments.
Precision Engineering and Manufacturing
Precision engineering and manufacturing requires the fabrication of parts with incredibly tight tolerances. This industry uses laser micrometers in a wide range of applications, such as specialized machinery, electronics, and even crafting musical instruments.
Why Choose KEYENCE?
KEYENCE is the world's leading provider of cutting-edge precision technologies and measurement sensors, which are often used by numerous industries for industry-specific applications. These include manufacturing, medical, food and beverage, and cosmetic industries, as well as semiconductor, aerospace, and industrial process control industries.
If you're looking to enhance your manufacturing, quality assurance, and quality control capabilities or need advice on how to choose a laser micrometer, don't hesitate to contact KEYENCE and inquire about the possible integrations of our equipment with your existing production lines.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
FAQs
How Do I Choose a Micrometer?
Choosing a micrometer will depend on the specific needs of your industry and application. Some important factors to consider include accuracy requirements, measurement range, environmental conditions, and the type of material being measured.
How Do You Determine the Accuracy of a Micrometer?
The accuracy of a micrometer is determined by comparing its measurement results to a known standard or reference. This can be done through calibration or by using a traceable measuring standard.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads
Related Products
Applications
Dimension Measurement
- Thickness and Width Measurement
- Step Height Measurement
- Inner and Outer Diameter Measurement
- Measuring Angles
- Meandering/Edge Measurement
Displacement Measurement
- Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
- Vibration and Runout Measurement
- Deflection Measurement
- Measuring Eccentricity