Measurement Sensors
Dimension Measurement
Displacement Measurement
Measurement Sensors for the Fiber and Cable
KEYENCE provides the fiber and cable industry with measurement and inspection sensors that deliver the speed and reliability required to meet customer demands. Check out some of the application examples below.
Fiber optic cables enable some of the fastest communication available, and much of that efficiency and transfer speed comes from the cable’s quality. To maintain product quality, the fiber optic cable industry heavily relies on measurement sensors to maintain material purity and fiber geometry, among other things.
Choose Case of Measurement Sensors for the Fiber and Cable
Importance of Precision Measurements in the Fiber Optic/Cable Industry
Precision measurements in the fiber optic cable industry ensure that final products can perform high-speed data transmissions and maintain reliable connectivity. The slightest imperfections in a cable’s core surface or a variation in its diameter, concentricity, or refractive index (the amount of light passing through) could severely impact the signal transmission quality.
Measurement sensors allow the fiber optic cable industry to maintain strict quality control, resulting in higher-quality products complemented by reduced manufacturing costs.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

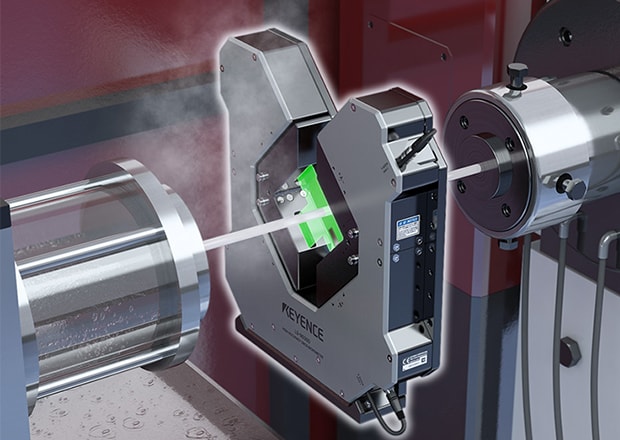
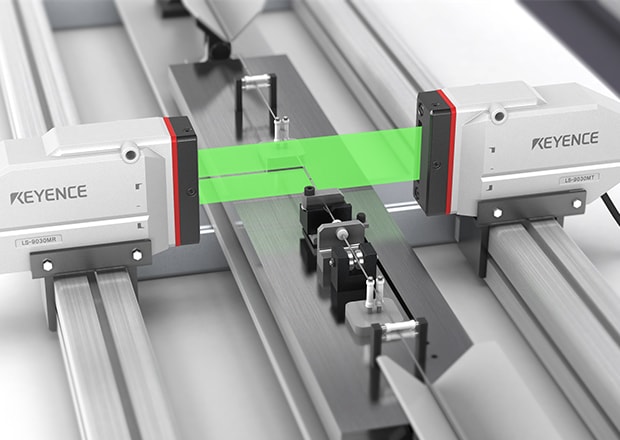
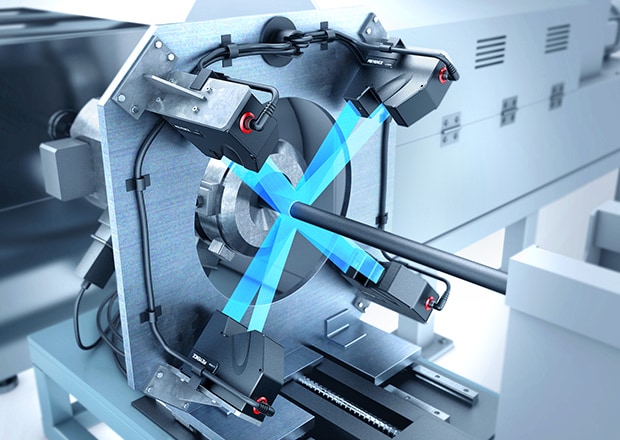
Outer Diameter Measurement in Harsh Environment
It's possible to stably measure outer diameter in harsh environments using the LS-9000 Series. The built in air purge filters and IP67 rating make it ideal for withstanding dusty environments.
Ultra-Fine Wire Diameter Measurement
Measure diameter of wires as small as ø10 µm. The optical design of the LS-9000 Series enables measurement of ultrafine diameters and gaps, or measuring multiple wires within the window simultaneously.
Flat Wire Width
Detect defects in flat wire by monitoring width. Even small edge breaks can be detected thanks to the high speed sampling of the LS-9000 Series.
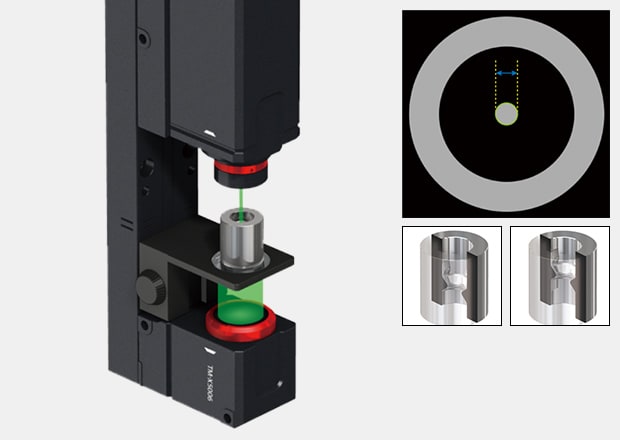
Die Inner Diameter Measurement
Check the internal diameter of wire drawing dies after re-grinding.
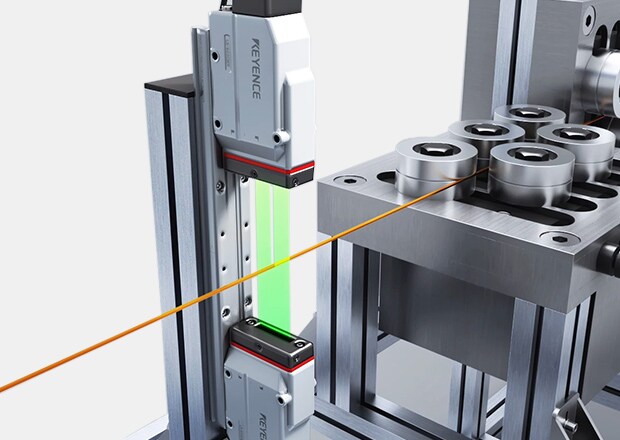
Measurement During Tensile Testing
Measure width/diameter during tensile testing. Inspect up to 100 areas at once, then record or output the data for analysis.
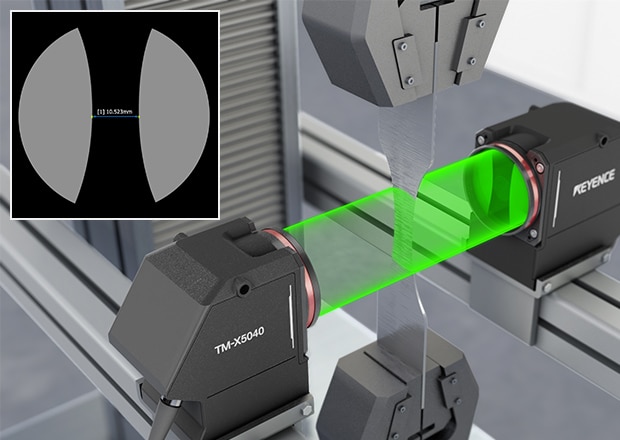
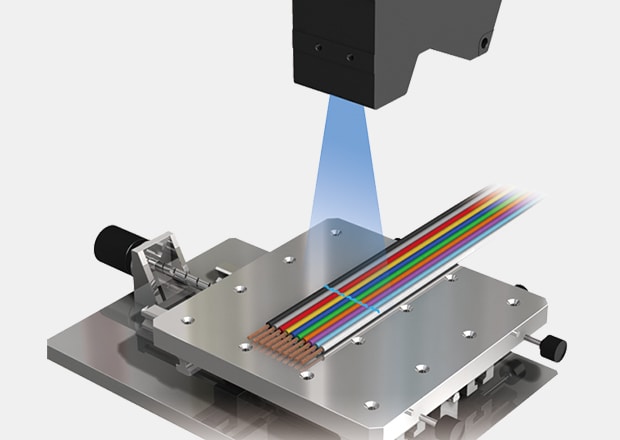
Flat Cable Shape Inspection
Laser profilers make it possible to inspect the width and shape of flat cable. Check for conductor position and width on cables of any color or material.
Uneven Cable Coating Detection
Profiling the outer diameter of a coated cable enables detection of dents or unevenness that would be impossible to catch using a thrubeam sensor.
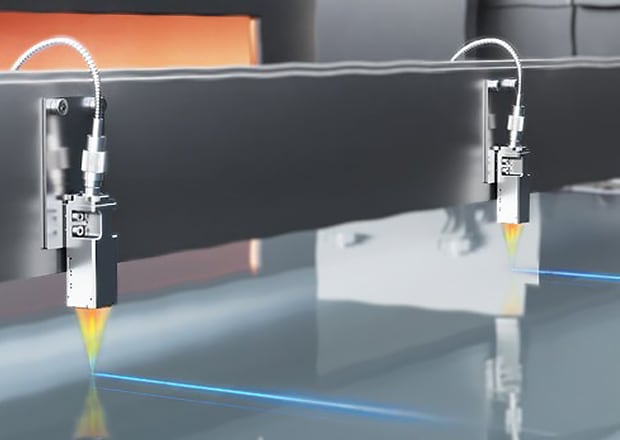
Glass Thickness Measurement in High-Temperature Environments
The CL-V020/V050 can handle ambient temperatures of up to 200°C (392°F), allowing for use in environments with drastic temperature fluctuations.
Fiber Optic Cable Inspection
The fiber optic cable industry relies heavily on measurement sensors to inspect and maintain the various properties of its products within acceptable tolerances. This is particularly true when it comes to the diameter of the fiber optic cable core, which must stay within a tight tolerance to avoid signal degradation.
KEYENCE’s LS-9000 Series of thrubeam sensors and laser micrometers do just that. These sensors project a beam of light from an emitter onto an object, whose shadow is transmitted onto a photosensitive light receiver. The diameter of the core is derived from measuring the projected shadow.
Furthermore, the LK-G5000 Series is a highly accurate laser displacement sensor with a max sampling speed of 392kHz. This, paired with µm range accuracy, allows the sensor to detect small changes in fast-moving objects. It also makes it ideal for quality control of the fiber optic cable’s coating, which can affect signal quality when light escapes from the cable.
These, and many other sensors produced by KEYENCE, can be connected to data loggers and data storage systems for processing, storage, and further analysis. Such data plays well into predictive maintenance and other practices that lead to significantly reduced downtime and the associated financial loss.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Cable and Wire Inspection
Fiber optic cable systems consist of several different components. The core, cladding, and the coating are particularly checked for inconsistencies in their diameter, as flaws can affect the performance of the cable.
The uniformity of strengthening fibers, as well as the cable jacket, aren’t controlled as strictly and don't affect the performance of the cable as long as they are within tolerance. However, optimizing the production of all parts of the cable considerably reduces costs associated with production.
Applications and Examples
Integrating Measurement Sensors into Fiber Optic/Cable Inspection Processes
Integrating precision measurement sensors in the fiber optic cable industry can significantly optimize the production process and increase the overall quality of the end product. Of course, these sensors are easily integrated into pre-existing industrial automation, ensuring consistency and efficiency—not just in the actual output of the product but also in data collection, processing, and analysis.
If you want to learn more about the aforementioned products and how to implement and integrate them into your existing industrial automation, don’t hesitate to contact KEYENCE for advice.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Related Downloads

Telecentric measurement systems and thrubeam optical micrometers—which can continuously measure the total length of targets—see heavy use at worksites where cables, fibers, and other long targets are handled. If you work with targets like this, you won’t want to miss the detailed usage examples in this booklet.
Applications
Dimension Measurement
- Thickness and Width Measurement
- Step Height Measurement
- Inner and Outer Diameter Measurement
- Measuring Angles
- Meandering/Edge Measurement
Displacement Measurement
- Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
- Vibration and Runout Measurement
- Deflection Measurement
- Measuring Eccentricity