Measurement Sensors
Dimension Measurement
Displacement Measurement
Finding the Right 3D Scanning Solution for Your Business
3D scanning solutions used to only be available to giant manufacturers and massive corporations. As 3D technology continues to advance and improve, it is becoming available to businesses of all sizes.
3D laser snapshot sensors capture complex 3D geometries with high speed and precision. However, it's essential to understand how the technology works in order to select the best 3D scanning solution for your processes.
The increasing popularity of 3D scanners can be attributed to their ability to scan surfaces using nothing but light. They can create accurate profiles of objects while eliminating the need for manual measurements.
In this guide, we'll discuss what 3D scanning solutions are, what key factors you should consider when buying a 3D laser scanning solution, and how owning one can benefit your business.
What Is 3D Scanning and How Can It Benefit Your Business?
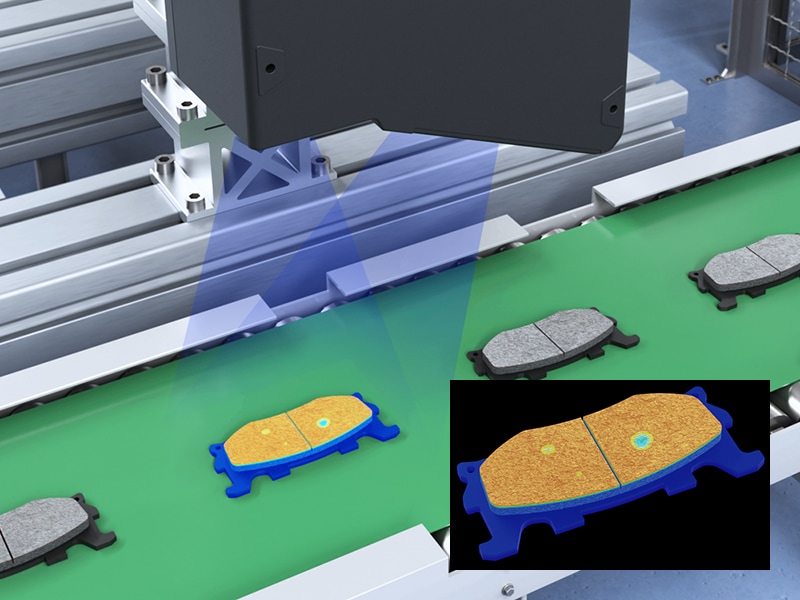
3D scanning involves using a scanner (like this measurement sensor) to capture data from an object’s surface and accurately digitize its shape into a three-dimensional format. Unlike CMMs, which require physical contact with the object, 3D laser scanners can quickly capture and store measurement data without ever touching the part. This allows for faster and more efficient inspection and analysis of the data.
These devices use laser emitters and receivers to emit, collect, and interpret the received light, but they also rely on specialized software to record the changes in the distance and shape of the laser line. This results in a continuous collection of points along all three axes (X-Y-Z) and their corresponding coordinates.
3D laser scanning solutions are often used to detect product and manufacturing defects. They're also used to reverse engineer components and parts, ensure adequate fit between parts and components, and capture an object's surface profile—among many other things.
Besides the various applications in prototyping, engineering, and production, 3D scanners are used for quality control during the aforementioned processes. They quickly inspect the overall shape and size of various parts and excel at detecting defects (such as warpage, scale issues, or surface defects).
When it comes to benefits, the increased accuracy and precision of 3D scanners make them suitable for use across numerous applications, including manufacturing, engineering, design, development, or testing. The technology is also applicable at any point during a typical manufacturing cycle, which saves time, money, and material, thus enhancing the efficiency of the overall process.
It's important to note that not all 3D scanning solutions are created equal, and there are many different types of 3D scanning solutions available on the market, suitable for a range of applications. For example, consumer-grade 2D or 3D scanners deliver reasonable performance and are pretty accessible. However, these devices can't really deliver manufacturing-grade accuracy and detail, which are necessary for industrial use.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Exploring the Benefits of Laser Snapshot Sensors for 3D Scanning
3D scanning has evolved over the past decade, and numerous competing technologies are vying for the same customer applications. Laser snapshot sensors for 3D scanning are transforming inspection practices by providing unmatched accuracy and repeatability. The most significant benefit of laser snapshot sensors is their ability to capture complete 3D images in a single snap. This technology eliminates the need for multiple captures from different angles, reducing inspection time and increasing productivity.
Moreover, the motor-driven scanning detection method used in LJ-S8000 Series sensors allows for ultra-high-speed imaging with an impressive 0.2-second scan time. This feature makes it possible to perform inline inspections at high speeds without compromising accuracy or repeatability.
Why 3D Laser Scanning with Laser Snapshot Sensors Is the Future of Inspection
3D laser scanning accelerates the data capture process compared to traditional scanning methods. 3D Laser scanners can quickly capture millions of data points within seconds, providing a comprehensive scan of the object.
This speed enables project teams to obtain accurate as-built information efficiently, saving time during the project's initial stages and expediting decision-making processes. Because they operate in real-time, these sensors reduce the time spent on manual measurements, helping businesses save costs and improve output in industries like the automotive industry.
Laser snapshot sensors also offer a non-contact solution for 3D scanning, eliminating the risk of damage or interference with delicate objects. This feature makes them suitable for inspecting fragile or sensitive parts, such as electronic components and medical devices.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a 3D Scanning Solution
3D scanning solutions are gaining utility across manufacturing and engineering, especially since they solve an age-old issue of digitizing parts for more effective inspection and measurement. However, as stated previously, not all 3D scanning solutions are made equal, and there are several important factors to consider when choosing a 3D laser scanning solution for your application.
Accuracy and Resolution
Accuracy and resolution are actually two different metrics, with the former referring to tolerances and the latter referring to the smallest of changes the scanner can detect during scanning. Modern 3D scanners generally provide high levels of accuracy and resolution, which makes them suitable for applications demanding highly precise measurements.
Speed
This refers to the sampling rate or the speed at which the data is captured. This consideration is pretty application-dependent; production environments, especially those with fast-moving production lines, greatly benefit from scanners with high sampling rates. For less time-sensitive applications, speed might be a less important consideration.
Compatibility
The image data processing software should be compatible with your existing systems of workflows. The software should also be user-friendly and capable of delivering data in a format that's compatible with your production processes and process control.
Cost
Last but not least is the budget. Industrial-grade 3D laser scanners do come with a price tag, which scales with accuracy and resolution. But that's not the only budgetary concern; there's also maintenance and staff training for off-line models.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Comparing Types of 3D Scanning Technology: Which Fits Your Needs?
Not all 3D scanning technology is the same. For example, laser triangulation sensors project a laser line onto a target and use the reflected light to calculate distance and position. These sensors are unaffected by ambient light and can capture textures in rather high detail.
On the other hand, pattern projection systems use cameras and structured patterns of light to take 3D scans. These systems capture the way light and shadows deform across a surface and use that data to construct a 3D image. These sensors are affected by ambient light and are typically less accurate than laser sensors.
However, from the manufacturing and production perspective, a more important categorization is between in-line and off-line 3D scanners. In-line scanners are integrated directly into the production line, and they usually require a more complex setup and calibration since they're more optimized for continuous, automated scanning at high speeds. This makes them suitable for real-time quality control in high-speed production lines.
Off-line scanners are standalone units that operate independently from the manufacturing process. As such, they're much easier to set up and work with due to higher flexibility, which is achieved at the expense of speed associated with in-line products. However, where the latter is more suitable for quality control, off-line scanners are better suited for reverse engineering, prototyping, and academic research applications.
Laser Snapshot Sensors for Industrial 3D Scanning
Laser snapshot sensors for 3D scanning excel in industrial environments where production is done in large quantities and also where production demands accuracy and speed. Their flexibility makes them suitable for inspecting a wide range of materials and surfaces, including metals, plastics, and composites.
Additionally, their durability ensures they can bear harsh environments, making them a reliable choice for heavy-duty industries.
In-line 3D Scanning Using Laser Snapshot Sensors for Seamless Production and Inspection
Laser snapshot sensors for 3D scanning, like KEYENCE’s LJ-S8000 Series, allow for seamless integration into production lines and effective monitoring. This approach minimizes error, as defective products can be identified and adjusted with immediate effect. The technology's adaptability to different line speeds and product geometries enhances productivity, helping businesses achieve higher levels of quality assurance and operational efficiency.
KEYENCE is the world's leading provider of precision measurement technologies, such as non-contact displacement sensors, laser profilers, and 3D scanning solutions that are often used in numerous industries for industry-specific applications.
If you're looking to enhance your 3D scanning capabilities or to improve the effectiveness of your quality control processes, don't hesitate to contact KEYENCE and inquire about the possible integrations of our equipment with your existing product lines.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Related Products
Applications
Dimension Measurement
- Thickness and Width Measurement
- Step Height Measurement
- Inner and Outer Diameter Measurement
- Measuring Angles
- Meandering/Edge Measurement
Displacement Measurement
- Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
- Vibration and Runout Measurement
- Deflection Measurement
- Measuring Eccentricity





