Fluorescence Microscopes
Capturing clear images without fluorescence blurring
Nerve cells are susceptible to fluorescence blurring during fluorescence observation due to structural complexity, and therefore are observed mainly with laser confocal microscopes.
Image capturing by sectioning allows for observation without blurring of green neuropeptides as shown in the image on the left.
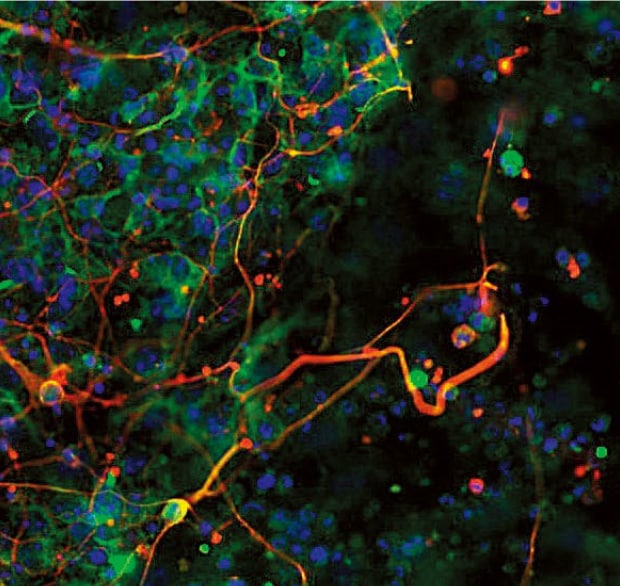
Normal observation
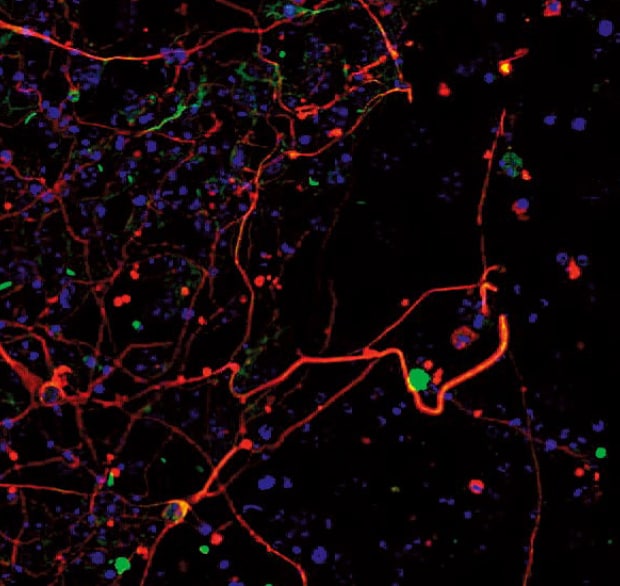
Sectioning observation
Objective lens: CPI Plan Apo λ 40xH
Using the All-in-One Fluorescence Microscope BZ-X
- The Sectioning function makes it possible to eliminate fluorescence blurring and capture clear images.
- A built-in Z-stack function captures multiple images at different focal positions and is able to create a fully focused image by combining only the areas that are at their sharpest focus.
- After capturing the focus data at each height, high-resolution 3D images can be created by incorporating the Z-pitch that was used. Not only does this help to give a better understanding of the structure of the cell, but also of the localization.
- When a slice of the target is too large to fall within a single field of view, images are captured while moving the stage and a high-resolution image can be created by stitching these images.
What is an ES cell?
ES cells (embryonic stem cell) are created from the inner cell mass of a fertilized egg at early stages. With pluripotency, cells can be proliferated almost without limit, so applications for such fields as regenerative medicine are expected.