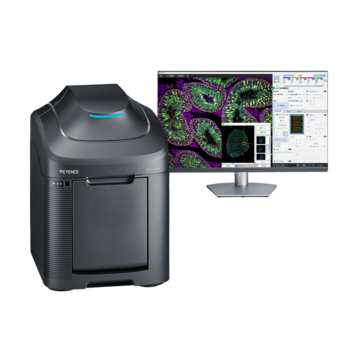
Fluorescence Microscopes
3D Structured Illumination Microscope
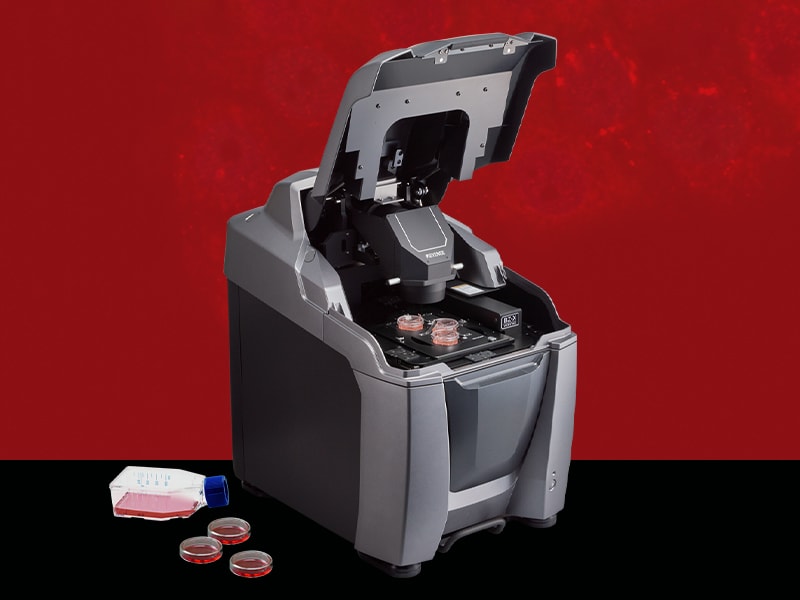

A 3D Structured Illumination Microscope (3D-SIM) utilizes a super-resolution imaging technique that projects patterned light onto a sample. By shifting this pattern of light and capturing multiple images, the system can reconstruct high-resolution 3D structures, offering detailed insights into cellular and molecular processes.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Quickly and Effortlessly Capture High-Resolution Images of 3D Sections with Minimal Photobleaching
- Removes out-of-focus fluorescence for sharper images and increased resolution
- Image thick samples and analyze 3D localization
- Faster and less damaging than laser confocal microscopes
- Supports nearly any wavelength
- Works with any media, including plastic
Our BZ-X All-in-one Fluorescence Microscope provides all the functionality of 3D Structured Illumination Microscopes without the limitations. Contact us to get more information, see a demonstration, or discuss your research requirements!
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Remove Out-of-Focus Fluorescence for Sharper, Higher Resolution Imaging
Conventional methods
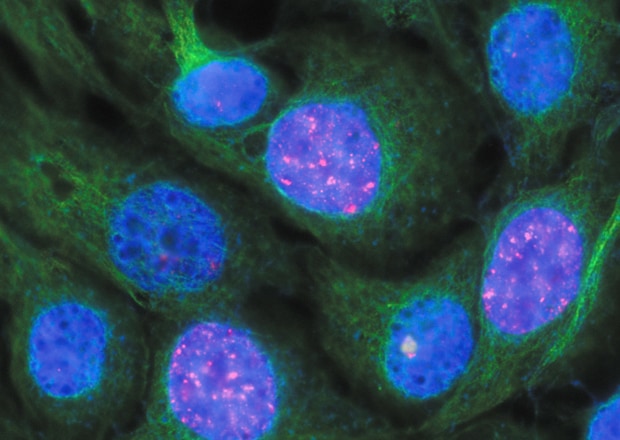
*Tubulin and H2AX Courtesy of Momoko Ishikawa, Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Tohoku University Graduate School of Dentistry
BZ-X
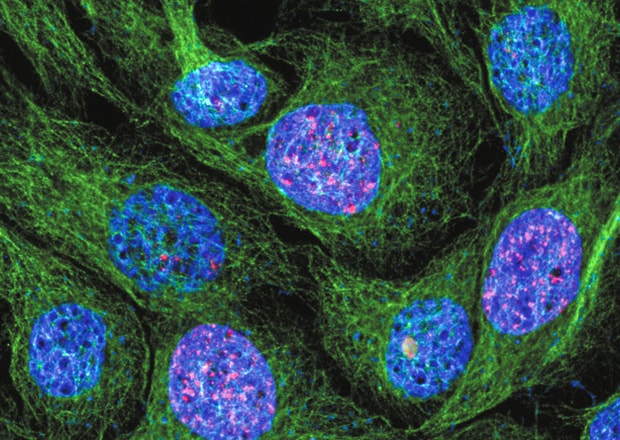
Benefits of Structured Illumination Microscopy
Capture Thick Specimens Clearly
Thick specimens such as animal cells, plant cells, and cultured tissues can be clearly captured by creating optical slices using structured illumination.
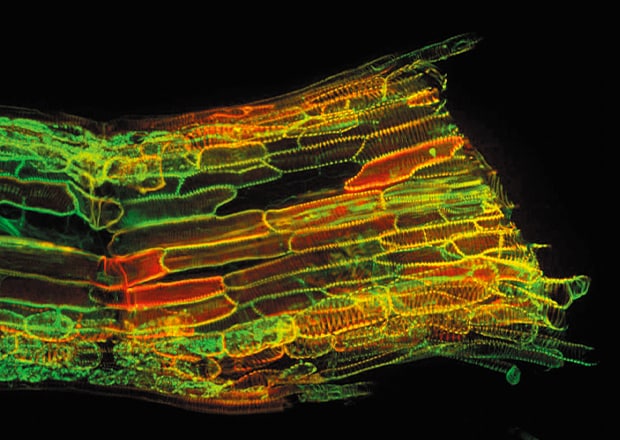
Thale cress vessel
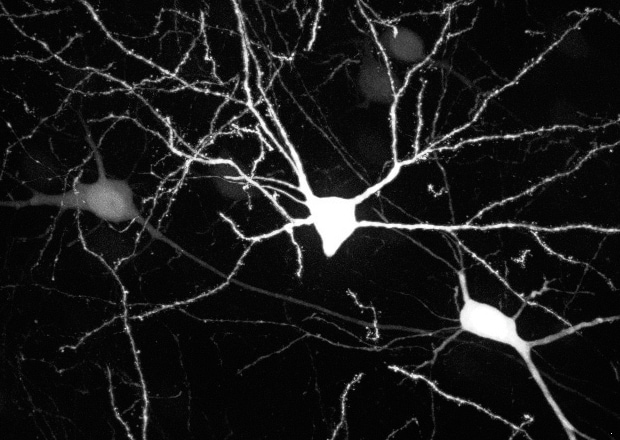
Mouse brain cells (Transparent specimen)
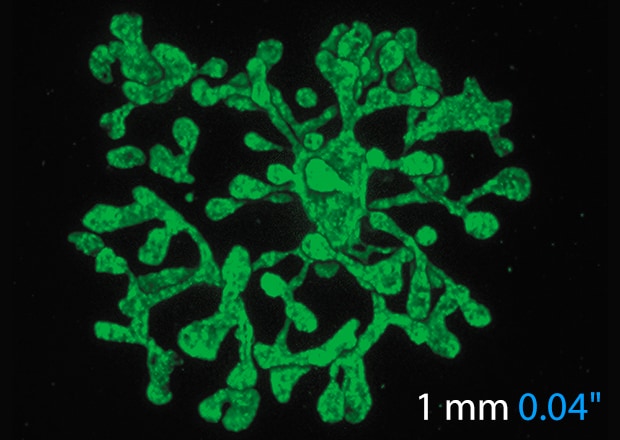
High-quality Imaging Even at Low Magnifications
Sectioning images can be captured easily regardless of the magnification. For large specimens, multiple fields of view can be quickly captured and stitched together for a seamless mosaic.
Before
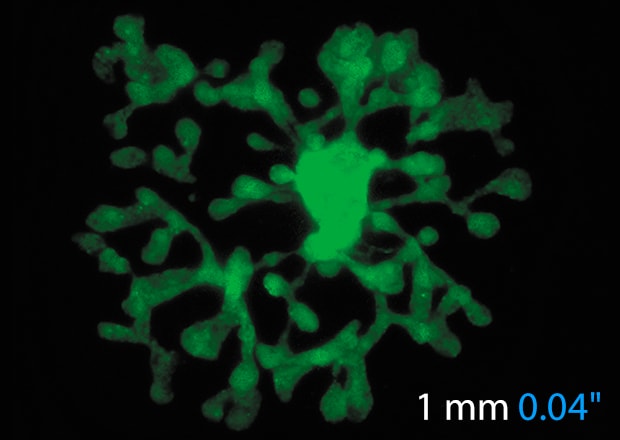
Tissue stem cell-derived 3D kidney-like structure
*Provided by Tetsuya Ohbayashi, Associate Professor, Research Center for Bioscience and Technology, Tottori University
After
Reduced Photobleaching and Phototoxicity
A monochrome, cooled CCD camera detects fluorescence with high sensitivity, enabling observation across a broad wavelength spectrum with minimal damage to specimens.
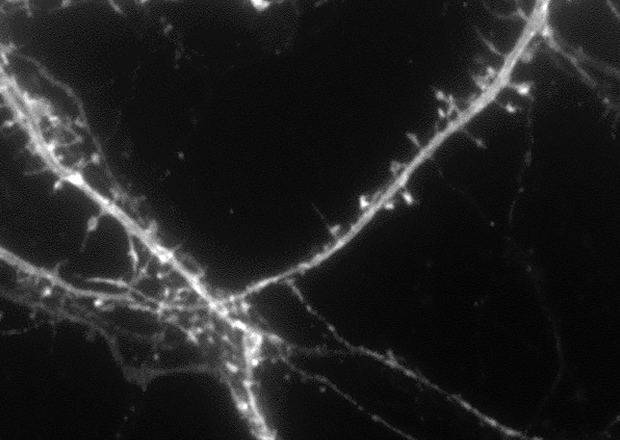
Dendritic spines (100x)
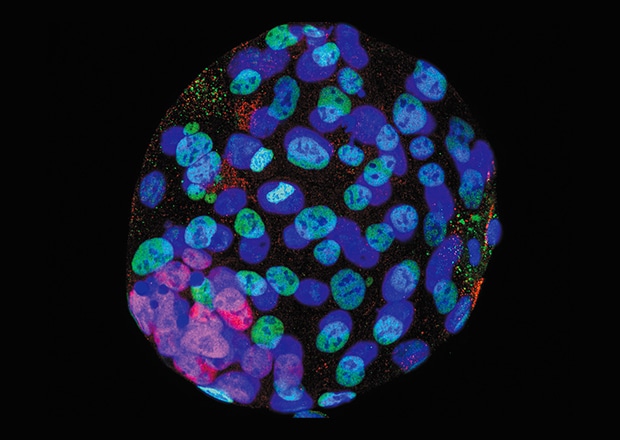
Early embryos of a mouse
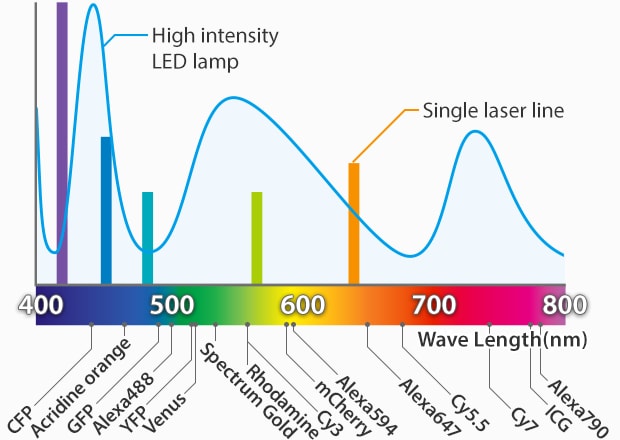
A Wide Range of Wavelengths Can Be Supported
Any wavelength, from ultraviolet to near infrared, can be detected by simply selecting the appropriate fluorescent filter. This allows the optimal fluorescent reagent to be used for each experiment.
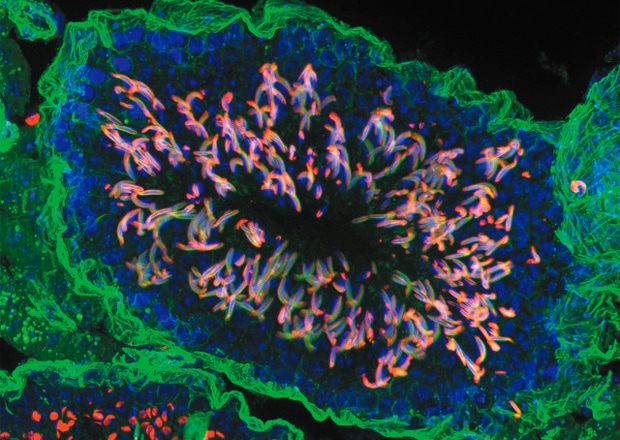
Testis
*Provided by Thumkeo Dean, Associate Professor, Department of Drug Discovery Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University
Image Specimens in Any Container
Samples mounted on glass slides, dishes, multi-well plates, and flasks can be easily viewed, even through those with plastic bottoms.
Before
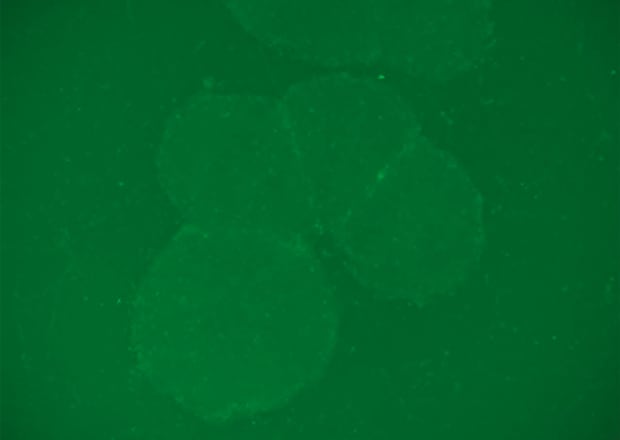
T-iPS cells on a plastic dish
*Provided by Kyoko Masuda, Assistant Professor, Hiroshi Kawamoto Laboratory, Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences, Kyoto University
After
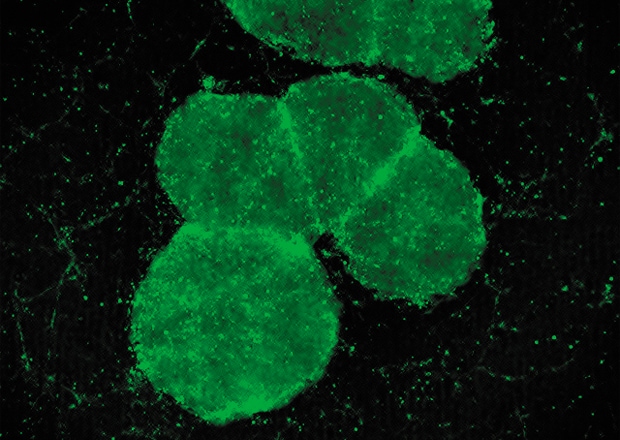
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Image Thick Samples and Analyze 3D Localization
Combine images from Z-stacks (images slices at different focal planes) to generate 3D images for analysis of volume or localization.
Conventional observation of 3D fluorescent beads
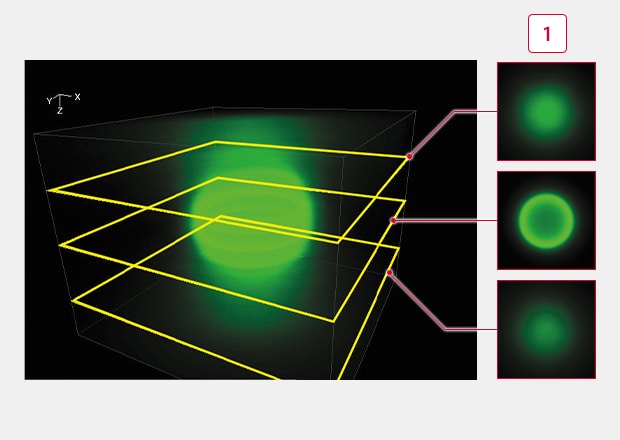
-
1HY cross section
Sectioning observation
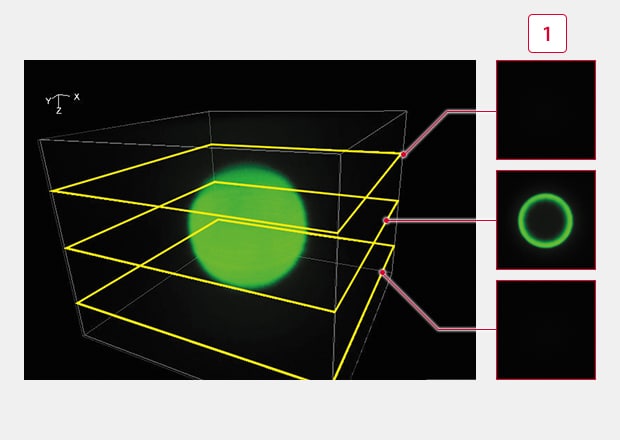
Fluorescence blurring is eliminated, enabling the signals from focused surfaces to be extracted.
-
1HY cross section
Operating Principles of Structured Illumination Microscopy
The electronic projection element enables a high-speed structured illumination scan. When compared to the effects of lasers, the white light source minimizes damage to the specimen. The use of white light also provides the ability to image over a wide wavelength range, delivering high-precision optically sectioned images.
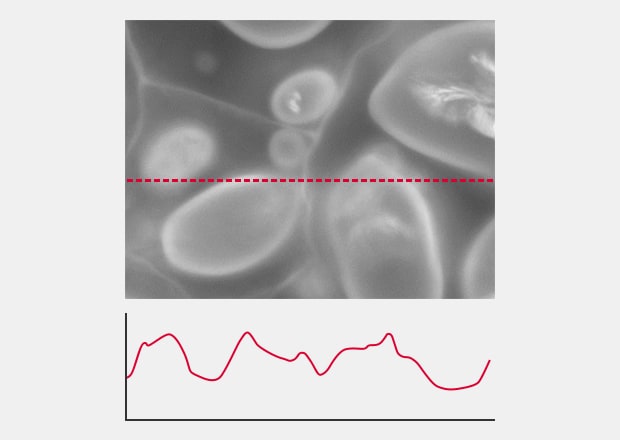
Brightness graph
Normal Image
Thick specimens cannot be captured with conventional widefield microscopes due to scattered light in the Z plane. This fluorescence blurring obscures true signals in the focal plane of interest.
BZ-X Sectioning
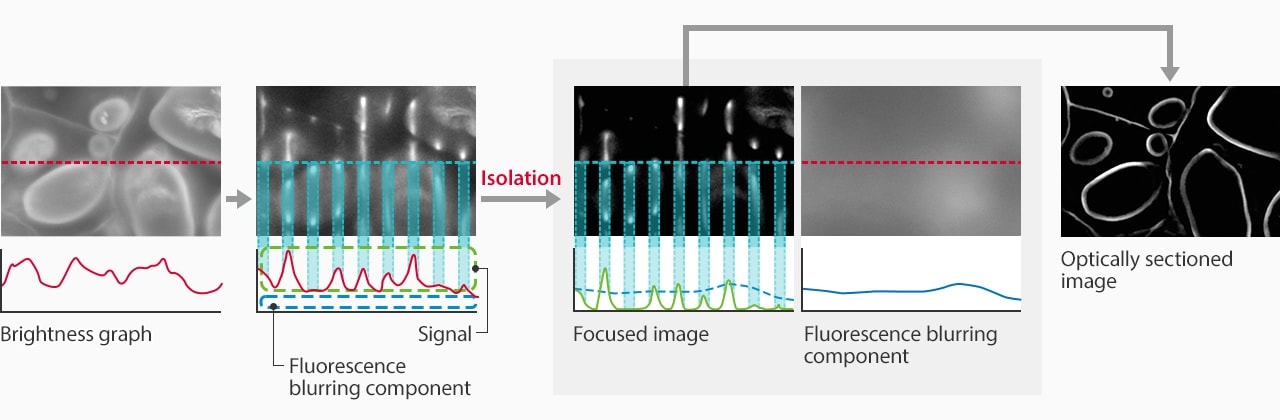
- STEP 1: Pattern projection
- The light passes through the electronic projection element and a structured pattern is projected onto the desired focal plane. Only signals within this focal plane are illuminated by the excitation light.
- STEP 2: Scan and capture
- Multiple images are captured while the illumination pattern scans across the sample. Since the brightness of scattered signals does not change significantly as the pattern moves, the fluorescence blurring can be extracted and eliminated.
- STEP 3: Sectioning image
- The fluorescence blurring is eliminated from the multiple images captured. These images are then automatically combined to produce a clear optical section.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Application Examples
Kidney, whole mount
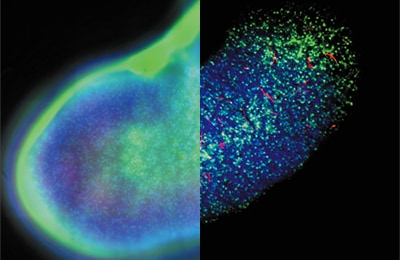
Normal / Sectioning
Mouse cranial nerves
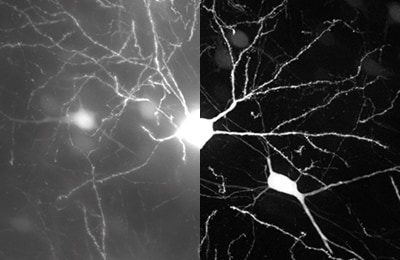
Normal / Sectioning
Neuropeptides
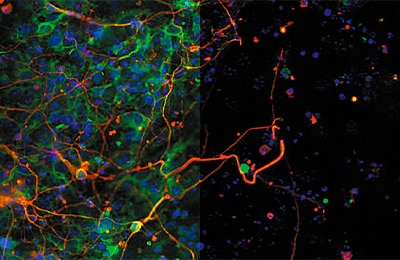
Normal / Sectioning
KEYENCE’s BZ-X Automated Fluorescence Microscope combines many of the capabilities and benefits of both epifluorescence and confocal microscopes into a single, modular platform. At its core, users can quickly and easily capture high-resolution, publication-quality images over wide areas in fluorescence, brightfield, and phase-contrast imaging methods.
This all-in-one fluorescence microscope can be used for routine checks or expanded to accommodate advanced techniques including live-cell incubation and time-lapse imaging, optical sectioning similar to a confocal, low-volume slide scanning, and image cytometry. With an integrated darkroom, users can install this system on any benchtop while taking up minimal laboratory space.
Discover why the BZ-X is the ideal choice for your imaging and high-resolution analysis needs. Download the brochure or request a demo in your lab.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us