Fluorescence Microscopes
Capturing clear images without fluorescence blurring
The cochlea in the inner ear is the sensory organ responsible for hearing.
Hair cells are arranged inside the cochlea and convert sound vibrations into nerve impulses.
When viewing slices of tissue, the cochlea has a three-dimensional structure.This structure causes hair cells inside the cochlea to be susceptible to fluorescence blurring during fluorescence observation. Hence, the cochlea is observed mainly with laser confocal microscopes.
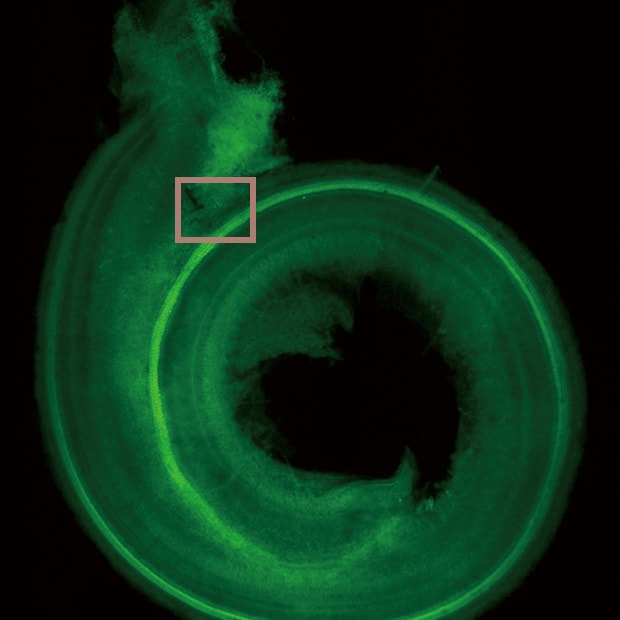
Navigation
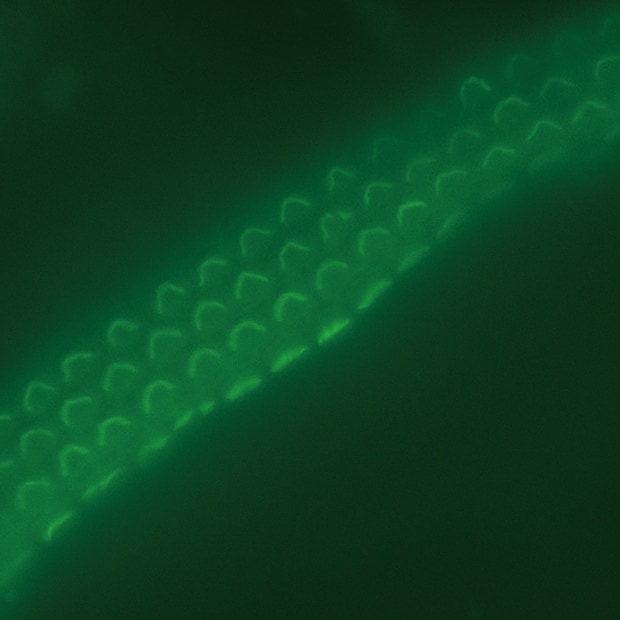
Normal observation
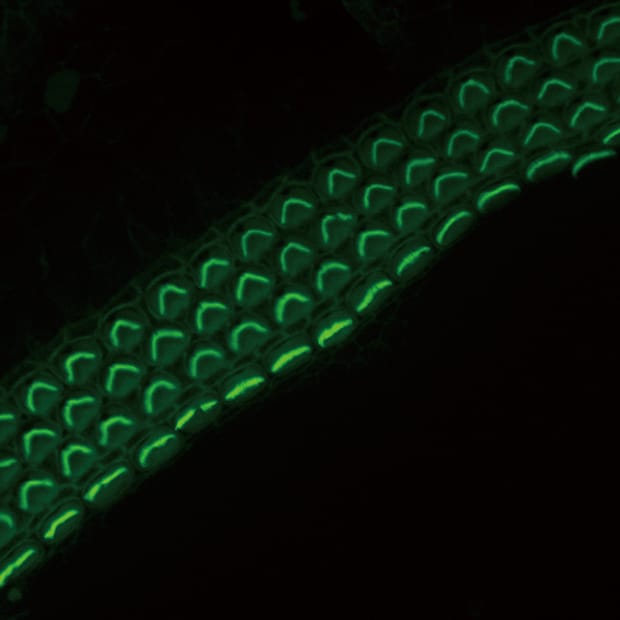
Sectioning observation
Objective lens: CFI60 CFI Plan Apo λ 100xH
Sectioning + Z-stack
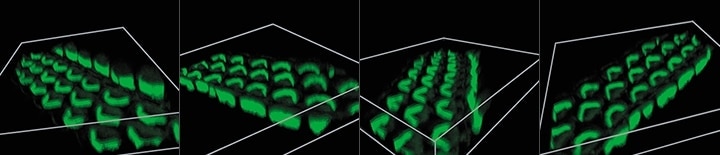
3D image construction
After images are captured at different focal planes, these images can be combined and displayed in 3D with a single click. Users can then rotate, zoom in or out, and analyze cross-sections of the 3D image to determine the fluorescent signal localization.
Using the All-in-One Fluorescence Microscope BZ-X
- The Sectioning function makes it possible to eliminate fluorescence blurring and capture clear images.
- A built-in Z-stack function captures multiple images at different focal positions and is able to create a fully focused image by combining only the areas that are at their sharpest focus.
- After capturing the focus data at each height, high-resolution 3D images can be created by incorporating the Z-pitch that was used. This makes it possible to observe localization clearly in the Z direction.