Fluorescence Microscopes
The BZ Series Helps Zhongke Jiadi Biomedical Technology Improve Research Efficiency

Guangdong Zhongke Jiadi Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Zhongke Jiadi) is a high-tech enterprise focused on biomedical research. The company was established on October 27, 2023, and launched its experimental center on January 12, 2024. Remarkably, within just 56 working days, Zhongke Jiadi obtained key milestone qualifications, including certification as a secondary laboratory of pathogenic microorganisms and accreditation for 1,000-level clean cell rooms.
Zhongke Jiadi is committed to driving biomedical innovation and accelerating the transformation of scientific research results. To achieve this, the company has assembled a technical team of more than 300 master’s and doctoral researchers, supported by advanced experimental facilities such as a flow cytometry platform, KEYENCE fluorescence microscopy platform, molecular detection platform, and cell/organoid research platform.
The company also holds both a laboratory animal production license (covering large animals and mice) and a laboratory animal use license (for large animals, mice, rabbits, guinea pigs, pigs, dogs, and monkeys), and operates an SPF-level animal facility. Working in collaboration with Guangdong Yiruibei Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. and Guangzhou Zhongke Jiadi Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Zhongke Jiadi has built a large, integrated platform offering research services, technical support, article publication assistance, and grant application consulting.
Focusing on Biomedical Technology and Keeping Pace with Market Trends
Market demand in biomedical services is increasingly concentrated in high-end, cutting-edge experiments that require advanced testing methods. Zhongke Jiadi focuses on frontier research in basic medicine, particularly in organoids, stem cells, mitochondrial transfer, organoid chimeric culture, and biomaterials.
For clients, Zhongke Jiadi’s expert team designs experiments tailored to specific research needs and validates the connection between theoretical hypotheses and experimental results. Common requirements include protein co-localization, live-cell time-lapse analysis, and quantitative protein expression studies, each of which typically requires multiple specialized instruments such as 3D confocal microscopes, live-cell imaging systems, and pathological scanners.
The introduction of the KEYENCE BZ Series all-in-one fluorescence microscope has streamlined this process. With its highly sensitive cooled CCD camera, the BZ Series directly outputs high-resolution fluorescence images, enabling researchers to visualize the localization and expression of fluorescently labeled proteins in cells and to investigate their functional mechanisms. By eliminating tedious post-processing steps, the BZ Series improves both the clarity of fluorescence imaging and the overall speed of research.
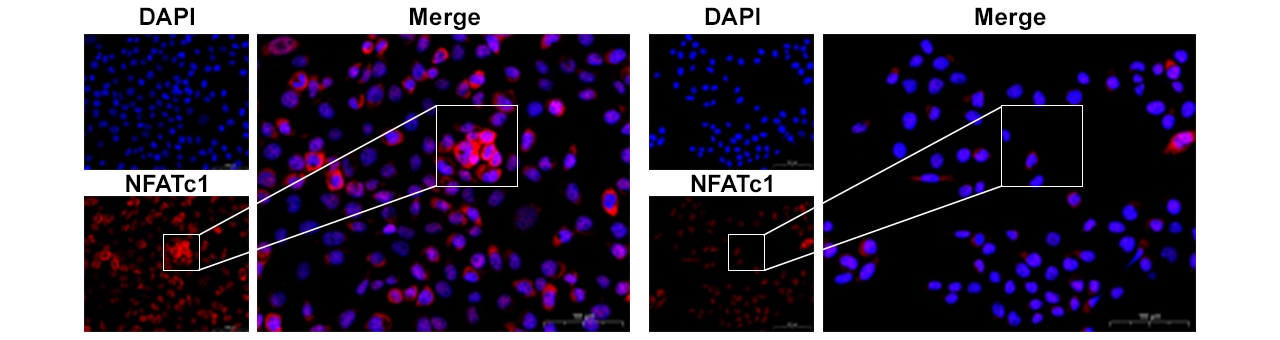
Blue: Cell nuclei, Red: NFATc1
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Detecting Calcium Ion Concentration in the Endoplasmic Reticulum
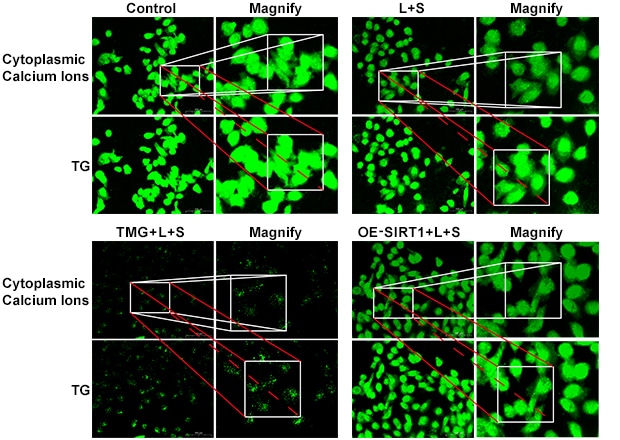
Target: Endoplasmic Reticulum
[1] Asselah T, Bieche I, Mansouri A, et al. In vivo hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress in patients with chronic hepatitis C[J]. J Hepatol, 2010, 52(4), 564-574. (Note: Corrected citation from original text)
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER), the largest membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells, accounts for nearly 50% of total cellular membrane area. It plays a central role in protein and lipid processing, calcium ion storage, and intracellular signaling. For secretory and transmembrane proteins, the ER ensures proper folding and structural stability before proteins are transferred to the Golgi apparatus for further modification. Misfolded proteins are retained and degraded within the ER.
Calcium ions are deeply involved in these processes, supporting protein folding, transcription factor activation, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Normally, calcium homeostasis remains tightly regulated; however, imbalances can disrupt ER function, leading to the accumulation of misfolded or unfolded proteins. Sustained ER stress can trigger apoptosis and has been linked to diseases such as osteoporosis, neurodegenerative disorders, cancer, Parkinson’s disease, and numerous liver conditions including viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, drug-induced liver injury, and liver cancer [1].
Thus, studying calcium ion dynamics in the ER is essential for understanding disease mechanisms and for developing targeted therapeutic strategies.
Using the BZ Series automated stage and imaging system, Zhongke Jiadi developed a novel method to detect ER calcium ion concentration. By applying consistent imaging and analysis parameters before and after treatment, researchers can accurately measure fluorescence intensity differences to calculate calcium concentration.
In practice, this requires capturing multiple fields of view and analyzing fluorescence values statistically to ensure validity. Traditionally, it is challenging to return to the exact same field of view after treatment, as even slight differences in imaging parameters or positioning can lead to significant errors.
The BZ Series solves this problem by automatically recording imaging conditions and stage coordinates with its high-precision XYZ motorized platform. Researchers can reposition samples with a single click to replicate the original conditions precisely, ensuring accuracy and improving experimental efficiency.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Application in FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching)
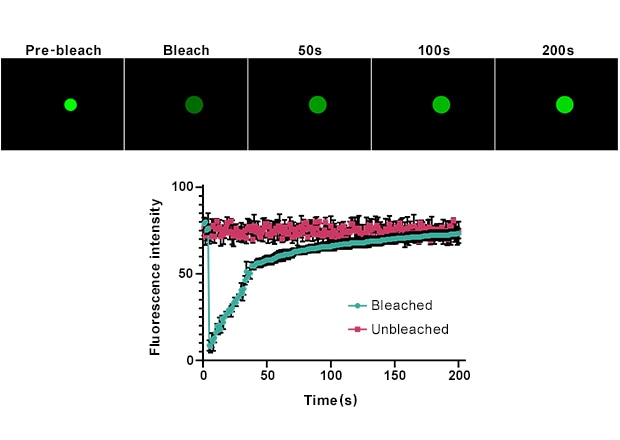
To minimize photobleaching, the BZ Series uses an adjustable-intensity fluorescent light source and an anti-bleaching mode, which blocks excitation light except at the exact moment of image capture. In FRAP experiments, this system allows precise control over bleaching conditions.
The stable, high-intensity LED light source (with a lifespan of up to 40,000 hours) ensures reliable and uniform bleaching while preventing overexposure. Its excellent heat dissipation maintains consistent output over long experiments, reducing errors caused by light source heating.
Combined with the BZ Series’ automation features, researchers can capture multiple fields of view at varying magnifications and conditions within a single experimental cycle. Time-lapse videos can then be generated under consistent conditions, enabling multiple sets of kinetic analyses to be completed in one run. This significantly increases throughput and efficiency.
Furthermore, the anti-bleaching mode provides more precise visualization of fluorescence recovery, giving researchers deeper insights into the dynamic behavior of biomolecules and their interactions.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Increased Efficiency and Research Output

Xu Yilin, Technical Director at Zhongke Jiadi, shared in an interview that before adopting the BZ Series, fluorescence imaging was unclear, operations were fully manual, experiments were slow, and only a limited number of images could be captured per unit time.
Since introducing the KEYENCE BZ Series, the laboratory has achieved fully automated multi-well fluorescence detection, high-precision co-localization imaging, and automated batch acquisition of images. As a result, imaging throughput has doubled, while both efficiency and data quality have improved. The system has also reduced costs by consolidating multiple imaging needs into a single platform.
Through its advanced automation, stability, and high-quality imaging capabilities, the KEYENCE BZ Series all-in-one fluorescence microscope has enabled Zhongke Jiadi to significantly improve experimental efficiency and accuracy. Its applications in ER calcium ion measurement and FRAP analysis exemplify how integrated imaging solutions can accelerate biomedical research and support breakthroughs in disease modeling and therapeutic development.