Optical Comparator (Profile Projector)
The Difference Between Extrusion and Injection Molding
Key Takeaways
- Injection molding makes complex 3D shapes; extrusion produces continuous 2D/linear profiles.
- Extrusion has lower upfront cost; injection pays off with high-volume, complex-part repeatability.
- Injection: molds, hopper, melt, inject, cool, eject; Extrusion: melt, force through die, cut, cool.
- Injection suits complex aerospace, automotive, medical parts; extrusion suits pipes, sheets, profiles.
- Fast, repeatable molding requires appropriate inspection: portable CMMs for large parts, optical CMMs for many small parts.
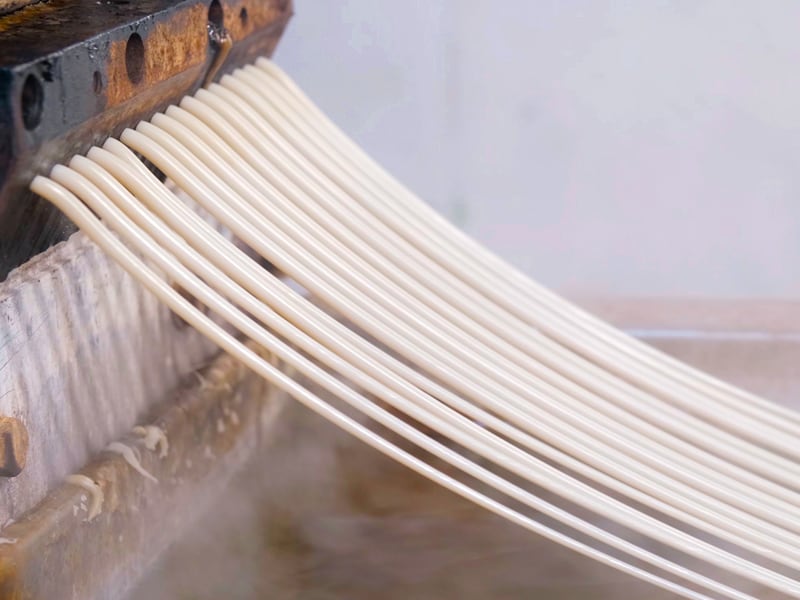

Dating back to the 1930s, extrusion molding and plastic injection molding have been the preferred plastic fabrication methods for repeatability, speed, and cost-efficiency. Both methods shape hot soft plastic into hard plastic parts for use in industries like automotive, aerospace, construction, and medical.
Although these molding processes are similar, they have a few key differences. In essence, plastic injection molding is more versatile in shapes and sizes than extrusion molding. Whereas extrusion molding is cheaper upfront than injection molding but it can only make basic shapes.
This guide will look deeper into the processes, applications, and integration of plastic extrusion vs injection molding.
What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a plastic fabrication process for complex-shaped 3D parts. The process uses a manufactured mold, so plastic injection has unlimited variance in precision, tolerance, and shape. Also, the mold is finalized with many different colors, cosmetics, polish, and texture options. The original molding process can be pricey, but the unlimited repetition means that this process is cost-effective when used over and over again and in the end, the repeated manufacturing pays back the cost of the mold.
Plastic Injection Molding Process
The process follows a few steps. First, plastic pellets are poured into the hopper. The hopper acts as the machine’s “mouth,” where the process begins. Once the pellets move through the hopper, they end up in the cylinder.
Next, the cylinder heats up and turns the pellets into liquid form. After liquifying, the melted hot plastic flows to the nozzle. The nozzle injects the mold with the melted plastic. Then, the mold cools and hardens the plastic. After cooling, the mold ejects the finished part.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

What is Plastic Extrusion Molding?
Plastic extrusion molding is a plastic fabrication process for linear 2D shapes like pipes and sheets. The process uses a hydraulic press and a die instead of a mold. Since there are no large molds or complex shapes, plastic extrusion molding has a cheaper upfront cost compared to injection molding. The most popular plastic for extrusion is polypropylene.
Plastic Extrusion Molding Process
The process starts with slowly melting plastic pellets or powder in an oven connected to the machine. After melting, the plastic flows into a die, and the die moves across the machine like a conveyor belt. As the die moves, more plastic flows to create a long, melted length. When the plastic reaches the desired length, the plastic is cut and cooled. The finished product can be one part or many parts cut from the die.
Applications for Injection Molding
Injection molding produces 3D parts of any shape and size. Because of this versatility, it is commonly used for internal and external parts for many consumer products, on aircraft and vehicles, and medical devices are just the tip of the iceberg.
Plastic Injection Molding Aircraft Parts
The aerospace industry is using plastic parts for their lightweight, moldability, and resistance to corrosion. The reduced weight means less fuel is needed to power airplanes and, therefore, makes it more economical and environmentally friendly. Moldability and corrosion resistance were attempted with materials like rubber and metal, but plastic has been found to be better.
It is also a cost-effective and precise way to manufacture parts like turbine blades, lenses, and panels. The mold is formed to any of these designs and follows the required industry tolerances. Also, the mold is reusable so these parts can be manufactured in larger batches compared to basic CNC machining or 3D printing.
Plastic Injection Molding Vehicle Parts
The automotive industry is also using plastic because of its lightweight nature and resistance to environmental factors. Plastic vehicle parts include external car parts, interior panels, and dashboard components.
This type of molding for parts allows manufacturers to scale part batches because of the mold’s repeatability and efficiency. Manufacturers also choose injection molding vs extrusion for these applications because injection molding has the ability to produce a variety of materials, colors, cosmetics, polish, and texture options needed for the automotive industry.
Plastic Injection Molding Medical Devices
Plastics like polypropylene resist contamination and corrosion and have high heat resistance for autoclaves (sterilization ovens). These characteristics are why the medical device industry uses plastic for surgical equipment, beakers, and x-ray components.
Plastic injection molding for these devices is ideal because the mold fits the tight tolerances and produces a sleek finish without additional processing.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Applications for Extrusion Molding
Extrusion molding uses a hydraulic press to produce linear shapes like sheets and pipes. The shapes range in length, from as small as a couple millimeters and up to 1,000 ft in length. Here are a few common applications.
Extrusion Molding Plastic Sheets
Plastic extrusion molding sheets are common in industries such as automotive, aerospace, defense, and construction. Unlike injection applications for these industries, extrusion plastics are for long, continuous plastic sheets that can be trimmed into smaller sections for components.
Bulletproof windows, windshields, skylights, and seating are all examples of these applications. The repetitive and cheap process means sheets are easily made and cut to scale.
Extrusion Molding Plastic Pipes
Extrusion molding plastics like polyethylene (PEX) and Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) are used for residential plumbing, outdoor pipes, vents, and drains. These plastics are chosen because of their resistance to temperature change, anti-corrosive properties, and ease of liquid flow.
Using extrusion vs injection molding for pipes is more cost-effective because the machine produces a continuous pipe that can be cut and shaped into specific applications.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Integrating Injection Molding or Extrusion Molding into Your Processes
Both processes offer repeatable, accurate, and cost-effective plastic fabrication capabilities that benefit many industries, including aerospace, construction, automotive, and medical. Their versatility allows you to scale your manufacturing above your standard CNC or 3D printing batches.
Whether you’re using injection or extrusion molding, then inspection will be a necessary step in your process. Since injection and extrusion molding produces at such fast and repeatable rates, missing one defect could snowball into thousands of defective parts. Regardless of if it involves visual inspection or measuring dimensions and GD&T data, having the right inspection devices is important.
A portable coordinate measuring machine (CMM) and optical inspection system are useful for measuring dimensions and GD&T features like flatness, parallelism, and angularity. Portable CMMs excel at in-process inspections for large parts, while optical CMMs can inspect hundreds of small parts simultaneously for final inspection. Contact us today to learn about KEYENCE’s inspection tools.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Related Downloads

Brochure for the XM-5000 Series Handheld CMM. Portable CMM to easily and accurately measure 3D and GD&T features anywhere including the shop floor and in the machine tool.