Measurement Sensors
Dimension Measurement
Displacement Measurement
Types of Industrial Manufacturing Sensors
Different types of industrial sensors and other transducers have come to play crucial roles in our lives and daily operations. They wake us up, measure our steps and heartbeat, and are used to make other sensors and nearly everything imaginable in our vicinity.
Industrial manufacturing sensors have also come to play vital roles in our manufacturing processes, as they’re used for monitoring, control, and optimization. These devices not only enable the detection and measurement of various physical properties, but they also monitor and guide the quality assurance and quality control processes.
Overall, industrial manufacturing sensors are used to ensure efficient and precise manufacturing operations, as well as making sure that the end product is the epitome of quality. So, in this guide, we’ll discuss various types of industrial sensors in manufacturing.
Role of Different Types of Industrial Sensors Used in Manufacturing
Different manufacturing processes rely on a wide range of application-specific sensors to monitor and guide the production process. Of course, each type of industrial sensor has a specific purpose and provides valuable information that’s used for monitoring and process control. You’ll find some of the most commonly used types of industrial sensors in the section below:
Temperature Sensors
As their name implies, temperature sensors measure the temperature of different materials, equipment, and environments. They’re crucial for precise temperature control processes, such as metal casting, food processing, and chemical production. Some of these sensors include thermocouples, resistance temperature detectors, and infrared sensors. They’re almost everywhere. For example, furnaces employ thermocouples to monitor and control temperature.
Pressure Sensors
Pressure sensors detect and measure the pressure of liquids and gasses within a system. They’re vital for maintaining the correct pressure levels in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, thus ensuring that these systems are running as efficiently as possible.
Proximity Sensors
Proximity sensors are most commonly used for position detection, object counting, and automation control in various assembly lines. There are several different types of proximity sensors, including capacitive, inductive, and ultrasonic sensors. All of these detect the presence or absence of objects without making any physical contact, making them perfect for applications involving fragile or thin workpieces.
Flow Sensors
Flow sensors measure the flow rate and volume of fluids within a pipe or a duct. They’re important for monitoring and controlling the flow of both liquids and gasses in water treatment plants and chemical manufacturing, and they’re even used in industrial HVAC systems.
Level Sensors
Level sensors are also heavily used in industrial settings, as they detect the level of materials within containers and tanks, such as liquids, granules, or powders. These sensors help prevent overflows, ensure proper material handling, and help maintain consistent production levels.
Load Sensors
Load and force sensors are used to measure the amount of force or weight applied to a particular object. They’re most commonly used in material testing, robotic gripping, conveyor belt tensioning, and other similar applications.
Vibration Sensors
As their name implies, these industrial sensors monitor the vibration levels of different machinery and manufacturing and operational equipment. They’re really important in predictive maintenance since measuring and monitoring vibrations might help identify potential issues before they lead to equipment failure and downtime.
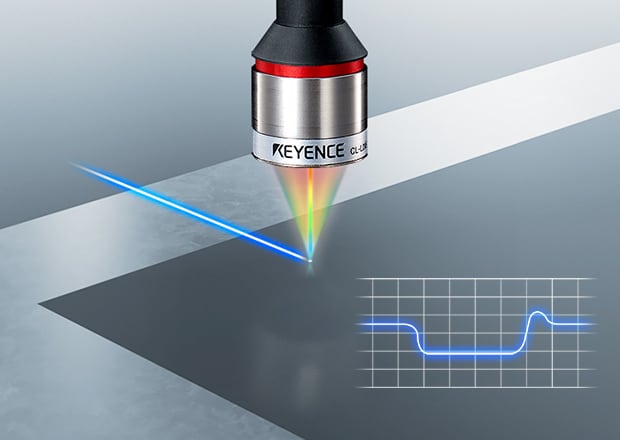
Laser Displacement Sensors
Laser displacement sensors (like the pictured CL-3000 Series) use lasers to measure the amount of movement or displacement of an object. KEYENCE’s displacement sensors enable non-contact measurement of height, position, interference, or distance measurement. Pairing several sensors together allows businesses to measure other physical properties such as thickness and width.
Vision Sensors
Vision sensors rely on highly advanced cameras and image processing algorithms to inspect and analyze different objects. Just like laser displacement sensors, they’re often used for quality control and defect detection. However, unlike laser displacement sensors, they can also be used for robotic guidance in assembly and packaging lines.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Key Considerations in Selecting Sensors for Manufacturing Applications
Choosing the right industrial measurement sensors depends on several key considerations that would ensure optimal performance and reliability of your production operations. To make the correct choice, you must understand the specific requirements of a particular application, including the type of measurement needed, the measurement range, and the required accuracy of your sensors.
There are also environmental considerations, such as temperature extremes, humidity, exposure to different chemicals, and potential mechanical stresses that can affect sensor operation. Be sure to select sensors that are specifically designed to withstand these conditions.
The last thing for your organization to consider (apart from cost) is integrability: whether or not the sensor is compatible with your existing control systems. By investing in the right sensors for your manufacturing processes, you can expect numerous benefits that will positively impact your business operations.
Benefits of Sensors in Manufacturing
The use of sensors in manufacturing isn’t just beneficial for the manufacturing process; for industrial settings, the use of sensors is borderline mandatory. Sensors enable precise monitoring and control of various production parameters, thus ensuring consistent product quality while also reducing the risk of defects.
Some sensors, like laser profilers, micrometers, and vision systems, are capable of detecting imperfections at a µm range, which means they’re capable of detecting defects that might be invisible to the naked eye. Apart from that, they’re often used to provide real-time data for process control, which optimizes production, leading to shorter cycle times, minimized waste, and lower energy consumption.
Additionally, industrial manufacturing sensors are often used to identify early signs of equipment wear and potential failure, allowing technicians to take a proactive approach to maintenance. This reduces the costs associated with unplanned downtime while also extending the life expectancy of machinery and equipment. All of this contributes to higher overall efficiency, which translates to increased profitability.
Explore KEYENCE Sensors for Improved Manufacturing Efficiency
KEYENCE is the world’s leading provider of precision technologies for measuring, quality assurance, and quality control applications. If you want to enhance the precision and accuracy of your manufacturing operations with different industrial sensors, don’t hesitate to contact KEYENCE and inquire about integrating their equipment with your current manufacturing lineup.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Related Products
Applications
Dimension Measurement
- Thickness and Width Measurement
- Step Height Measurement
- Inner and Outer Diameter Measurement
- Measuring Angles
- Meandering/Edge Measurement
Displacement Measurement
- Positioning and Stroke Length Measurement
- Vibration and Runout Measurement
- Deflection Measurement
- Measuring Eccentricity






