Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Laser Labeling
Laser labeling is the process of using a laser marking machine to put a label on a product. The label can be used for traceability, identification, or adding regulatory information. Replacing a labeler with a laser can have benefits across many aspects of production.
Using a laser marking machine rather than a standard inkjet printer for labeling will improve value with time, money, and production. Laser markers decrease production time, increase permanency of labels, and decrease use of extra materials.
In addition, manufacturers using laser markers don’t have to deal with consumables such as physical labels, adhesives, or industrial ink. Laser labeling machines are a versatile innovation in the labeling world that can help reduce waste pollution, various costs, and a long list of other benefits, ranging from the manufacturers to the end consumer and even the environment.
Below, we will discuss the differences between laser marking and standard labeling, the characteristics of each, and the best machines to use.
Laser Labeling Machine
KEYENCE offers a UV laser marking machine that marks high-contrast, damage-free, clear labels. To ensure ease of use, this UV laser marking machine contains easy-to-use software that controls the marking. The software can be programmed based on font, size, contrast, materials, and more, depending on your specific requirements.
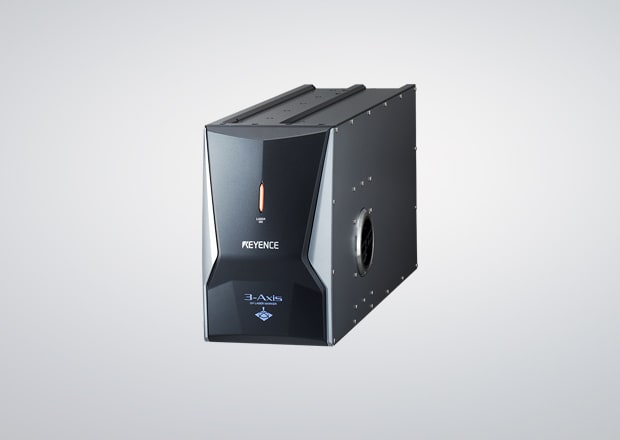

3-Axis UV Laser Marker MD-U Series
The UV Laser MD-U Series is the world’s first 3-Axis Control UV laser. It uses a UV laser and 3-Axis Control to mark a variety of shapes, sizes, and materials. The 3-Axis Control marks uniformly and without distortion. It achieves this by using an edge-to-edge laser uniform line width rather than cylindrical lines.
Due to the dramatically shortened wavelength, the MD-U’s beam can be absorbed by even the most highly heat-resistant materials. It marks with high contrast and permanent marks that do not fade over time. It leaves a clean mark that aesthetically prints any label needed. The MD-U can be used across industries and various needs. It automatically adapts, even with a surface with multiple materials, such as PCBs, battery packs, and lighting equipment.



Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Comparison of Laser Labeling with Traditional Labeling Methods
When you stack up laser labeling against the capabilities of traditional methods, the differences are glaring. This isn't to say traditional methods are obsolete, but laser labeling is optimal for manufacturing from many standpoints. Some of the main comparisons between the two labeling methods can be found below.
| Focal Point | Laser Labeling | Traditional Labeling |
|---|---|---|
|
Permanency
|
Laser Labeling
Laser labeling guarantees permanency throughout the product's lifecycle. It is also more resistant to external stressors such as light and temperature.
|
Traditional Labeling
Known to eventually start to peel and fade with time. Due to the fading print, it can be hard to read vital information.
|
|
Efficiency
|
Laser Labeling
Laser label machines require very little, to no, maintenance and have no consumables to track or refill.
|
Traditional Labeling
Required to handle consumables, causing downtime in the production process. Switching rolls and ink cartridges are common to this process.
|
|
Cost-Effectiveness
|
Laser Labeling
With no need to purchase physical labels, laser labeling is very cost-effective and reduces consumable waste and downtime.
|
Traditional Labeling
More expensive due to ongoing consumable purchases. Excess labels can also waste time and money.
|
|
Visual Quality
|
Laser Labeling
Much more pristine and clear in readable quality. Fewer chances for mistakes or errors in the print.
|
Traditional Labeling
High-quality traditional labeling is possible but susceptible to smudging or rubbing off.
|
|
Material Compatibility
|
Traditional Labeling
Label adhesives are limited to some degree. They don’t work on every material, even with varying types of adhesive. They’re also bound to lose adhesive strength against the material over time.
|
This table could lay out many other unique differences, but these points provide a comprehensive look at the comparisons. Traditional labeling has been relevant for decades and will be for many more years. Eventually, the evolving nature of labeling and laser marking technology will put conventional methods on the back burner for many people in the manufacturing business.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Advantages of Laser Labeling Machines
While comparisons are important, it can be more helpful to review the advantages of direct laser engraving and marking over traditional means. These upsides are pretty universal, regardless of the application.
Some of the most prominent advantages of laser labeling technology include:
- Readability
- Adaptability to varying surfaces
- Reduced downtime and maintenance
- Better cost-effectiveness
- Unmatched permanency
- Better production integrations
- Lesser environmental impact
The list of laser marking advantages goes far beyond this, so it is evident that laser marking will continue revolutionizing labeling on many scales. Manufacturers have many angles to consider regarding production, with product authentication and traceability being high on the list.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
The Role of Labeling and Laser Marking in Product Authentication and Traceability
Laser marking machines also improve product authentication and traceability. Laser labeling systems guarantee uniformity and quality from origin to product integrity and other important details.
Providing a digital footprint for each product that doesn't waver over time will always benefit consumers as well as the manufacturer. These details are equally crucial regarding some aspects of laser labeling requirements within the industry on a local, national, and international level.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Labeling and Laser Marking Characteristics
Laser markers operate differently than standard labeling systems. Ink labeling systems need extra materials to minimize damage to the product and get an intense mark. These extra materials are usually ink ribbons or thermal heads. Because of the precision of a laser, labeling with a laser marker only requires a UV laser machine.
UV lasers work by passing a standard wavelength through two crystals, which creates a thin laser with high absorption. The high absorption is not synonymous with high heat, a UV laser is gentle on materials and can independently mark without needing protective materials. Because of the high absorption rate, the marks are permanent and do not fade over time.
Inkjet labeling machines were standard, but new laser marking technology outperforms these machines.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Related Downloads

This quick guide introduces the basics of metal marking. Learn why different wavelengths matter and discover the various ways laser light interacts with metal parts.

Choosing the right laser marker wavelength is extremely important for plastic marking. Learn what lasers work best for marking, processing, and coloring plastic in this guide.

2D codes have become a near-universal standard for traceability. This must-read document covers everything from code scanning principles, laser installation, predictive maintenance, and more.

2D codes are used to store date codes, lot codes, serial numbers, and more. Users who are considering 2D code marking should read this laser marking guidebook.

Some laser marking applications require integration with multiple devices. KEYENCE provides a total marking solution, from X/Y stages and indexing systems to head traversal systems. Learn more in this brochure.

This booklet covers a wide range of laser processing techniques - such as cutting, drilling, and deep engraving - as well as welding and soldering that are unique to lasers.




