Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Laser Marking in the Electric Vehicle Industry
-
Tags:
- Laser Marking , Battery , Laser Cleaning
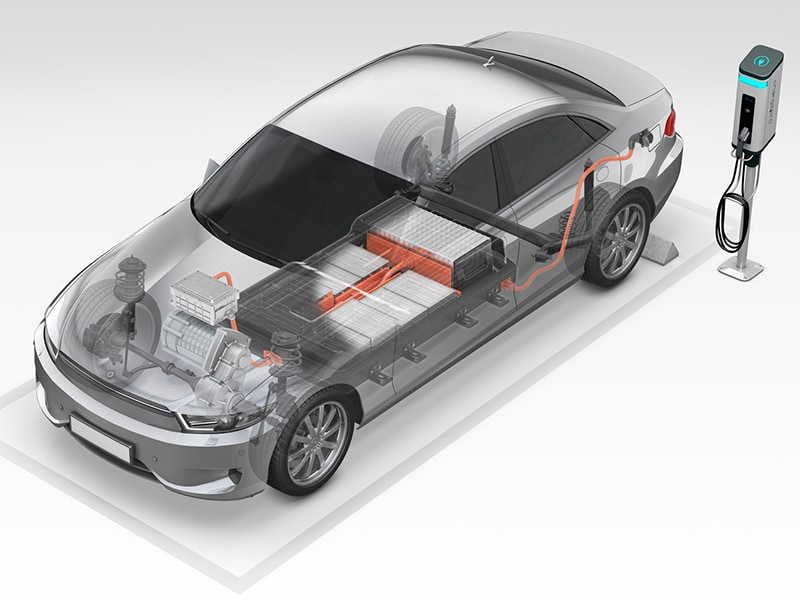

Amid growing exhaust regulations around the world, the development of electric vehicles is accelerating. The components needed for electric vehicles differ drastically from the conventional gas vehicle; however, similar to gas vehicles all these components need some form of identification or traceability marks. The intricacies of electrical components like batteries, connectors, converters, inverters, ECU's, etc., make traceability a concern for most marking methods. Laser marking for electric vehicles, on the other hand, delivers the precision, quality, and permanency that alleviates these concerns.
Applications of Laser Marking in Electric Vehicles
Many components in the EV manufacturing process need to be precisely marked. Laser marking produces reliable results on all sizes, from small connectors to larger battery packs. Traceability systems rely on these marks to track parts through the manufacturing process and through their entire life cycle.
Battery management benefits greatly from laser-marked identification. Each cell can receive unique codes that help monitor performance and safety parameters. The automotive industry continues to develop new applications as vehicles become more sophisticated and component counts increase. With that said, EV laser technology will continue to assist.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Key Benefits of Laser Marking for the Electric Vehicle Industry
Since EV parts must endure severe environments, permanent identification is essential. Laser marking for electric vehicles is not affected by heat, chemicals, or friction, unlike labels or ink. This benefit of quality control ensures EV component traceability throughout a vehicle's life.
Laser marking significantly increases production efficiency. Systems have less downtime and integrate readily into assembly lines. Another significant benefit is waste minimization, as laser marking does away with consumables like labels and ink. The precision technology also allows for marking in hard-to-reach areas without compromising part integrity.
Direct Part Marking in the Electric Vehicle Industry
This section introduces marking and printing applications useful in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. In recent years, laser marking has become widely used to mark electric vehicle parts and components, such as the vehicle's make and model, as well as its serial number. This helps to ensure that these parts and vehicles can be traced back to their manufacturer when they need to be repaired or serviced.
Laser marking electric vehicles is a quick, efficient, and reliable way to provide this information, and it can be used on a wide variety of surfaces, including metal, plastic, and glass. It is often used on both EV batteries and ECUs. Additionally, laser marking can be used to add aesthetics to EV parts. This can include company logos, slogans, or other designs.
The Importance of Direct Part Marking (DPM) in Electric Vehicles
Since fake components pose significant safety issues in electric vehicles, component authentication becomes essential. Only authentic parts are allowed to enter the supply chain thanks to the tamper-proof identification provided by direct part marking for electric vehicles. Every step of the production process is improved by this degree of security.
Supply chain management in the EV industry relies heavily on DPM technology. With thousands of parts in each vehicle, tracking becomes impossible without reliable EV laser marking. Warranty service also depends on proper identification to determine if components are original and within their service period. This verification system protects both manufacturers and consumers.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Laser Marking on Batteries (Electrodes and Insulation)
Batteries are the primary power source of electric and hybrid vehicles. They regain their power through direct charging or vehicle deceleration. Automotive manufacturers recently started using lithium-ion batteries, which have a larger capacity and a more compact/lightweight design compared to traditional options.
As a vital component of EVs, batteries need clear markings as they become more common in vehicles worldwide, helping track each part from factory to road. EV battery marking handles many applications, including:
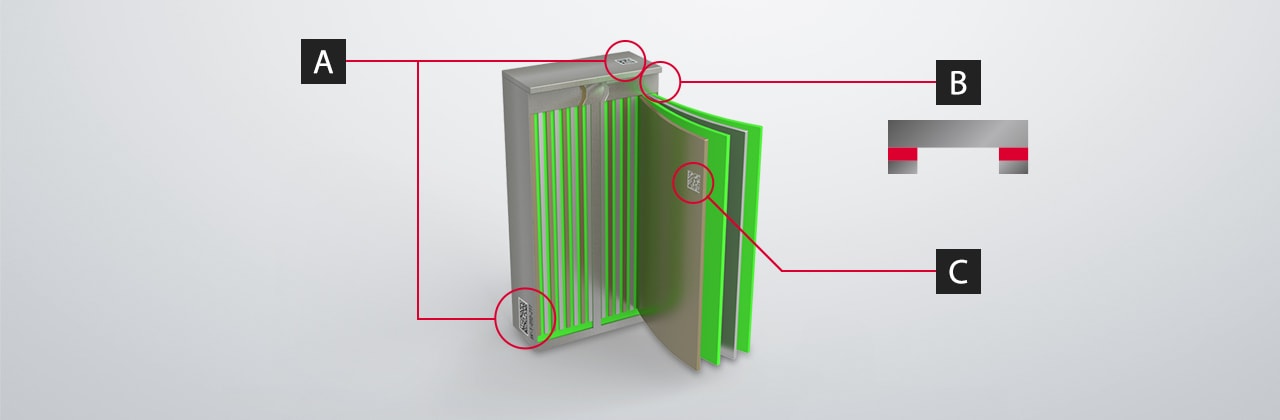
A: 2D Code and Serial Number Marking on the Battery Cover
A battery has a case and a cover, which are marked for traceability to optimize manufacturing and assembly.
B: Battery Cover Surface Roughening
Laser light is used to roughen the adhesion surface of the battery cover and case to improve the bonding strength.
C: 2D Code Marking on Electrodes
2D code marking is becoming widespread. In the past, only battery cases were marked. Now, there's an increasing need to mark individual electrodes along with the case.
Laser Marking on Inverters
Inverters convert stored electricity from DC to AC and supply AC to the motor. Because motors rotate over a wide angle while a vehicle is operated, inverters must meticulously control the supplied electricity.
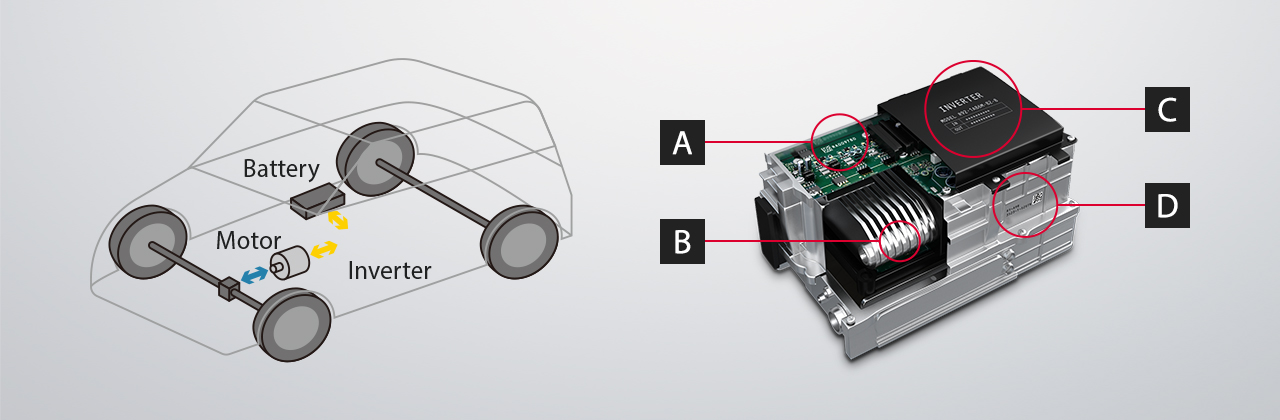
A: 2D Code and Character String Marking on PCB
Glass epoxy PCB marking must be damage-free to prevent particle generation on photo-resist removal.
B: 2D Code Marking on Cooling Device
Marking a 2D code on the cooling device makes it very easy to ascertain the device specifications.
C: Serial Number Marking on the Case Cover
Affixing labels to an inverter's case is common, but labels are expensive to produce and can't accommodate design changes well. Laser markers don't incur running costs and are very easy to adjust.
D: 2D Code and Character String Marking on Aluminum Cast Parts
Cast aluminum cases can vary in size depending on product tolerances. It's important to have a marking system that can compensate for these size changes, otherwise you run the risk of defective, out-of-focus marks that aren't readable.
Laser Marking on Sonar Sensors
These sensors are installed in the bumper and detect obstacles up to about 1 m away. They are used in parking and notify the driver of nearby obstacles.
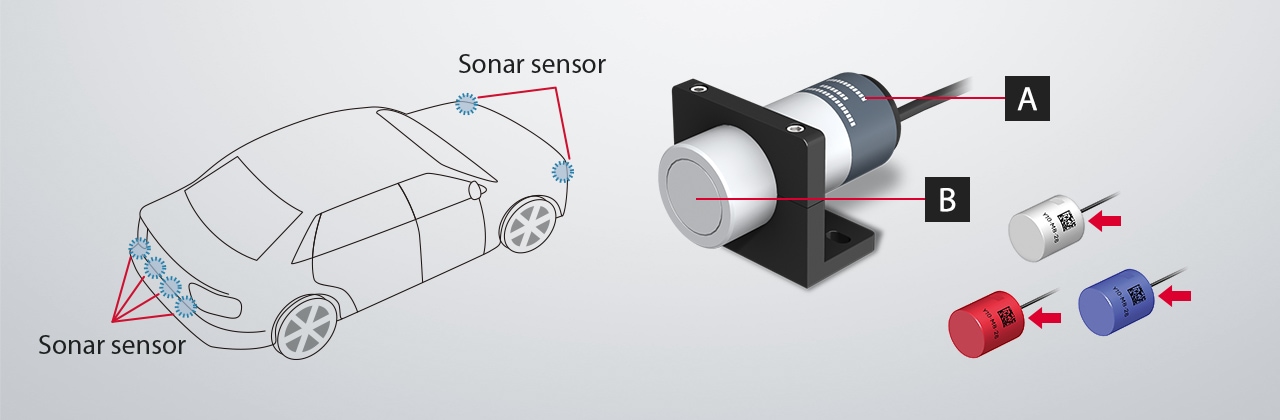
A: Identification Marking on Case
Identification marking is applied to the numerous sonar sensors in the vehicle.
B: 2D Code Marking on Sensor Parts
Sonar sensors come in a wide variety of colors so they can match different colored vehicles. As a result, traceability systems must be able to cleanly mark a wide range of colors in sonar marking applications.
Laser Marking on Front Cameras
Forward vehicle cameras are used to alert the driver of other vehicles, pedestrians and traffic signs. Cameras are good at detecting relatively close objects and can recognize white lines indicating traffic lanes, crosswalks and speed limit signs.
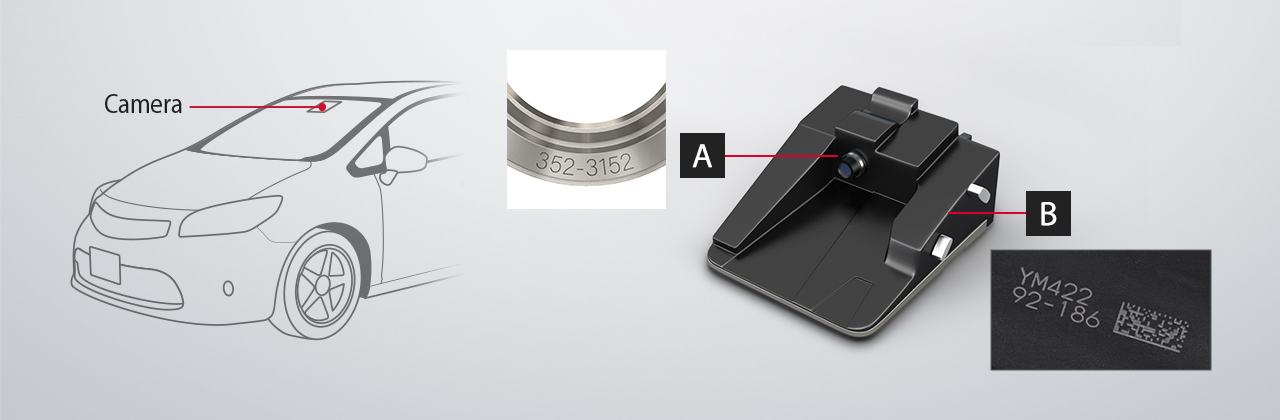
A: Identification Marking on Lens Unit
Identification marks are placed on the ring that fits around the camera lens.
B: Character String and 2D Code Marking on E-coated Parts
Lasers are used to mark e-coated parts on the camera's base. To ensure rust prevention, the marks must not completely remove the paint.
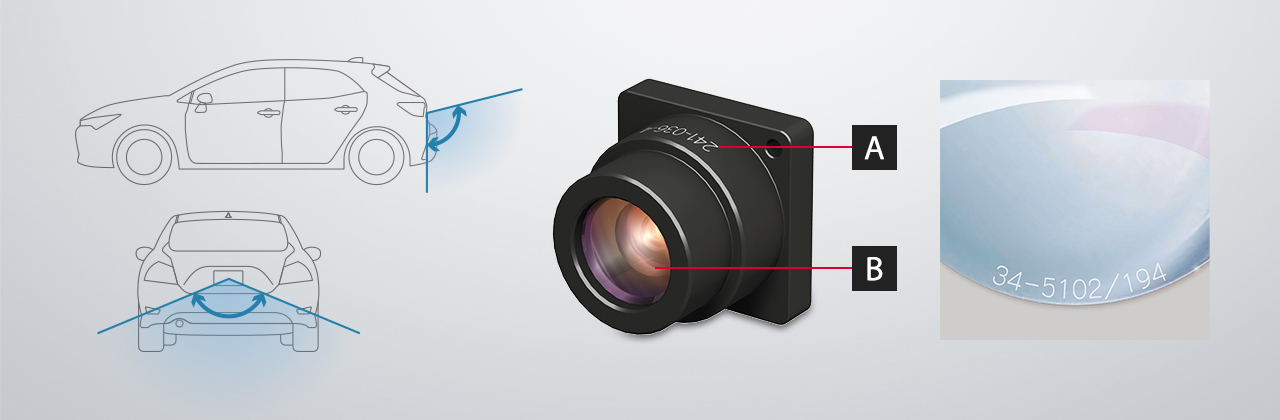
Laser Marking on Rear Cameras
Rear-facing vehicle cameras display the area behind a vehicle. This video feed is displayed on the navigation monitor when the vehicle is backing up. Rear cameras often use CMD lenses because they are able to display the left, right and center areas behind a vehicle.

A: Serial Number Marking on Camera Case
Identification marking is performed to distinguish the installed vehicle model and specifications.
B: Lot Number Marking on Lens
Identification marking is performed on the lens to distinguish the assembled case.
Laser Marking on DC-DC Converters
A DC-DC converter drives electrical components in vehicles such as the headlights, wipers, and audio system by converting stored high voltage to a low voltage direct current. Electrical components in vehicles require more and more power, resulting in a need for increased power capacity and a compact, lightweight design.
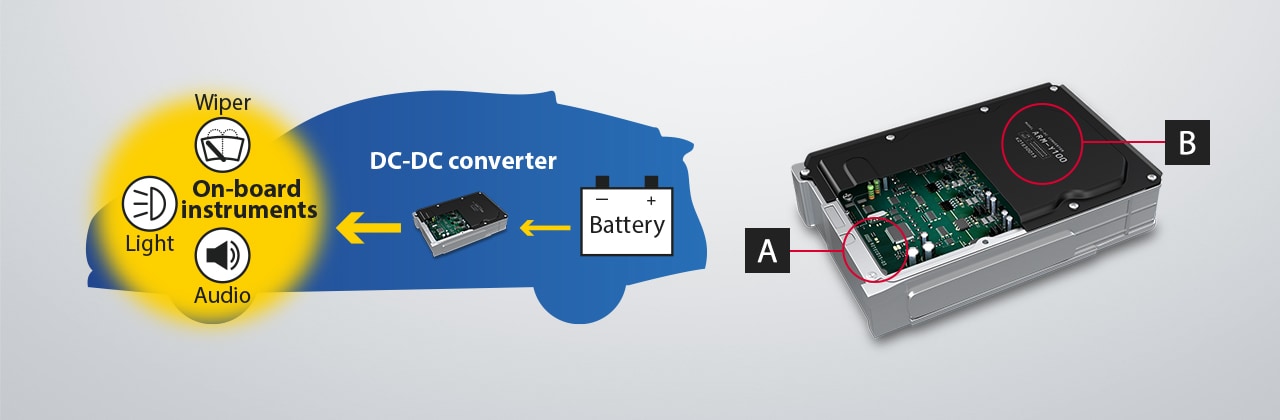
A: 2D Code and Character String Marking on PCB
Glass epoxy PCB marking must be damage-free to prevent particle generation on photo-resist removal.
B: Serial Number Marking on the Case Cover
Conventionally, affixing labels to the case was common, but laser marking is becoming more popular to reduce costs and simplify design changes.
Laser Marking on ECUs
The ECU is the brain of the vehicle, optimizing the movement of the various drive mechanisms. It electronically controls the engine, airbags, transmission, and other parts according to operating conditions. ECU development continues to evolve, with higher levels of control obtained every day.
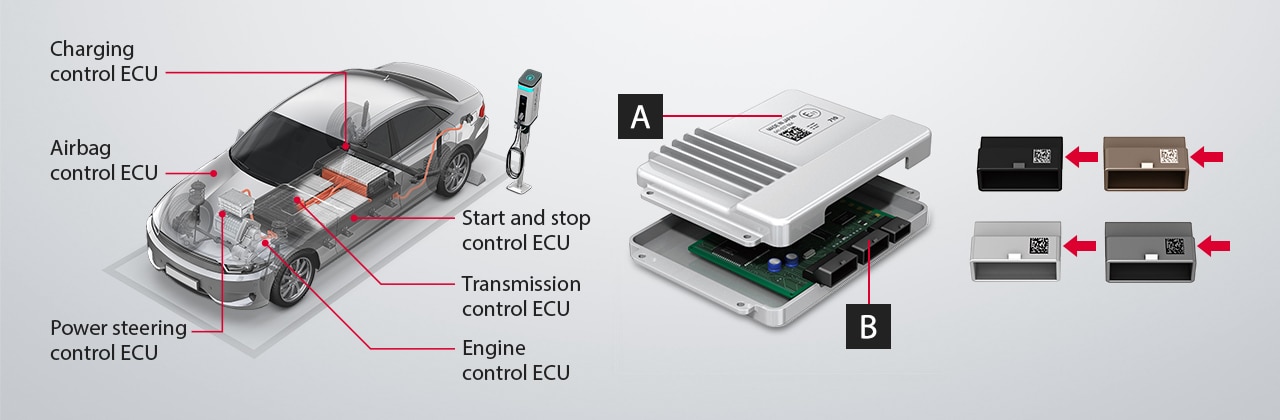
A: Serial Number Marking on the Case Cover
Affixing labels to an ECU's case is common, but labels are expensive to produce and can't accommodate design changes well. Laser markers don't incur running costs and are very easy to adjust.
B: 2D Code Marking for Connector Identification
ECU connectors often use cream-colored and gray resins, which are difficult to mark with infrared lasers. However, UV lasers are capable of producing high-contrast marks on these materials very easily.
Laser Marking on Milliwave Radars
Milliwave radar sensors detect objects in a large area up to 100 m ahead. Forward sensors measure the distance to the preceding vehicle, rear sensors detect vehicles and pedestrians in blind spots, and front sensors help prevent crossing accidents (that commonly occur at intersections).
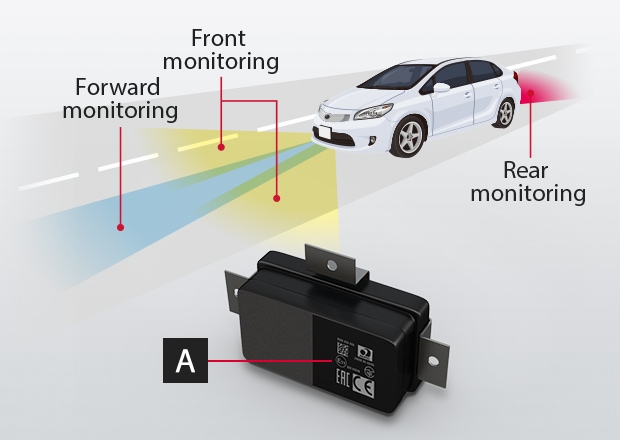
A: Standard Marking on Case
All equipment that emits radio waves (such as a milliwave radar) must obtain standard certifications in each country it will be used. Standard certification marks are added each time a new targeted export country is added. Laser markers are optimized for these applications because they easily adapt to design changes.
The Importance of Direct Marking in the Electric Vehicle Industry
The electric vehicle industry has seen massive growth in recent years. In 2020, EV sales reached 2.1 million units, up from 1.6 million in 2019. This trend is expected to continue, with Bloomberg estimating just over half of passenger cars sold in the US will be electric vehicles by 2030. The industry has also seen rapid expansion in terms of manufacturing capacity.
This rapid growth is being driven by increasing consumer demand, as well as government incentives and regulations. With EVs becoming increasingly affordable and convenient, the need for laser marking in the industry will continually rise.
Because laser marking is permanent and can be done on a variety of materials, it is an ideal choice for EV manufacturers. Direct laser marking (DLM) is a type of laser marking that is done without the need for any intervening material. This makes direct laser marking perfect for marking objects made of heat-sensitive or delicate materials, which are common inside EVs.
The benefits of laser marking in the automotive industry are numerous. Laser marked components are easier to trace and identify, and they are less likely to be damaged or tampered with. In addition, laser marking can be used to add aesthetic appeal to electric vehicles. When considering all of these factors, it is clear that laser marking is an important part of the electric vehicle industry.
As the industry continues to grow, laser marking electric vehicles will play an increasingly important role in ensuring the safety and traceability of their parts. KEYENCE is a worldwide leader in laser marking systems. Contact us today at 1-888-539-3623 to discuss our EV-specific laser marking solutions.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Application Video
Frequently Asked Questions
What materials can be marked in electric vehicles?
Laser marking works on metals, plastics, ceramics, and composite materials used in electric vehicles. The technology can be adjusted to different material properties without damaging sensitive electronic components.
How does laser marking help with EV component traceability?
Laser marking helps with quality control and traceability by permanently identifying battery cells and packs. In the event that safety concerns emerge, manufacturers can promptly identify and recall particular batteries and improve vehicle safety.
Is laser marking suitable for high-speed production lines?
Yes, the latest laser marking systems operate at speeds measured in milliseconds per mark. They easily integrate with automated production systems and can keep pace with even the fastest EV manufacturing lines.
Can laser marking be used for custom branding on EV parts?
Laser marking excels at creating logos, text, and decorative elements on visible EV components. The precise technology creates sharp, detailed markings that look good and stay durable over time.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads

This quick guide introduces the basics of metal marking. Learn why different wavelengths matter and discover the various ways laser light interacts with metal parts.

Choosing the right laser marker wavelength is extremely important for plastic marking. Learn what lasers work best for marking, processing, and coloring plastic in this guide.

2D codes have become a near-universal standard for traceability. This must-read document covers everything from code scanning principles, laser installation, predictive maintenance, and more.

2D codes are used to store date codes, lot codes, serial numbers, and more. Users who are considering 2D code marking should read this laser marking guidebook.

Some laser marking applications require integration with multiple devices. KEYENCE provides a total marking solution, from X/Y stages and indexing systems to head traversal systems. Learn more in this brochure.

This booklet covers a wide range of laser processing techniques - such as cutting, drilling, and deep engraving - as well as welding and soldering that are unique to lasers.







![Laser Marker Application Guide [Electric and Hybrid Vehicles]](/img/asset/AS_108515_L.jpg)




