Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
What is Laser Marking | How Laser Marking Machines Work
Laser marking can be used for marking or processing various types of materials. There are also several different marking and processing methods. Due to the varying capabilities and features of laser marking technologies, this inherently leads to many different applications.
However, the appropriate laser marking system and peripheral equipment vary depending on the material and desired marking or processing method. The laser light being used can also vary. This section introduces the basic knowledge required for performing laser marking.
What is Laser Marking?
Laser marking is a marking method that uses a focused laser beam to alter the surface of a target. This manufacturing technique creates permanent identification marks on surfaces using focused light to alter material properties without removing substantial amounts of base material.
The laser beam is emitted by an oscillator and scanned using a mirror (known as a scanning mirror), and a focusing lens is then used to focus the beam on the target and mark it by altering the surface. Because laser marking involves using light to change the target surface, this method is more resistant to abrasion than ink-based marking, and the marking does not fade over time.
Unlike alternative marking methods, a laser marking machine uses controlled energy to alter surface characteristics. The beam creates marks by oxidation, annealing, or a little bit of material removal, depending on the settings. Because of its adaptability, it can be used for both decorative and industrial purposes.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Key Benefits of Laser Marking
Laser marking creates marks that last forever. These marks won't fade, scratch, or wear away even in tough conditions. Durability like this keeps important information readable throughout a product's life.
Speed makes laser systems popular for busy factories. Modern laser marking machines can mark thousands of parts each hour with consistent results every time. This efficiency cuts costs and gets more work done than old manual methods.
The eco-friendly process also helps companies go green, as laser marking needs no inks, chemicals, or solvents that create waste. This saves money and helps the environment at the same time.
Components of a Laser Marking System
Laser sources are the main part of any marking system. Fiber lasers work best on metals, UV lasers are best for plastics, and CO2 lasers handle wood and leather better. Typically, higher power means faster marking when compared with the same sources.
Control software runs the entire marking process. Modern systems let operators easily import designs, change settings, and watch production. This automation saves time and keeps results consistent.
Industry-Specific Applications of Laser Marking Technologies
The list of industry-specific applications where marking lasers are used is growing year by year. Some of these include:
Engine parts, transmissions, and safety components are tracked by automotive firms via laser marking. Over the course of a vehicle's life, these permanent codes aid in quality control and recalls.
Medical device producers want precise, safe branding for surgical instruments, implants, and equipment. Even after sterilization, laser marks remain readable and comply with strict medical rules.
Electronics manufacturing uses a laser machine for marking to label circuit boards and tiny components.
This brief list of examples doesn’t scratch the surface of where laser marking systems are used. Nevertheless, the points above show how diverse the technology’s applications can be. Because laser markers can work with many materials, it’s easy to see why the technology is relevant to almost any product. While alternative methods have been able to accomplish some impressive feats in manufacturing, the world is demanding change.
From production quality to traceability, consumer satisfaction, laws, and regulations, manufacturers are being forced to adapt to changing times. This is for the better in more ways than one, as learning how laser marking works will lead to better efficiency, cost savings, employee satisfaction, consumer retention, and more.
Different Types of Laser Marking Techniques
A few main options exist for marking surfaces. Annealing gently heats metal surfaces to change their color without melting them. This creates high-contrast marks that stay visible for years while keeping the surface integrity intact.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Laser Marking on Metal
Laser marking can be performed on metal through black-annealed marking, where the laser causes oxidation; white marking, where the laser is used to scrape away the target surface; and engraving, where the laser is used to carve deep into the target surface. Each method is used for a specific purpose. This section explains the characteristics of each method, providing additional insight into how laser marking works from several angles.
Black-annealed (oxidation) Marking

When the laser beam is applied to the marking target, the focus is shifted so that only the heat will be conducted. Applying heat without engraving the target forms an oxide film on the surface. This film appears black and represents black marking.
White Etching Marking

The laser beam is applied to the marking target at the focal point. The metal surface is slightly removed to expose an uneven surface. This causes irregular reflection of light to create markings that appear white.
Engraving Marking

Laser light irradiates the focal point and etches the surface of the target for marking. A deeply engraved impression can be made by increasing the amount of engraving by increasing the laser irradiation count.
Metal Marking Machine
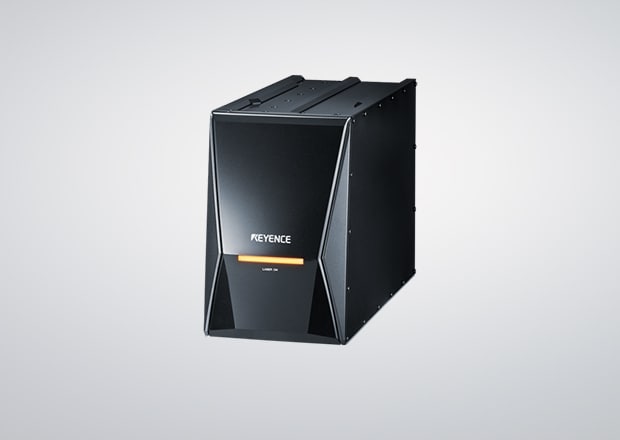

3-Axis Hybrid Laser Marker MD-X Series
The 3-Axis Hybrid Laser Marker MD-X Series combines the strengths of a conventional fiber laser with those of a YVO4 system. Fiber lasers are designed for long service life and high output power for high-speed marking and deep engraving applications. YVO4 lasers are designed for high quality, delicate marking and increased depth of focus for flexibility. Together, these lasers create the MD-X with high peak power and a short pulse laser.
Combining these 2 marking methods creates a laser that is powerful enough to meet stringent cycle time requirements, but also robust enough to achieve quality markings on any metal. Paired with KEYENCE's 3-Axis control, full field auto-focus, and automatic position adjustment, the MD-X Series is ideal for any metal marking need.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Laser Marking on Plastic
There are three patterns for marking on plastic using a laser: Foaming, where the laser causes bubbling; chemical change, where the laser reacts with the pigments in the plastic; and carbonization, in which a high-energy laser is applied to the target surface.
Foaming

When the base material is irradiated with a laser, bubbles are generated inside the material. These bubbles are sealed under the surface layer of the base material, causing them to appear white. Foaming is more visible on darker base materials.
Foaming heats plastic materials to create light bubbles inside without burning. This makes bright marks on dark plastics while keeping surfaces relatively smooth.
Chemical Change

As the laser light reacts with the metal ions in the base material pigment, a chemical change occurs, resulting in color development. The appearance varies depending on the color and material of the target.
Carbonization

When high energy is continuously applied to an area, macromolecules of the element around the base material are carbonized and turn black. The polycarbonate material shown above is transparent but produces a beautiful black color when carbonized.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Laser Marking Be Used on Curved or Irregular Surfaces?
Yes, a laser marking machine can mark curved and irregular surfaces with the right setup. Many systems include rotary attachments for complex shapes, whereas KEYENCE laser markers have built-in 3-axis that can accommodate curved or irregular shapes without the need for additional attachments.
How Long Does a Typical Laser Mark Last?
Laser marks are permanent and last the product's entire lifetime when done correctly. Most marks stay readable for decades and resist fading, scratching, and chemicals.
Is Maintenance Required for Laser Marking Systems?
Laser systems need very little maintenance compared to other marking methods. Regular cleaning and occasional part replacement keep them running well. Some systems can even alert you when maintenance is needed.
What Materials Can Be Marked Using Laser Technology?
Lasers marking machines can mark almost any material, including metals, plastics, glass, wood, and leather. Fiber lasers work best on metals, while CO2 lasers handle organic materials better.
What Are the Main Types of Laser Marking?
The three main types are laser marking (color change), laser etching (material expansion), and laser engraving (material removal). Each works differently depending on what your goals are.
Is Laser Marking Suitable for High-Volume Production?
Yes, laser systems are ideal for high-volume production. They can mark thousands of parts per hour with consistent quality and minimal setup time.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads

This quick guide introduces the basics of metal marking. Learn why different wavelengths matter and discover the various ways laser light interacts with metal parts.

Choosing the right laser marker wavelength is extremely important for plastic marking. Learn what lasers work best for marking, processing, and coloring plastic in this guide.

2D codes have become a near-universal standard for traceability. This must-read document covers everything from code scanning principles, laser installation, predictive maintenance, and more.

2D codes are used to store date codes, lot codes, serial numbers, and more. Users who are considering 2D code marking should read this laser marking guidebook.

Some laser marking applications require integration with multiple devices. KEYENCE provides a total marking solution, from X/Y stages and indexing systems to head traversal systems. Learn more in this brochure.

This booklet covers a wide range of laser processing techniques - such as cutting, drilling, and deep engraving - as well as welding and soldering that are unique to lasers.



