Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
EV Laser Marking Applications
-
Tags:
- Electric Vehicle , Laser Cleaning , Laser Labeling
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular as the demand increases for cleaner, safer, and environmentally friendly alternatives to gas vehicles. Because of the newness of EVs, traceability and manufacturing efficiency is essential. As such, laser-marking electric vehicles is a critical task in the booming EV industry.
EVs are known for their lightweight parts that increase energy efficiency. Manufacturers are using materials such as aluminum, resin, and glass epoxy instead of heavy materials like steel. However, lightweight materials can be delicate and prone to heat damage.
EVs have several internal components that need to be marked, including batteries, DC-DC converters, inverters, and ECU connectors. UV laser electric vehicle marking provides permanent, damage-free, and high-contrast marking for traceability and assembly. In this article, we discuss each of the parts and how a UV laser marking machine can be an essential tool for marking.
EV Internal Parts : Batteries, DC-DC Converters, ECU, and Inverters
Batteries
Batteries are the backbone of electric and hybrid vehicles. They are the power source instead of a gas engine.
EV batteries gain power through charging stations or vehicle deceleration. The most common type of battery used for EVs is made from lithium-ion due to its high energy capacity, compact size, and lightweight design.
Laser marking parts of lithium-ion batteries is essential for identification, use, assembly, and traceability purposes. Lithium-ion batteries should have 2D codes, serial numbers, and rough surface adhesion to improve bonding strength.
Serial numbers can provide information about the vehicle the battery is used in, the date it was manufactured, and the manufacturer’s identity. All of this information can be useful for recalls or supply chain management. 2D codes are particularly useful as they can be scanned to easily access this information. Additionally, 2D codes are beneficial for assembly purposes. They can signify how to put a battery together by markings or be scanned for assembly instructions. Because of how lightweight lithium-ion batteries are, they are easily damaged if marked too harshly.
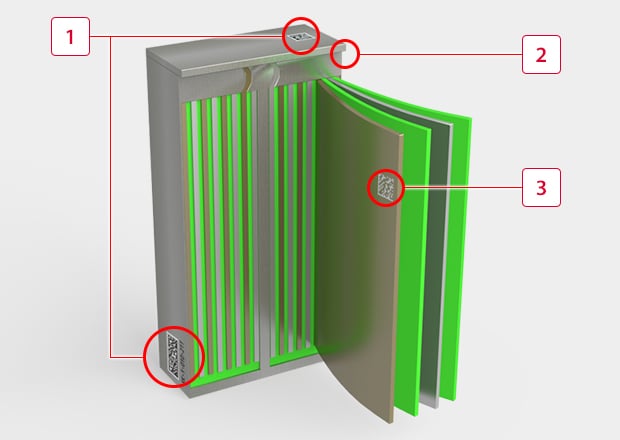
-
12D code and serial number marking on the battery cover : The battery is composed of a case and a cover, which are marked for traceability to be manufactured and assembled more efficiently.
-
2Battery cover surface roughening : Laser light is used to roughen the adhesion surface of the battery cover and case to improve the bonding strength.
-
3Electrode 2D code marking : 2D code marking is becoming more widespread not only on battery cases but also on the electrodes themselves. Damage-free marking is required on copper materials.
DC-DC Converters
A DC-DC converter is a device made from glass epoxy PCB that converts high-voltage DC from an EV’s battery supply into low-voltage DC electricity. DC-DC converters power EV instruments such as headlights, windshield wipers, and audio systems.
To identify and track DC-DC converters for supply chain management and assembly, serial number marking and 2D codes are necessary. Similar to batteries, the 2D code can give insight into a DC-DC converter's manufacturing history. Additionally, serial numbers created by character marking can also be helpful in aligning a DC-DC with the correct EV.
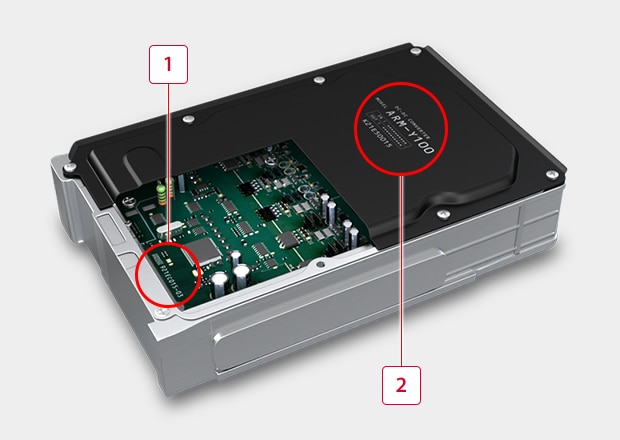
-
1PCB 2D code and character marking : Glass epoxy PCB marking. This requires damage-free marking to prevent the production of foreign particles when the resist is removed.
-
2Serial number marking on the case cover : In the past, it was common to affix labels to the case, but laser marking is becoming more popular to reduce costs and simplify design changes.
Inverters
An inverter is a device made of glass epoxy PCB that converts DC electricity stored in a battery into AC electricity. This AC electricity is used to power a synchronous motor, which controls the flow of electricity. The flow of electricity powers the car and allows it to move.
Inverters need 2D code marking on two parts : the aluminum cast and the cooling equipment. Both of these parts need 2D marking for identification purposes because of the variety of specifications. Cooling equipment can vary with the same type of inverter, so 2D marking ensures the correct form. Additionally, an aluminum cast must be identified by millimeters depending on product tolerance.
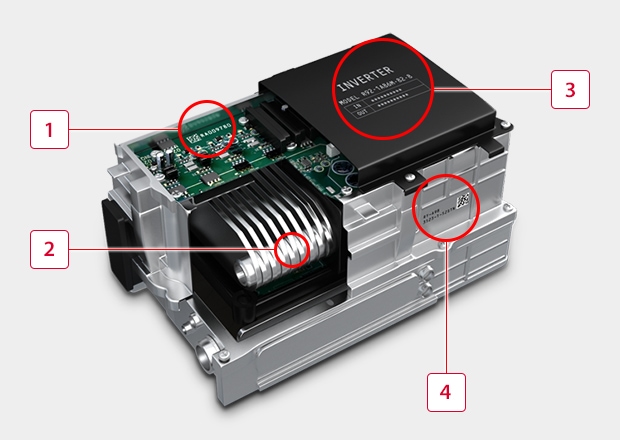
-
1PCB 2D code and character marking : Glass epoxy PCB requires damage-free marking to prevent the production of foreign particles when the coating is removed.
-
22D code marking on cooling equipment : By marking a 2D code on the cooling equipment installed on the inverter, it is possible to ascertain specifications of the equipment.
-
3Serial number marking on the case cover : In the past, it was common to affix labels to the case, but laser marking is becoming more popular to reduce costs and simplify design changes.
-
42D code and character marking on aluminum cast parts : The size of cases cast from aluminum can vary by millimeters depending on product tolerance. Many types of cases must be able to be read by a handheld reader, which requires laser marking without defects as a result of being out of focus.
ECU
As EVs evolve, it is likely that ECU capabilities will also evolve and grow.
ECUs need to be marked with both a serial number on the case cover and a 2D code for connector identification and traceability purposes. ECU connectors are often made from cream-colored and gray resin. Because the resin is heat-sensitive and fragile, damage free marking is essential.
ECU connectors control many aspects of an EV, such as :
- Engines
- Airbags
- Power steering
- Transmission
- Stop/Start
- Charging
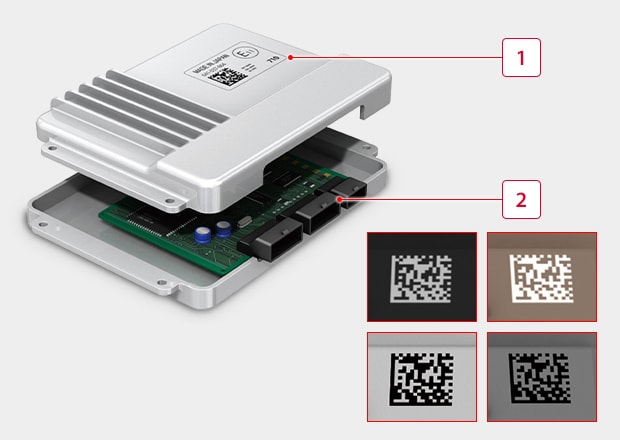
-
1Serial number marking on the case cover : In the past, it was common to affix labels to the case, but laser marking is becoming more popular to reduce costs and simplify design changes.
-
22D code marking for connector identification : ECU connectors often use cream-colored and gray resin, which are difficult to mark with IR laser markers, so a UV laser with high contrast marking is effective.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Tips for Laser Marking on Internal Parts
The best laser for laser marking on EV batteries is a UV laser marking machine. UV lasers have a higher absorption rate than fiber lasers, due to their shorter wavelength, so they can mark parts through photolytic degradation as opposed to relying on the thermal (heat) effect. Because of this high absorption rate, a UV laser can be used on a variety of materials, including resin, plastic, rubber, metals, and glass.
KEYENCE recommends the 3-Axis UV Laser Marker MD-U Series because of its extra features that make it optimal for EV parts.
The high absorption rate of the MD-U Series is also optimal for creating high contrast markings. The MD-U Series specializes in 2D codes, character marking, and serial numbers, which are all essential markings for EV parts. Another aspect of EV parts is their fragile materials and need for damage-free marking. The MD-U’s reduced heat allows for perfect finishes on materials.
Batteries, ECUs, inverters, and DC-DC converters are small and complex-shaped designs. Unlike a conventional laser, the MD-U Series has a 3-Axis control that creates distortion-free marking. This eliminates the need for external equipment, like rotaries, and additional communication that conventional lasers need to mark non-flat geometries. The 3-Axis control uses a variable lensing system to adjust the focal distance which creates the same shape and thickness from edge to edge of the marking field.
The MD-U also has a software called the Marking Builder 3 that has an easy-to-use graphical interface. It understands a variety of targets, including 3D stepping heights, inclines, cylindrical, and cone targets. The software will check the alignment of the 3D parts with on-screen guidance and mark curved or flat moving targets. The 3-axis component of the MD-U also allows it to auto-focus on each target to eliminate mismarking and distortion.
Most importantly, the MD-U provides electric vehicle marking that is resistant to environmental contamination. Resisting contamination is extremely necessary when creating marks for parts, as extra residue can harm the vehicle.
Conclusion
It’s clear that laser marking electric vehicles and their parts have helped EV manufacturers with traceability objectives. However, not all laser marking machines are created equal, so it’s essential to be particular about the laser marking you use on any internal EV part. Accordingly, the benefits of using KEYENCE’s 3-Axis Control UV Laser Marker MD-U Series have been realized by many.
The 3 Axis Control UV Laser Marker is the world's first of its kind and can easily follow the evolving trends of the EV industry. Additionally, KEYENCE’s MD-U laser marking machine comes with one-click language switching and support on both a local and national level for anywhere your manufacturing takes place.
If you still have questions about laser marking EVs, simply ask KEYENCE, and our knowledgeable team will get back to you quickly. We support our customers during the selection process, through operations with on-site operating instructions, as well as with industry-leading after-sales support.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads

This quick guide introduces the basics of metal marking. Learn why different wavelengths matter and discover the various ways laser light interacts with metal parts.

Choosing the right laser marker wavelength is extremely important for plastic marking. Learn what lasers work best for marking, processing, and coloring plastic in this guide.

2D codes have become a near-universal standard for traceability. This must-read document covers everything from code scanning principles, laser installation, predictive maintenance, and more.

2D codes are used to store date codes, lot codes, serial numbers, and more. Users who are considering 2D code marking should read this laser marking guidebook.

Some laser marking applications require integration with multiple devices. KEYENCE provides a total marking solution, from X/Y stages and indexing systems to head traversal systems. Learn more in this brochure.

This booklet covers a wide range of laser processing techniques - such as cutting, drilling, and deep engraving - as well as welding and soldering that are unique to lasers.






