Industrial Laser Marking Systems / Laser Markers
Laser Marking on Die-Cast Components: An Introduction to the Process and Materials Involved
-
Tags:
- Laser Marking , Laser Engraving , Automotive
Laser marking is a popular method for permanently marking a range of materials because of its precision, flexibility, and ability to automate. In fact, laser marking machines can even mark difficult products like die-cast components.
Die-cast components are made from molten metal—typically aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, magnesium alloy, or copper alloy—and poured into a precision mold under pressure. These components are used because of their dimensional stability, ability to form complex shapes, durability, and high production rate. Die castings are commonly used as the skeletons for planes and cars but can quickly lose strength if processed incorrectly.
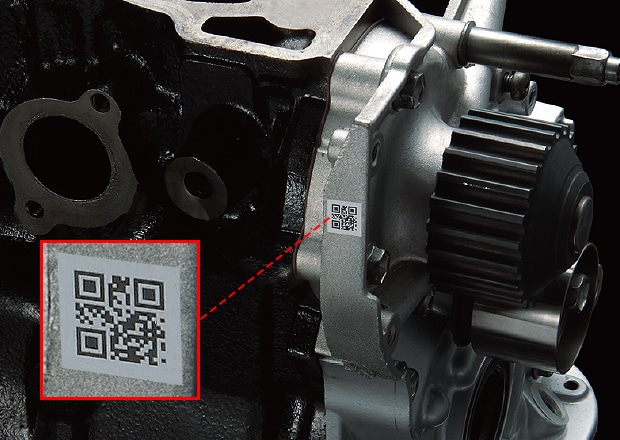
Since die-casting components are so susceptible to deformities, marking dies and/or casted components with traceability marks is key for accountability. Die-cast components rely on 2D codes for traceability to ensure effective recall, supply chain tracking, and quality assurance.
Marking of these components can often present a plethora of issues. Due to the complex shapes and sensitivity, laser markers have become a preferred method of combatting these concerns. Marking these parts with lasers provides a precise and permanent mark that does not require physical contact with the product and will not change any of the material properties. The 3-Axis control featured in all of KEYENCE's laser systems even allows for marking in hard to reach or odd-geometry areas where conventional laser systems would struggle to maintain focus.
Learn more about the complexities of die-cast components, from surface finish to material type to marking depth, in this blog. We will also introduce you to applications of die-cast components in industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.

Considerations for Laser Marking on Die-Cast Components: Surface Finish, Material Type, and Marking Depth
Surface Finish Considerations
Die-cast components wear easily and are susceptible to deformities. In high-stakes industries like aerospace and automotive, considering these surface finish problems is crucial when marking dies. In particular, friction and corrosion are detrimental to the performance of die-cast components. Because of these vulnerabilities, ensuring that your marking technology does not pose a threat to the product. Systems like KEYENCE's MD-X Hybrid laser Series ensures that there is no thermal damage to the part by controlling the level of heat being applied.
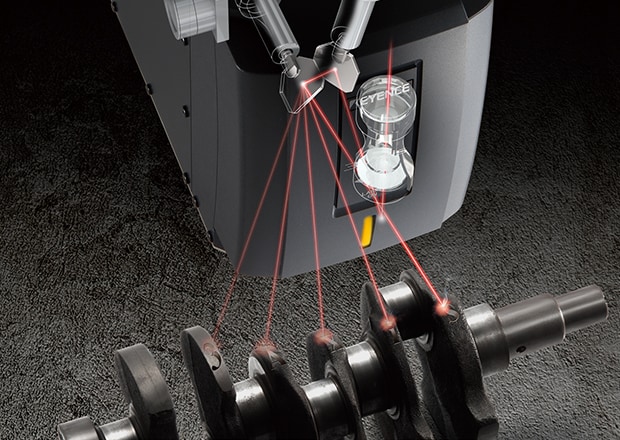
Perfectly focused marks are able to be applied to any surface in the valid marking range. Uninterrupted marking can be performed even on different surfaces without changing fixtures or moving the part.
Material Type Considerations
Die-cast components are made from metals with low melting points, like aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, and magnesium alloys. Steel casings are sometimes put over these components for increased corrosion resistance. Considering these material types is necessary when moving forward with laser marking.
Another material type condition to consider for marking is the shape and size of die-cast components. Die-cast components are widely used because of their flexibility. Components range in shapes and sizes from small and rectangular in the electronics industry to large airplane parts in the aerospace industry.
KEYENCE’s laser markers feature 3-axis control, autofocus, and surface fitting function, meaning they have a superior ability to mark complex parts that conventional lasers may struggle with. The surface fitting function analyzes the component shape and adjusts the Focal point of the laser accordingly, allowing the laser to variably change where it comes to focus, ensuring a quality mark regardless of the shape.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Applications of Laser Marking on Die-Cast Components: Industries and Use Cases
Automotive Industry Applications
The majority of all die-cast components are used in the automotive industry, particularly aluminum alloy die-casting. Aluminum alloy is known for high electrical and thermal conductivity, high corrosion resistance, lightweight, high strength, low cost, and high recycling ability.
Common applications of die-cast components in the automotive industry include cylinder blocks, transmission cases, and rocker covers. Each of which is often marked with some sort of traceability (2D code, part numbers, etc.).
Aerospace Industry Applications
The aerospace industry and automotive industry have similarities when it comes to die-cast components. The aerospace industry also uses aluminum alloy frequently for die-casting for all the same reasons that the automotive industry does. An example of aerospace die-casting components is aluminum airplane frames.
Electronics Industry Applications
Unlike the aerospace and automotive industry, the electronics industry typically uses small die-cast components. Some examples of die-casting components in the electronics industry include electronic control panels, servo drives, flow meters, and PC board assemblies.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Learn More About Die-Cast Components
Die-casting is a tricky manufacturing process that is the backbone of industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Since die-cast components are so susceptible to defects, making sure you have adequate traceability is essential. Using a laser marker for traceability on die-cast components ensures that you won’t have any more defects than needed.
Ready to learn more about how to integrate laser marking into your die-cast components? Contact KEYENCE, and our expert sales team will discuss with you how laser marking can be a great fit for your die-cast components.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Related Downloads

This quick guide introduces the basics of metal marking. Learn why different wavelengths matter and discover the various ways laser light interacts with metal parts.


![MARKING APPLICATIONS - Component Traceability in Automotive Manufacturing [Engine Compartment]](/img/asset/AS_46961_L.jpg)


