Digital Microscopes
Observation and Measurement of Food Containers and Packaging Using Digital Microscopes
As the scale of supermarkets and other retail stores expands, and convenience stores increases, the variety of food containers and packaging is growing more diverse. This section provides an overview of food containers and packaging and introduces examples of their observation using a digital microscope.
Purposes of Food Containers and Packaging
Food containers and packaging are used for the following purposes.
- Prevention of spoiling
Sealing food in an airtight container prevents spoiling by ensuring that the food is not exposed to oxygen. - Ease of distribution
The improved thermal insulation and strength provided by food containers and packaging make it easier to distribute food by preventing deterioration and damage. - Health and safety
Helps prevent contamination by foreign particles, ensuring health and safety even if consumers touch the food directly with their hands. - Ease of use
Food containers and packaging are shaped to make their contents easy to remove while also having improved stability that makes it difficult for their contents to spill out. - Environmental consideration
Food container and packaging materials are recyclable. - Information transmission
Display information on the food they contain, transmitting this information to consumers. This displayed information improves the effectiveness of advertising for sales promotion.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Typical Food Container Materials and Features
Typical food container materials, features, and applications are as follows.
- Polystyrene
Used in room-temperature applications, this material has excellent stiffness and good formability.
Heat resistant temperature : 80°C (176°F) - Foamed polystyrene
Used in room-temperature applications, these containers have excellent stiffness, good formability, moisture-retaining properties, and thermal insulation properties.
Heat resistant temperature : 80°C (176°F) - Polypropylene
This material is resistant to oil and heat and can be used in microwaves.
Heat resistant temperature : 110°C (230°F) - Foamed polypropylene
The foaming process provides this material with thermal insulation properties, allowing consumers to hold hot food contained in this material in their hands.
Heat resistant temperature : 130°C (266°F) - Polypropylene with filler
This material is resistant to oil and heat and can be used in microwaves.
Heat resistant temperature : 130°C (266°F) - Amorphous polyethylene terephthalate
Although this material is weak to heat, it is transparent and resistant to oil and is used in applications such as salad and side dish containers.
Heat resistant temperature : 60°C (140°F) - Polylactic acid
A biodegradable plastic made from plants, this eco-friendly material helps reduce CO2 emissions. After they are used, products made from this material are broken down into water and carbon dioxide by microorganisms. This material has excellent transparency and is used in salad and cut fruit containers.
Heat resistant temperature : 50°C (122°F)
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Typical Food Packaging Types, Features, and Applications
Various types of food packaging are available. Typical food packaging types, features, and applications are as follows.
- Pillow packaging
In pillow packaging, the film is shaped into a tube, sealed, and then the base is welded to cut the package free. An inert gas such as nitrogen, carbon dioxide, or a mixture of these gases is then enclosed in the package.
Application : Snack food - Vacuum packaging
The package is sealed with its interior close to a vacuum state, preventing oxidation and the generation of aerobic bacteria.
Applications : Ham, bacon, and sausages - Deep-draw packaging
The bottom material is thermal shaped into the container, the contents are inserted, and then the air within the container is removed via the process that thermocompresses the top material, resulting in a vacuum seal.
Applications : Ham, bacon, and sausages - Skin packaging
This is a type of vacuum packaging in which a film is placed on top of the contents and a piece of backing paper, and then the film is heated to form a gapless seal. This hermetic seal prevents drippage from the food, allowing for later expiration dates.
Applications : Meat and dried food - Top seal packaging
Film is used as the lid to the container. Applying heat to the top seal pressure bonds it to the container.
Applications : Jello, pudding, and tofu - Shrink wrapping
Thermal contracting film is used to package products with a tight seal that matches the product shape.
Applications : Frozen pizza, multipack yogurt, instant noodles sold in a cup, alcohol sold in a box
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Observation and Measurement Examples of Food Containers and Packaging Using a Digital Microscope
These are the latest examples of observation and measurement of food containers and packaging using KEYENCE’s VHX Series 4K Digital Microscope.
Observation of foreign materials on food trays
Optical Shadow Effect Mode can be used to observe three-dimensional images of foreign particles.
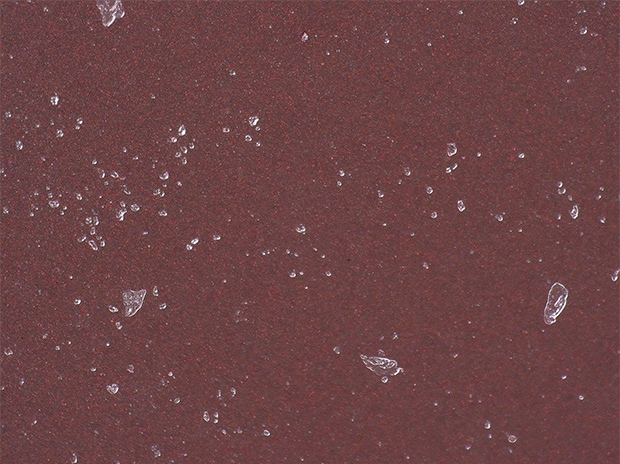
ZS-200, 500×, ring illumination, normal image
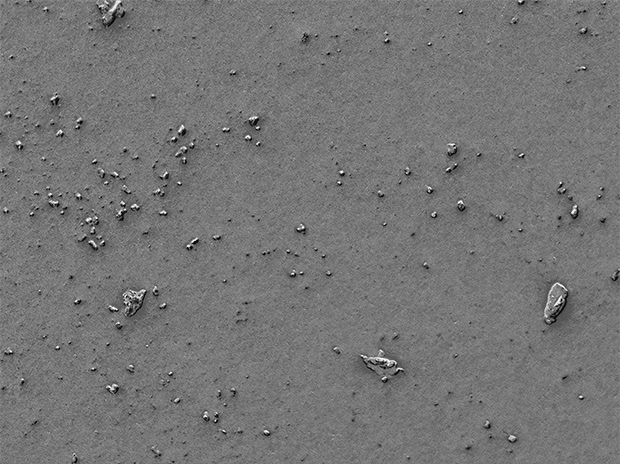

Optical Shadow Effect Mode image
Observation of the surface of the foaming agent for food containers
The Multi-lighting function can be used to visualize microscopic irregularities on the surface of the foaming agent.
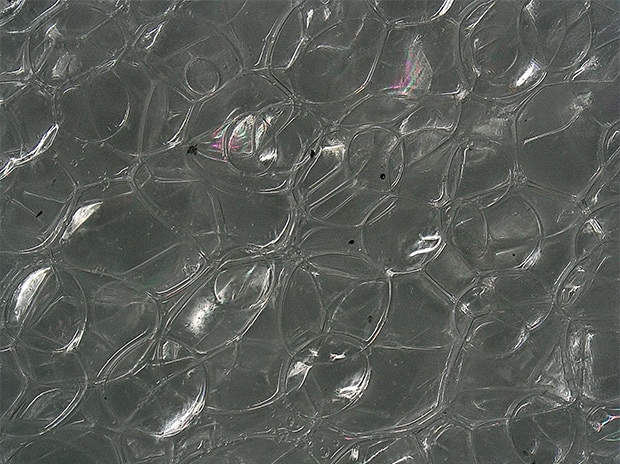
ZS-200, 200×, ring illumination, normal image
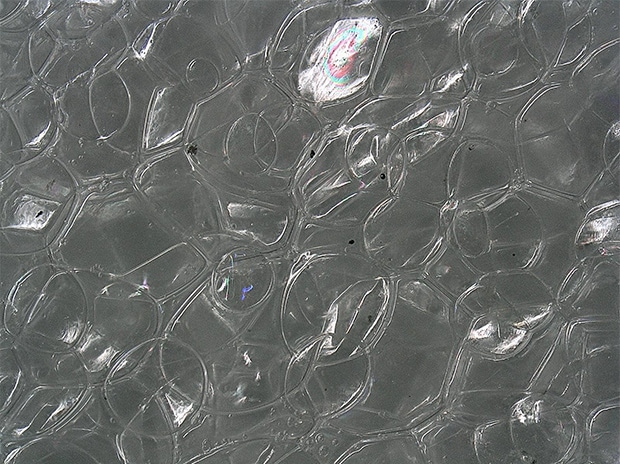
Multi-lighting image
Observation of foreign particles in food containers
The polarizing filter can be used to suppress the influence of surface scratches.
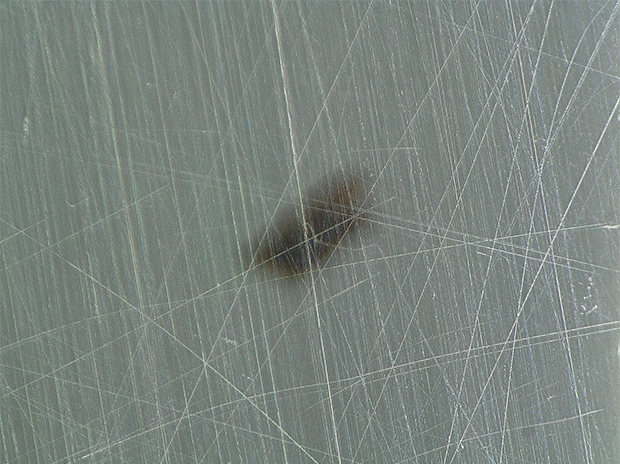

VH-Z20, 200×, ring illumination, normal image
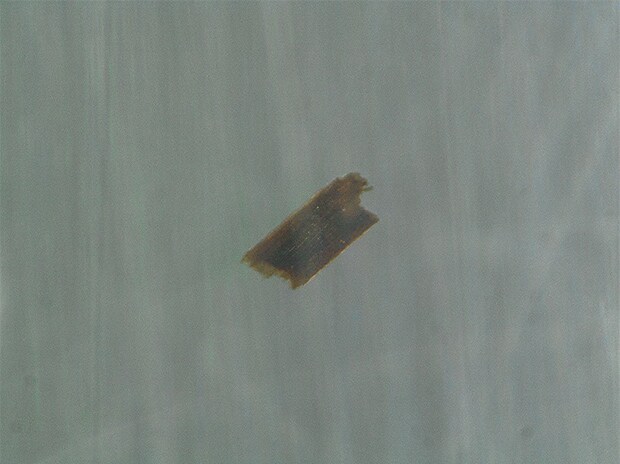

Ring illumination + polarizing filter image
Observation of foreign particles on food containers
The ring-reflection removal function can be used to suppress the influence of glare from the surface of the container.
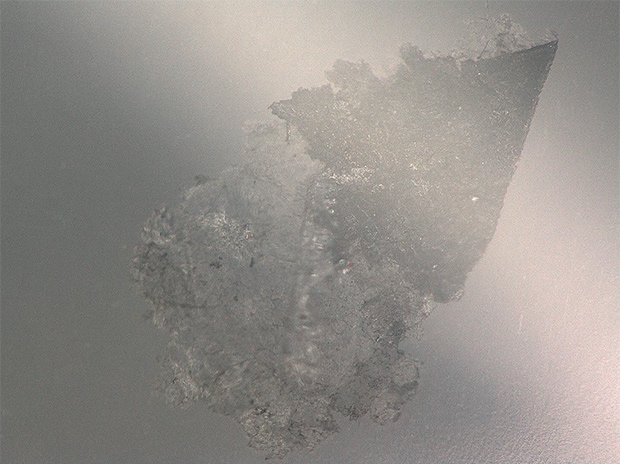

VH-Z20, 150×, ring illumination, normal image
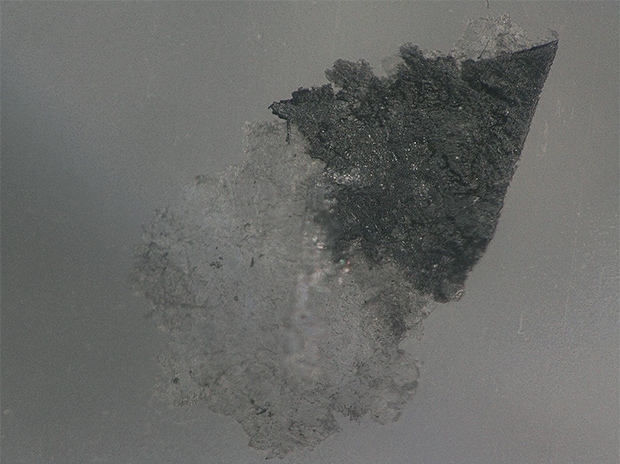

VH-Z20, 150×, image after ring-reflection removal
Observation of the surface of food packaging film
The Multi-lighting function can be used to suppress the influence of glare from the surface of the film.
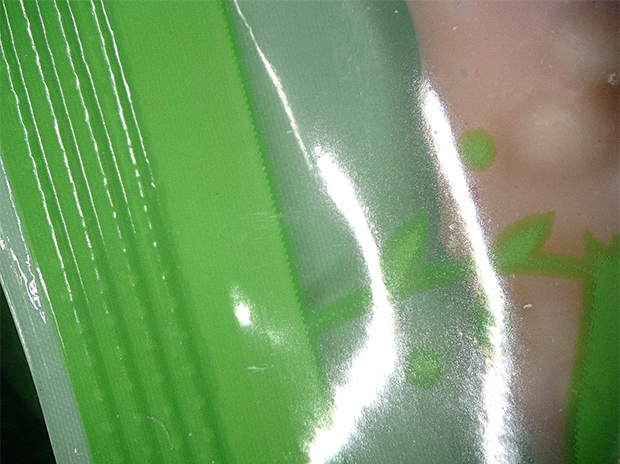

ZS-20, 20×, ring illumination, normal image
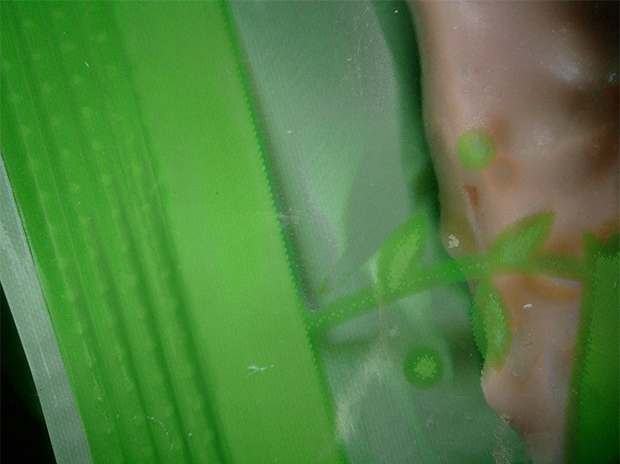

ZS-20, 20×, Multi-lighting image
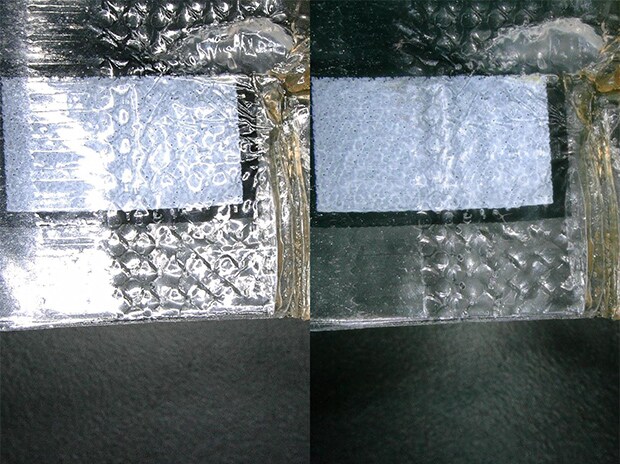
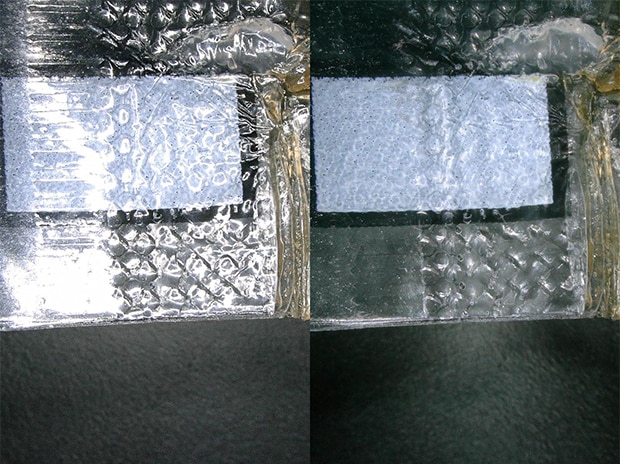
VH-Z20, 20×, ring illumination
left : normal image, right : image after ring-reflection removal
Observation of food packaging film leakage
The ring-reflection removal function can be used to suppress the influence of glare from the surface of the film.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog




