CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
8 Plastic Fabrication Methods & How They Are Used
Key Takeaways
- Eight core plastic fabrication methods: molding, machining, extrusion, thermoforming, welding, lamination, pultrusion, forging.
- Choose method by material: thermoplastics (molding, welding, extrusion, blow, vacuum) vs thermosets (thermoforming, lamination, compression).
- Use portable CMMs for 3D/GD&T in‑machine inspection; reduce part transport and distortion.
- Non‑contact optical comparators suit plastic parts <1 ft; prevent touch‑induced distortion and enable fast QC.
- Shift to in‑process/in‑machine inspection (laser scanner/CMM) to find defect sources early and cut scrap.
The plastic industry reached a $609.1 billion market size in 2022 with expectations of future growth. Why? Plastic is affordable and flexible, making it ideal for so many different plastic fabrication methods, components, applications, and industries.
What is Plastic Fabrication?
Plastic fabrication encompasses the design, manufacturing, and assembly processes involved in plastic manufacturing methods. Almost every plastic product goes through some form of fabrication.
There are eight main types of plastic fabrication: molding, machining, extrusion, thermoforming, welding, lamination, pultrusion, and forging. Let’s take a look at each method to help you decide which is best for your applications.
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Plastic Fabrication Methods
1.Plastic Molding Fabrication
- Compression Molding
- Compression molding is a method that works by heating plastic inside of a mold and compressing it with a power presser to form a product.
- Rotational Molding
- Rotational molding is a method that makes a product by putting heated powdered plastic inside a mold and rotating it. When the mold rotates, the heated plastic sticks and layers against the mold’s internal walls.
- Injection Molding
- Injection molding is a process where a hopper shoots melted plastic into a mold, the machine cools it in place and then ejects it.
- Blow Molding
- Blow molding works by placing a molten thermoplastic tube—also known as a parison—into a mold. Then, pressurized air is “blown” onto the parison and the parison expands inside of the mold. When the parison expands, it sticks to the internal walls and creates a hollow product.
- Vacuum Casting
- Casting also uses a mold but in a different way. The mold, made of silicone, is filled with urethane. The mold is then sealed and a technician uses a vacuum to suck out the air pockets and bubbles. When the bubbles are sucked out, the mold is finalized in the oven and results in a sleek surface.
2.Plastic Fabrication Machining
Plastic Fabrication Machining is used to shape a hard plastic piece by cutting, drilling, or shearing.
3.Extrusion Plastic Fabrication
Extrusion is a process that heats plastic and then pushes it through a die to shape it.
4.Thermoforming Plastic Fabrication
Thermoforming combines various fabrication processes like vacuum casting. It forms plastic sheets instead of a shaped mold.
5.Plastic Welding
Plastic welding is similar to metal welding. The process involves pressing two plastic pieces together, heating them to create a molecular adhesion bond, and then cooling them for the final adhesion.
6.Lamination Plastic Fabrication
Lamination is when at least two layers of plastic film are held together by covering another material.
7.Pultrusion Plastic Fabrication
Pultrusion is the process of pulling plastic fibers through liquid resin and a heated metal die. It works to create fiber-reinforced plastics with constant cross-sections.
8.Forging Plastic Fabrication
Forging is the process of forming a plastic shape by hitting it with intense force.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Applications for Plastic Fabrication
Each plastic fabrication method has compatible applications with either thermoplastic or thermoset plastic.
Thermoplastic Plastic Fabrication Methods
Thermoplastic is a type of plastic that can be softened, melted, and reshaped many times to make new products. If you work with thermoplastic, then you can use molding, welding, forging, extrusion, or vacuum casing.
- Injection Plastic Molding Fabrication
- Injection molding is ideal for making a high volume of custom-made thermoplastic parts. Injection fabrication makes car parts, medical devices, special tools, and bottle caps.
- Plastic Welding
- Plastic welding adheres two thermoplastic parts together. This is commonly used for conjoining plumbing pipes.
- Forging
- Forging shapes thermoplastic parts into tools or kitchen cutlery.
- Rotational Plastic Molding Fabrication
- Rotational molding makes large, hollow products like tanks, playground slides, and bins. This plastic fabrication method has low tooling costs and is straightforward.
- Blow Plastic Molding Fabrication
- Blow molding works with thermoplastics to make hollow products with thin walls. This includes products like soda, water, and sauce bottles.
- Extrusion
- Extrusion makes basic geometrical shapes like rectangles, squares, and spheres. Extrusion products include gutters, pipes, straws, tubes, and window frames.
- Vacuum Casting
- Vacuum casting is ideal for thermoplastic projects that need an extra smooth surface texture. Since it produces a sleek surface, it’s popular for transparent or opaque products.
Products made from vacuum casting include items such as phone cases, display cases, plastic storage boxes, and refrigerator liners.
Thermoset Plastic Fabrication Methods
Thermoset plastics can be molded, but only once, as it utilizes a polymer that is irreversibly hardened by heat. They cannot be recycled into new products. If you work with thermosets, you use thermoforming, laminating, or compression.
- Thermoforming
- Thermoforming works well for low production volumes of auto parts.
- Lamination
- Lamination is good for improving the durability or cosmetics of labels, packages, and prints.
- Compression
- Compression plastic fabricating creates high volumes of small parts and is known for its ability to make complex shapes.
- Pultrusion
- Pultrusion plastic fabrication makes flat bars and tubes out of thermosets.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Plastic Fabrication Machines
Each type of plastic fabrication generally has its own machine. The main categories are computer numerical control (CNC) mills and lathes, molding machines, and extrusion machines.
Plastic Fabrication Inspection Machines
During the plastic fabrication process, technicians need to measure and inspect the products before moving to the next stop in the supply chain. Technicians can use QC tools like a portable coordinate measuring machine (CMM) and automated optical comparators to ensure they are manufacturing their plastic parts as precisely as promised.
CMMs for Plastic Fabrication
A portable CMM utilizes a probe to gather coordinates for inspection purposes. They can inspect 3D features, compare back to a CAD model, and even inspect GD&T features. Portable CMMs are particularly useful for in-machine and in-process measuring, eliminating the need to transport parts to different locations. This not only ensures accurate measurements but also minimizes the risk of distortion during transportation.
Optical Comparators for Plastic Fabrication
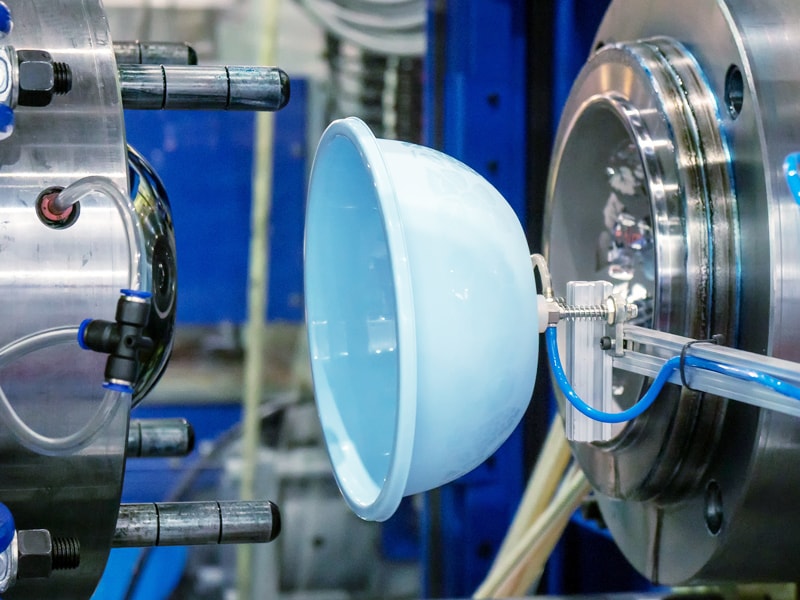
Automated Optical Comparators, like this one, are non-contact measurement devices, and are ideal for plastic part applications under 1ft in size. Their non-contact nature eliminates the risk of plastic distortion, making them ideal for sensitive items like plastic bottles that are susceptible to touch-induced changes.
Get detailed information on our products by downloading our catalog.
View Catalog
Plastic Fabrication Inspection Practices
Plastic is dominating the market by being a cheap and flexible material to manufacture products across industries. But, defects arise in plastic fabricating when machines break down or misalign. If technicians are only doing final inspections, they can’t catch the source of the defect because the product is far removed from the machine.
Instead of waiting until the very end, switching to in-process and in-machine inspections prevents thrown out batches and wasted money. Integrating a laser scanner or a CMM for inspection is your answer.
Ready to learn how to choose a CMM or an optical inspection device? Contact us today.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Related Downloads

Brochure for the XM-5000 Series Handheld CMM. Portable CMM to easily and accurately measure 3D and GD&T features anywhere including the shop floor and in the machine tool.
Brochure for the WM-6000 series Wide-Area CMM. A portable setup with a wireless handheld probe that enables users measure large parts and equipment.

![WM-6000 series Measurement / Application Examples [System Versatility Examples]](/img/asset/AS_116820_L.jpg)


