Vision Systems
- Vision System with Built-in AI VS series
- Intuitive Vision System CV-X series
- Customizable Vision System XG-X series
- GigE camera and lighting for PC-based machine vision VJ series
- Inline 3D Inspection 3D Vision series
- 3D Vision-Guided Robotics 3D VGR series
- Line Scan Technology Line Scan series
- 2D Vision-Guided Robotics 2D VGR series
- LED Lighting CA-D series
- Lenses (for Machine Vision) CA-L series
- Machine Vision System Database VisionDatabase series
- Automotive
- Automation Equipment/Machine Building
- Electric Vehicles
- Medical Device Manufacturing
- Food/Beverage Packaging
- Semiconductor/Manufacturing Electronics
- Vision-Guided Robotics
- Solar
- Logistics
- Commodities
- Paper Manufacturing
- Machine Tools
- Electronic Device
- Printing
- Mining/Metals
- Fabric/Textile
- Tobacco
- Marine
- Aerospace
Basics of Lighting Selection

Understand the essentials of machine vision lighting selection and illumination techniques to improve accuracy and efficiency in industrial applications.
Logical Steps for Lighting Selection
Image processing is the process of detecting changes in pixel density data through calculation. As such, stable detection requires projection of a clear image. The lighting selection plays an important role in determining the performance of image processing–based inspection. This section introduces the basic knowledge required for selecting the correct lighting.
Three Steps for Selecting Lighting
- 1. Determine the type of lighting (specular reflection/diffuse reflection/transmitted light).
- Confirm the characteristics of the inspection (flaw, shape, presence/absence, etc.).
Check if the surface is flat, curved, or uneven. - 2. Determine the shape and size of the necessary light.
- Check the dimensions of the target and installation conditions.
Examples: ring, low-angle, coaxial, dome. - 3. Determine the color (wavelength) of lighting
- Check the material and color of the target and background.
Examples: red, white, blue.
Shapes of Typical Lights (LED Lighting)

Coaxial vertical: CA-DX

Low-angle: CA-DL

Direct ring: CA-DR

Backlight: CA-DS

Dome: CA-DD

Bar: CA-DB
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Lighting Selection: Step 1 (Specular Reflection, Diffuse Reflection, Transmitted Light)
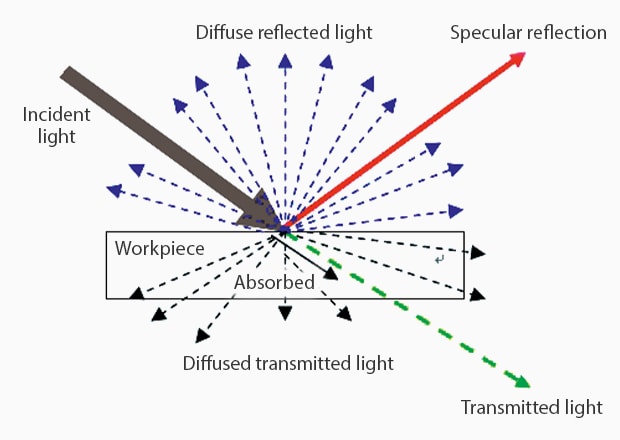
LED Lights can be roughly divided into the following three types:
- 1. Specular reflection type:
- Light is applied to the target and the lens receives the direct reflection.
- 2. Diffuse reflection type:
- Light is applied to the target and the lens receives uniform ambient light.
- 3. Transmitted light type:
- Light is applied from behind the target and the lens receives the transmitted silhouette.
1. Sample Image of Specular Reflection: Inspecting for the Presence or Absence of Inscriptions on Metal Surfaces
Normal lighting

The inscription is unclear.
It is necessary to bring out the contrast between the flat metal surface and depressions of the inscription.
Using illumination

The inscription is clear.
Since a metal surface reflects light easily and the inscription does not, the optimum method is to use specular reflection to enhance the difference between the surface and inscription.
2. Sample Image of Diffuse Reflection: Inspecting the Print on a Chip Through Transparent Film
Normal lighting
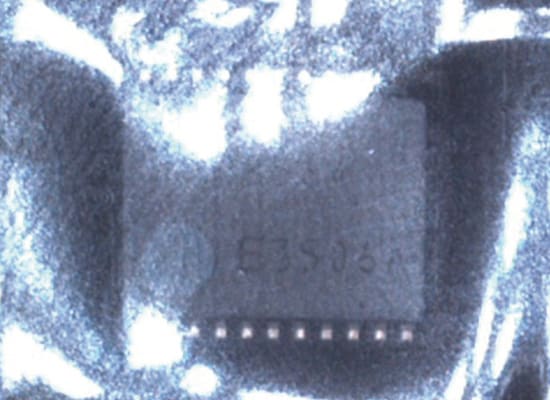
The Lighting reflects on the film surface.
It is necessary to bring out the contrast between the surface of the chip and the print by eliminating the reflection from the transparent film (halation).
Using illumination
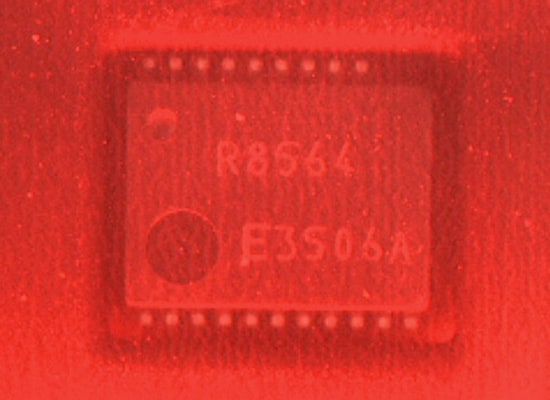
The image is not affected by the film.
The optimum method is to use diffuse reflection to prevent specular reflection on the transparent tape.
3. Sample Image of Transmitted Light: Inspecting Foreign Matter on Nonwoven Fabric
Normal lighting
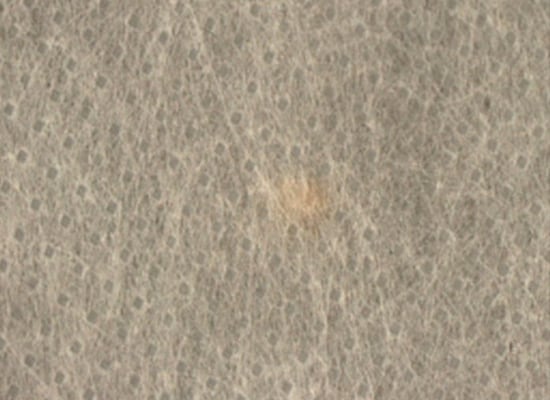

The Lighting reflects on the film surface.
It is necessary to bring out the contrast between the target surface and the foreign matter, which is difficult to recognize because of the subtle difference in color.
Using illumination
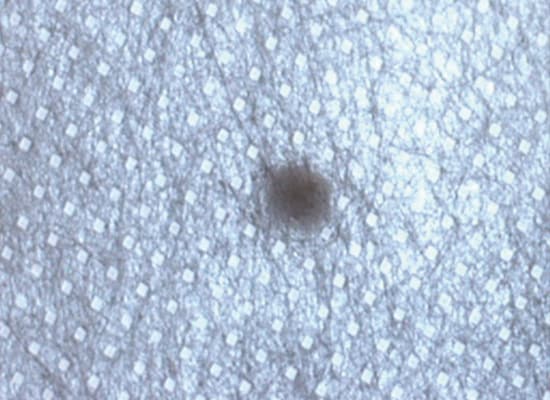
The silhouette of the foreign matter is clearly recognized.
Even when no difference can be detected with reflected light, applying transmitted light from behind the target will show foreign matter as a black silhouette.
The first step of light selection is to select the lighting method, specular reflection, diffuse reflection, or backlighting, according to the shape of the target and the inspection purpose. Then, select the size and color of light that allows you to capture an optimum image for processing.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Lighting Selection: Step 2 (Lighting Method and Shape)
1. Sample Image of Specular Lighting: Detecting Chips in the Edge of a Glass Plate
- Selecting lighting according to the work piece characteristics and detection details:
- 1. The light reflects on the glass surface.
- 2. It is necessary to enhance the difference between the glass plate and background.
- 3. It is best to apply lighting vertically to the work piece.
- 4. A space can be provided above the work piece.
The best selection is coaxial-vertical lighting.
Simple reflected light
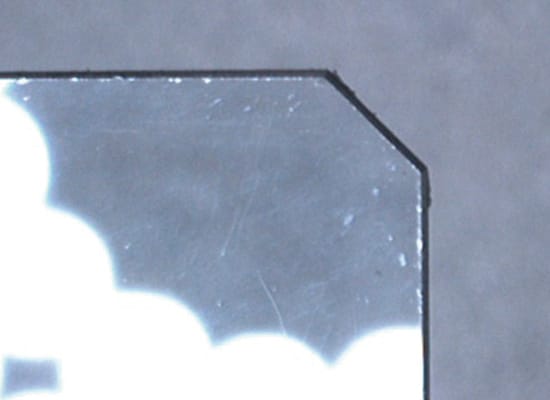
Reflected light is reflected randomly on the glass surface.
Coaxial-vertical illumination

The entire glass surface can be illuminated uniformly.
2. Detection Example of Diffuse Reflection: Inspecting Chips in Rubber Packing
- Selecting lighting according to the work piece characteristics and detection details:
- 1. The work piece is black rubber which does not reflect specular light.
- 2. The chipping is also black and will not reflect specular light.
- 3. Illuminating the work piece from an angle to reflect the specular light from the chipped area proves effective.
- 4. A light can be installed close to the target.
The best selection is low-angle light.
Simple reflected light
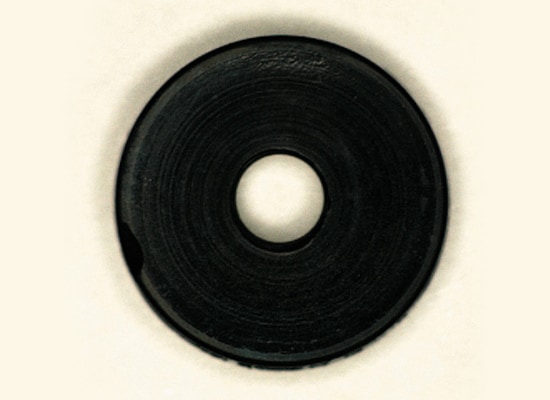

The chips on the outer-circumference cannot be recognized.
With low-angle illumination
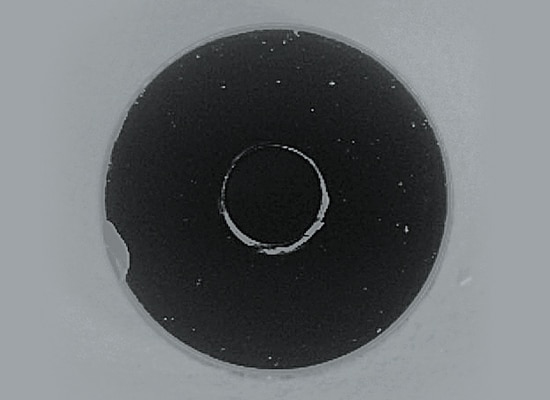
The chip at the edge appears white.
3. Detection Example of Transmitted Light: Inspecting Lead Shapes
- Selecting lighting according to the work piece characteristics and detection details:
- 1. The target is a metal object with projections and depressions, resulting in irregular specular reflection.
- 2. By using a transmitted light, the edge of the target can be detected without the influence of the projections and depressions.
- 3. A light can be installed behind the work piece.
The best selection is a backlight.
Simple reflected light
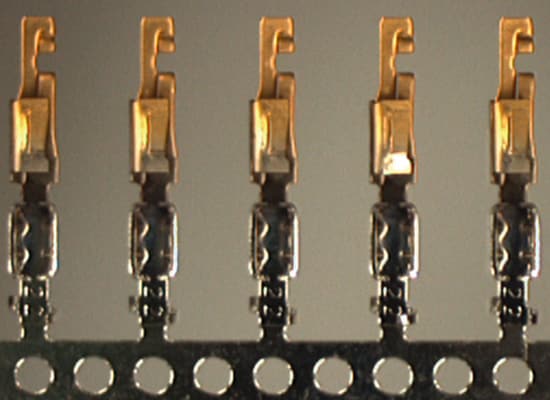
The edges show little contrast.
With a backlight
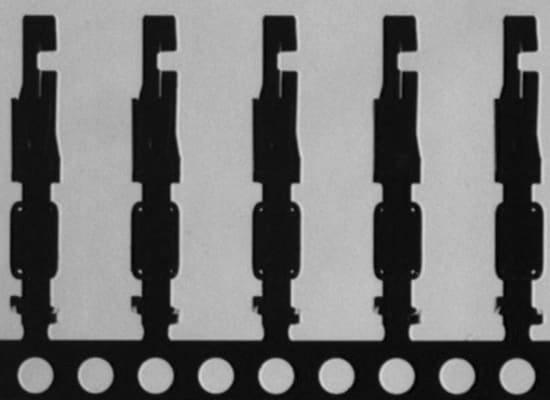
The complicated outline can be recognized clearly.
After you choose the lighting method, select the type of light based on the detection purpose, background, and surrounding environment.
Basic selections are: coaxial illumination, ring illumination, or bar lights for specular reflection; low angle lights, ring illumination, or bar lights for diffuse reflection; and area illumination or bar lights for backlighting. Ring illumination and bar lights are generally used in particular because they can be used for various purposes by adjusting the installation distance.
See the benefits firsthand by signing up for a free trial now.
Free Trial
Lighting Selection: Step 3 (Color and Wavelength of Lighting)
The last step is to determine the color of illumination according to the target and background. When a color camera is used, the normal selection is white. When a monochrome camera is used, the following knowledge is required.

Work piece
Detection Using Complementary Colors
A red candy wrapper is in a cardboard box. The following is a comparison of the contrast when LED illumination is used to detect the presence or absence of the candy.

With a white LED
The brightness is uniform for the entire image and there is almost no contrast between the work piece and background.

With a red LED
The red work piece is shown brighter, but the contrast is still insufficient.

With a blue LED
A blue LED is optimum
The red target appears black, allowing for stable detection.
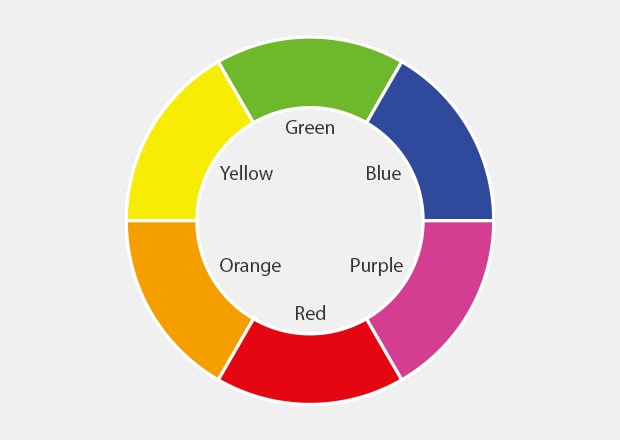
Color wheel
Reference
What is a complementary color?
A complementary color is the opposite color in the hue circle. When a light of the complementary color is applied to an object, the object will appear nearly black.
Detection Using Wavelength
The following is an image comparison of print on a chip in carrier tape taken through a transparent film. The contrast is higher with red illumination than with blue illumination, because of its higher transmittance (lower scattering rate).
Color camera image White illumination

Color camera image Red illumination
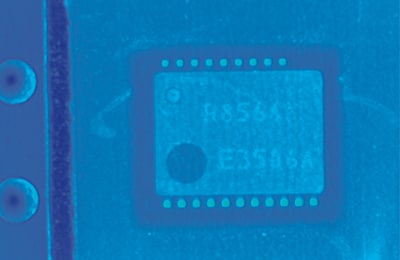
Color camera image Blue illumination

Gray camera image Red illumination
The contrast between the print and chip appears clearly through the film.

Gray camera image Blue illumination
Lights of different wavelengths appear as different colors. The wavelength determines the characteristics of a particular color such as being transmitted easily (red light - long wavelength) or being scattered easily (blue light -short wavelength).
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Summary of Logical Steps for Lighting Selection
Light selection determines the conditions of captured images, which is most important for image processing. Instead of trying every light without consideration, you can select the right one efficiently by following the procedure below:
- Decide which of specular reflection, diffuse reflection, or backlighting is most appropriate.
- Decide on the type and size of the light.
- Decide on the color of the light.
The next volume will cover “the effects of color cameras and image enhancement”. It is an important factor for processing the image to the optimum application such as appearance inspection and position detection. The next guide will outline points for selecting the optimum color extraction and image enhancement.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Techniques in Vision System Lighting
The applications of some vision system lighting techniques require a special kind of light and geometry or different placement of the camera relative to the observed object, while other applications don’t. Whatever the case might be, most lighting manufacturers offer lights with various combinations of illumination techniques for vision systems available within a single product. This allows for greater flexibility and reduction in potential costs associated with lighting for different inspection methods.
Backlighting
Backlighting projects even illumination from behind the observed target to highlight its silhouette. This type of lighting is mostly used for presence/absence detection, detection of holes and gaps, and measurements of target outline shape. However, this type of lighting isn’t best suited for the detection of surface details.
Bar Lighting
Bar lighting illuminates the target along its edge or provides uniform lighting along a localized area. It can be combined with other bar lights to illuminate the target from all directions. This type of light can enhance or reduce specular reflection, depending on light and camera placement and angle. It’s typically used to add contrast to matte surfaces and to highlight surface features of matte objects.
Dark Field Lighting
This type of machine vision lighting provides light in a way that exposes surface defects, such as scratches, imprints, notches, and all imperfections, which reflect the light back to the machine vision system camera.
Diffuse On-Axis Lighting
Also known as co-axial lighting- is a machine vision lighting technique that transmits light perpendicular to the target. All surfaces hit at an angle to the camera will be dark and thus more visible. It’s an exceptionally useful technique for detecting flaws on flat, shiny surfaces.
Dome Lighting
Dome lighting provides uniform illumination from various angles, resulting in the absence of glare. It’s perfect for inspecting shiny, bumpy, or cured surfaces, but it needs to be close to the target to be effective.
Applications of Machine Vision Illumination
Machine vision lighting follows machine vision systems across innumerable applications within the industrial setting. This includes automated inspection and quality control during manufacturing processes, electronic assemblies, and food and beverage packaging and labeling.
Uniform illumination also helps robots identify different items for pick-and-place applications and capture clear images on fast-moving conveyors in the packaging and logistics industries. Machine vision lighting is also used to detect whether the pills are the correct size, shape, and even color before they’re packed and shipped to the local pharmacy.
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
Machine Vision Lighting FAQs
What is Machine Vision Lighting, and Why is It Crucial for Vision Systems?
Machine vision lighting helps optimize the visibility of objects that are viewed and captured by cameras, enabling more precise image capture for analysis. It often enhances contrast, reduces shadows and reflections, highlights specific features, and enhances the effectiveness of image processing.
Are There Specific Considerations When Choosing Machine Vision Lighting for Certain Applications?
Yes, there are specific considerations when choosing machine vision lighting for specific applications, and they mostly relate to object characteristics, such as color, size, and surface properties. However, it also depends on the features that need highlighting.
How Does Machine Vision Backlight Enhance the Visibility of Certain Features in a Vision System?
Backlight projects illumination from behind the object, creating a silhouette. Depending on the light source, this type of machine vision lighting can also be used to measure the dimensions of a particular object precisely or detect its presence/absence. Illumination selection is crucial in machine vision as it affects the accuracy and reliability of a vision system. For instance, ring illumination versus dome illumination for printed images on aluminum.
What Considerations Should Be Taken Into Account When Implementing Vision System Illumination for Optimal Performance?
The most important considerations when implementing machine vision system illumination are illumination type, lighting geometry, color and wavelength (as they can significantly improve the visibility of certain objects), and camera compatibility. There can also be differences in lens structure and material that can impact image quality, as seen in KEYENCE's high-resolution lens CA-LH16 and standard lens CV-L16. This can affect the amount of contrast in captured images and general image resolution.
Have More Questions About Machine Vision Lighting and Techniques?
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads

This guide is a compilation of trivia pertaining to vision systems. Figures are used to provide easy-to-understand explanations of principles and characteristics for items ranging from lenses, image capturing, lighting, and color to communication and preprocessing. This guide is a must-read for anyone wanting to learn all about vision systems.
Related Products
Industries
- Automotive
- Automation Equipment/Machine Building
- Electric Vehicles
- Medical Device Manufacturing
- Food/Beverage Packaging
- Semiconductor/Manufacturing Electronics
- Vision-Guided Robotics
- Solar
- Logistics
- Commodities
- Paper Manufacturing
- Machine Tools
- Electronic Device
- Printing
- Mining/Metals
- Fabric/Textile
- Tobacco
- Marine
- Aerospace







