Vision Systems
- Vision System with Built-in AI VS series
- Intuitive Vision System CV-X series
- Customizable Vision System XG-X series
- GigE camera and lighting for PC-based machine vision VJ series
- Inline 3D Inspection 3D Vision series
- 3D Vision-Guided Robotics 3D VGR series
- Line Scan Technology Line Scan series
- 2D Vision-Guided Robotics 2D VGR series
- LED Lighting CA-D series
- Lenses (for Machine Vision) CA-L series
- Machine Vision System Database VisionDatabase series
- Aerospace
- Automation Equipment/Machine Building
- Automotive
- Commodities
- Defense
- Electric Vehicles
- Electronic Device
- Fabric/Textile
- Food/Beverage Packaging
- Logistics
- Machine Tools
- Marine
- Medical Device Manufacturing
- Mining/Metals
- Paper Manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Printing
- Semiconductor/Manufacturing Electronics
- Solar
- Tobacco
- Vision-Guided Robotics
Optimizing Pick and Place Robot Performance with 3D Vision Systems
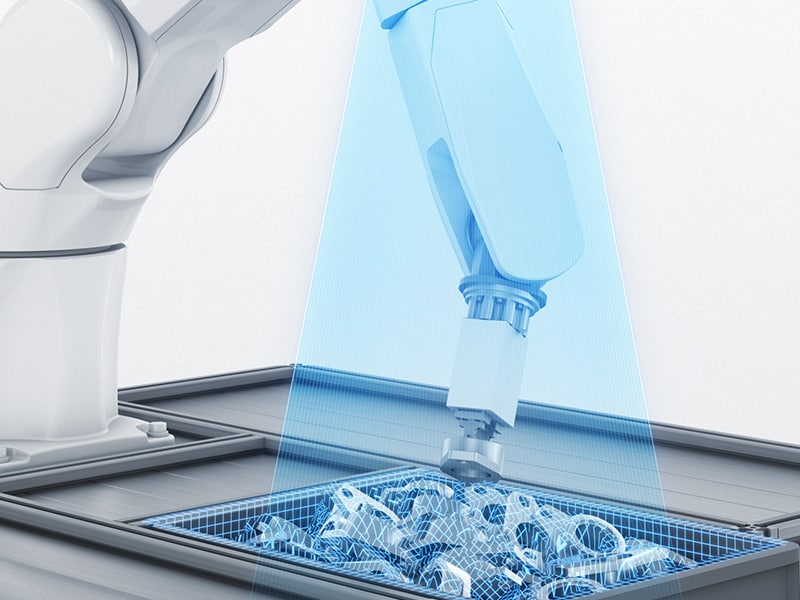

The advancements in machine vision technologies and automation have increased productivity and efficiency across numerous industries, enabling employers to reallocate their human workers to more meaningful positions elsewhere in the company.
This is particularly true in manufacturing and e-commerce. The former now relies on massive production lines in which robots pick up parts and components and place them in designated locations to complete a particular assembly. The automotive industry relies heavily on such robots.
The e-commerce industry also relies on vision system-guided pick and place robots for their warehouse operations, as they provide increased efficiency and speed (they usually work 24/7), significantly higher accuracy in order fulfillment, and reduced labor costs.
In this guide, we’ll discuss how 3D vision systems optimize pick and place robot performance and the benefits associated with integrating 3D vision systems with your pick and place automation.
Key Features and Capabilities of Pick and Place Automation
As explained in the examples above, pick and place automation, particularly in the context of pick and place robots, has become a cornerstone of various industries. These machines are now in charge of manufacturing and packaging parts, components, and goods, as well as e-commerce.
The reason behind their adoption by numerous industries is their precision, speed, and efficiency. While those features and capabilities are their main selling points, pick and place robots also come with a variety of different features and capabilities, some of which include:
- Repeatability
- Pick and place robots are designed to perform the same set of tasks repeatedly with consistent precision, essential for operations such as quality control in production processes.
- Versatility
- Many pick and place systems are designed for multiple uses. This might include pick and place robots with different end-effectors, such as grippers or suction cups, that allow them to handle products and materials of various shapes, sizes, and weights.
- Easy Integration
- Pick and place robots can be easily integrated into existing production lines and pre-existing automated systems. This also includes compatibility with different sensors and software, facilitating seamless operation.
- Enhanced Safety
- Automating tasks that are otherwise hazardous to humans, such as lifting and handling heavy objects or otherwise dangerous items, enhances workplace safety.
- Real-time Feedback and Control
- Integrating 3D vision systems into pick and place robots enhances control, thus ensuring optimal performance. Additionally, 3D vision systems can simultaneously act as real-time feedback in quality control.
Discover more about this product.
Click here to book your demo.

Types of Pick and Place Robots
The availability of pick and place robots for a wide range of applications also implies that these machine systems come in different shapes and sizes. However, choosing the best type of pick and place robot depends on your application requirements.
Here’s a breakdown of different types of pick and place robots:
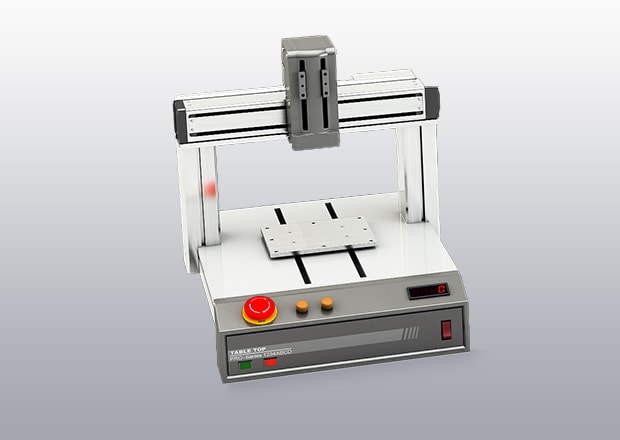

Cartesian Robots
Cartesian robots got their name from the linear X-Y-Z coordinate system. They’re known for their precise movements, and they’re mostly used for tasks that require straight-line motion, such as placing electronic components onto a PCB.
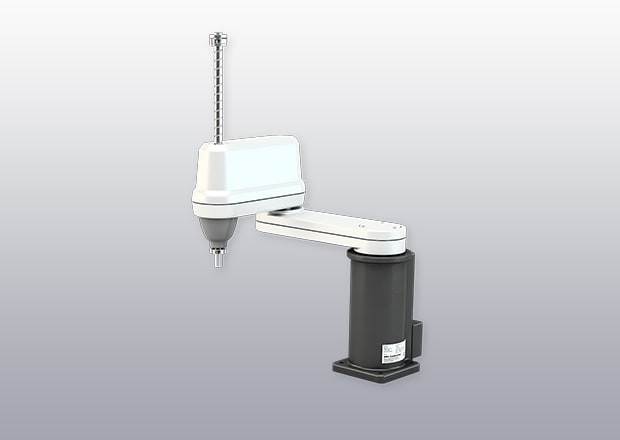

SCARA Robots
Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm robots feature two rotary joints that provide compliance in one selected plane, making them perfect for high-precision assembly operations.
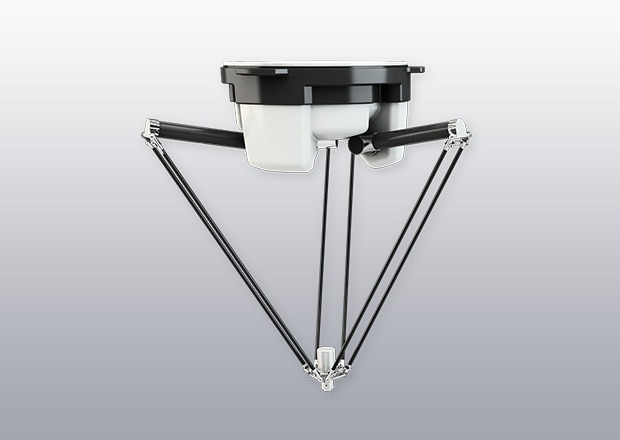

Delta Robots
Delta robots are best known for their spider-like structure, which offers high-speed and precise operation.
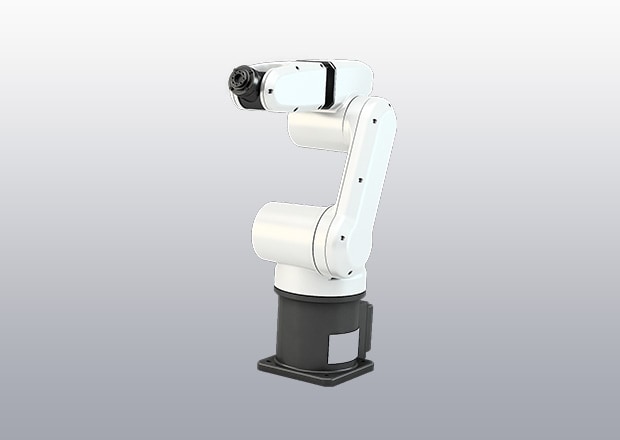

Articulated Robots
Articulated robots feature multiple rotary joints, which provide the machine system with a greater range of motion. With a high degree of flexibility and reach, they’re incredibly versatile and great at handling complex tasks.
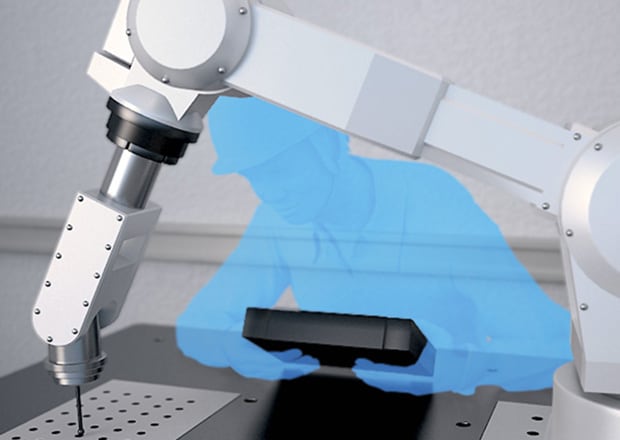

Collaborative Robots
Cobots are designed to work alongside human operators without compromising their safety. They’re gaining popularity among small- and medium-sized businesses, as they are much easier to integrate into existing workflows.
Ultimately, choosing the correct pick and place robot type depends on several factors, such as speed, precision, payload capacity, reach, flexibility, and industry-specific requirements. The advent of robot technologies and their integration with 3D machine vision systems and AI make pick and place robots indispensable assets in modern automation.
Curious about our pricing?
Click here to find out more.
Challenges of Pick and Place Robots
The main challenges associated with pick and place robot technology are mainly associated with their initial cost, complex setup and programming, maintenance, and integration with existing systems.
There are also challenges inherent to the technology, such as bin-picking implementations. However, these are slowly being alleviated by integrating 3D vision systems and machine learning.
Benefits of Implementing 3D Machine Vision for Pick and Place Automation
Bin picking is a common application for 3D machine vision and pick and place automation. Often, pick and place robots are charged with picking up an object from a container and placing it onto a conveyor or into a manufacturing process.
However, the parts and components inside the container are often loose and randomly piled, making it hard for the pick and place robot to differentiate the part, pick it up, orient it correctly, and place it in a designated area.
And that’s where 3D vision systems come in, as they allow differentiation between randomly oriented and loose parts. In most cases, such integration allows pick and place automation to completely outperform human capabilities across a wide span of applications.
Other benefits of integrating 3D machine vision systems into pick and place automation include:
- Enhanced accuracy and precision
- Improved versatility
- Better adaptability to the changes in the environment
- Enhanced object recognition
- Reduced product damage
- Safety improvements
- Cost-effectiveness
Contact us to learn more about how our advanced technology can help take your business to the next level.
Contact Us
FAQs about Pick and Place Robots
What is a Pick and Place Robot?
A pick and place robot is an automated solution for lifting objects from one location and placing them elsewhere.
What Information Will a 3D Vision System Provide to a Pick and Place Robot?
A 3D vision system provides comprehensive spatial and visual information to a pick and place robot, including object shape and size, object orientation, surface geometry, and spatial relationships, all of which enable the pick and place robot to perform complex tasks with high precision and efficiency.
What Is the Accuracy of a High-Speed Pick and Place Robot?
The accuracy of high-speed pick and place robots varies depending on several factors, including robot design, component quality, the precision of its control system, and the capabilities of any sensing technology or integrated vision system. That said, the accuracy of advanced pick and place robots can be measured in the range of ±0.01 mm to ±0.1 mm.
Have More Questions about Pick and Place Automation?
We’re here to provide you with more details.
Reach out today!

Related Downloads
Related Products
Industries
- Aerospace
- Automation Equipment/Machine Building
- Automotive
- Commodities
- Defense
- Electric Vehicles
- Electronic Device
- Fabric/Textile
- Food/Beverage Packaging
- Logistics
- Machine Tools
- Marine
- Medical Device Manufacturing
- Mining/Metals
- Paper Manufacturing
- Pharmaceuticals
- Printing
- Semiconductor/Manufacturing Electronics
- Solar
- Tobacco
- Vision-Guided Robotics




